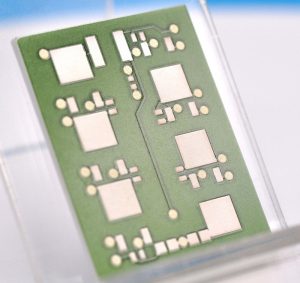
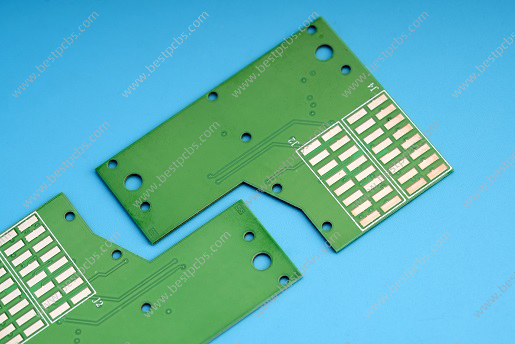
Al2O3 ceramic PCB fabrication is the process of producing printed circuit boards using alumina (Al2O3) ceramic substrates. Alumina ceramics have high mechanical strength, hardness, heat resistance, electrical insulation and corrosion resistance, and are one of the most cost-effective materials in the electronic packaging industry.
Unlike ordinary PCBs, ceramic PCBs are made by directly bonding copper foil and ceramic substrates under high temperature environments. They have strong bonding strength, the copper foil will not fall off, and have high reliability and performance stability under high temperature and high humidity environments.
As a ceramic PCB manufacturer with 18 years of manufacturing experience, BEST Technology has accumulated rich professional strength in the manufacturing of alumina ceramic PCBs. In terms of manufacturing technology, it adopts advanced manufacturing processes to ensure that each alumina ceramic PCB meets high quality standards.
What is Alumina Ceramic PCB?
Alumina ceramic PCBs are circuit boards made using aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) as the substrate material. This type of PCB is known for its excellent thermal management, high insulation resistance, and mechanical strength.
Compared to conventional FR-4 boards, alumina ceramic PCBs offer better heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-power applications like LED lighting, automotive electronics, and aerospace systems.
Unlike standard PCB materials, alumina ceramic is highly resistant to chemical corrosion and environmental stress. It can endure extreme temperatures without degrading, ensuring long-term reliability in demanding conditions.
How Do You Make Al₂O₃ Ceramic PCB?
Fabricating an alumina ceramic PCB requires a specialized manufacturing process. Unlike FR-4 boards, which are processed using laminates, ceramic PCBs are created through advanced sintering techniques.
The process typically involves:
- Material Preparation – High-purity alumina ceramic is selected based on thermal and electrical requirements.
- Substrate Formation – The ceramic is shaped and sintered at high temperatures to achieve a dense, strong structure.
- Metallization – Copper, silver, or gold is deposited onto the ceramic surface using thick-film or thin-film technology.
- Circuit Patterning – The conductive layer is etched or laser-processed to define the circuit layout.
- Component Assembly – SMD or through-hole components are mounted using high-temperature soldering or wire bonding.
- Final Testing – The finished PCB undergoes electrical and thermal testing to ensure optimal performance.
This fabrication method results in a robust, high-performance PCB with excellent electrical insulation and thermal efficiency.
What Are the Advantages of Alumina Ceramic PCB?
Al₂O₃ ceramic PCBs come with a range of benefits that make them superior to traditional materials.
- Exceptional Heat Dissipation – The ceramic substrate effectively transfers heat away from components, preventing overheating.
- High Mechanical Strength – Alumina ceramic is incredibly strong, resisting mechanical stress and impact.
- Superior Electrical Insulation – This material prevents electrical leakage, ensuring stable circuit performance.
- Corrosion Resistance – Unlike metal-based PCBs, alumina ceramic does not rust or degrade over time.
- Dimensional Stability – It maintains its structure under extreme conditions, including high temperatures and humidity.
These advantages make alumina ceramic PCBs a top choice for advanced electronic applications requiring reliability and efficiency.
What Are the Materials Used in Ceramic Substrate?
Ceramic PCBs can be made using different types of ceramics, each offering unique properties:
- Alumina (Al₂O₃) – The most widely used ceramic material, known for its affordability and strong thermal performance.
- Aluminum Nitride (AlN) – Offers higher thermal conductivity than alumina but comes at a higher cost.
- Beryllium Oxide (BeO) – Provides outstanding thermal properties but has limited use due to toxicity concerns.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) – Used in specialized high-temperature applications.
Each material is selected based on specific electrical, thermal, and mechanical requirements.
Is Alumina Ceramic Better Than Zirconia Ceramic?
Alumina and zirconia ceramics are both high-performance materials, but they serve different purposes.
- Alumina Ceramic (Al₂O₃) – Offers better thermal conductivity, making it ideal for PCBs that require efficient heat dissipation.
- Zirconia Ceramic (ZrO₂) – Has superior mechanical toughness and is often used in wear-resistant applications.
For electronic circuit boards, alumina is the preferred choice due to its balance of strength, electrical insulation, and heat management.
How Thick is Alumina Ceramic PCB?
The thickness of an alumina ceramic PCB varies based on application needs. Typically, the substrate thickness ranges from 0.25mm to 5mm, depending on thermal and mechanical requirements.
Thinner PCBs are used in compact electronics, while thicker substrates are chosen for heavy-duty applications requiring robust performance.
What is the Difference Between Al₂O₃ Ceramic PCB and FR-4?
FR-4 and alumina ceramic PCBs are widely used, but they differ in key ways:
- Material Composition – FR-4 is a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy, while alumina ceramic is a solid ceramic substrate.
- Thermal Conductivity – Alumina ceramic dissipates heat much more efficiently than FR-4.
- Durability – Ceramic PCBs can withstand harsh environments, whereas FR-4 boards are more prone to degradation.
- Electrical Performance – Alumina has superior insulation and minimal signal loss, making it ideal for high-frequency circuits.
For applications where heat management and longevity are critical, alumina ceramic PCBs offer a clear advantage.
What Are the Applications of Alumina Ceramic PCB?
Due to their exceptional properties, alumina ceramic PCBs are used in various industries:
- LED Lighting – Ensures efficient heat dissipation for high-brightness LEDs.
- Power Electronics – Used in high-voltage circuits requiring stability and durability.
- Automotive Electronics – Found in electric vehicles, sensors, and power management systems.
- Aerospace & Defense – Used in radar, communication, and avionics due to reliability under extreme conditions.
- Medical Devices – Integrated into imaging systems and surgical instruments for their biocompatibility and precision.
As electronic devices continue to demand higher efficiency and performance, alumina ceramic PCBs are becoming an essential part of modern technology.
Conclusion:
Al₂O₃ ceramic PCBs provide a superior solution for applications requiring durability, thermal efficiency, and electrical reliability. Compared to traditional FR-4 boards, they offer better heat dissipation, mechanical strength, and longevity.
For high-quality alumina ceramic PCB fabrication, choosing the right manufacturer is crucial. At Best Technology, we specialize in custom ceramic PCBs designed to meet the most demanding requirements. Contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com to discuss your project needs!
Tags: Alumina PCB, aluminum nitride pcb, Ceramic PCB manufacturer, Ceramic PCB VS FR4