DC and AC inverters are essential components in today’s energy systems. Whether you’re harnessing the power of the sun with solar panels, working with backup power solutions, or simply need a way to power your devices, understanding how these inverters work is crucial. This blog breaks down the purpose, advantages, and practical use of DC and AC inverters, helping you make informed decisions based on your needs.
What is a DC and AC Inverter?
Inverters are electrical devices that convert DC (direct current) to AC (alternating current), or vice versa. Typically, DC power comes from sources like batteries or solar panels, while AC is what you use to power most household appliances. A DC to AC inverter is used to convert the DC power into usable AC power. On the other hand, an AC to DC inverter does the reverse, converting AC power into DC to charge batteries or power DC devices.
In simple terms, a DC to AC inverter allows you to use power from sources like batteries or solar panels in everyday devices that require AC power, such as fans, lights, and even refrigerators. Without inverters, it would be challenging to use energy from renewable sources for traditional home appliances.

What is the Purpose of a DC to AC Inverter?
The primary purpose of a DC to AC inverter is to make DC power usable for AC appliances. Whether you’re working with a solar power system or simply need backup power, inverters are the key to making this energy conversion happen. For example, if you’re using a solar panel setup, you typically generate DC power. Since most home appliances run on AC, you need an inverter to convert that energy into a form you can use.
Inverters are essential in off-grid applications, such as in remote areas, where the electricity grid is unavailable. They provide an efficient way to use stored DC power, converting it into AC electricity for devices that would otherwise be useless.
How Does an Inverter Work When There is No Electricity?
When there’s no grid electricity, inverters can still work by drawing power from other sources like batteries or solar panels. This is particularly helpful in off-grid or emergency situations. The inverter takes the DC power from your stored energy and converts it into AC power to keep your appliances running.
For example, if you have a solar power system with a battery backup, and the power goes out, the inverter allows you to keep your appliances on, as long as your batteries have enough charge. In this way, inverters provide an essential role in maintaining power continuity during outages.
DC Inverter AC Advantages and Disadvantages
DC inverters come with several benefits, particularly in renewable energy applications like solar power systems. They are highly energy-efficient and help convert power from DC sources into usable AC power without much loss. This makes them perfect for off-grid living or areas where solar panels are the primary source of energy.
However, there are some drawbacks. DC inverters may have higher upfront costs, and the complexity of conversion can lead to minor energy losses. They also tend to require more maintenance due to the way they manage energy conversion.
On the flip side, AC inverters are generally more efficient in household and industrial settings because AC power is more compatible with most appliances. Their downside lies in the additional energy needed to convert AC power into usable DC energy when dealing with solar systems or battery charging applications.
Despite these differences, both types of inverters have their place, and their advantages often outweigh the disadvantages when used in the right scenarios.

Which is Better: AC Inverter or DC Inverter?
Choosing between an AC and DC inverter depends on your specific needs. AC inverters are more commonly used for residential and industrial applications, as they are designed to power traditional household appliances. They are easy to integrate into existing power systems and typically provide a reliable power source for most needs.
On the other hand, DC inverters are especially useful for renewable energy applications. If you’re installing solar panels or using a battery backup, a DC inverter is the best choice, as it can convert the stored DC power into AC power for your home. They are also more energy-efficient in off-grid situations, where you rely entirely on solar or battery power.
Ultimately, the “better” inverter is the one that fits your particular power needs. If you’re on the grid or need to power AC devices from a DC source, an AC inverter is the way to go. But for renewable energy setups, DC inverters are a better fit.
How Long Will a 12V Battery Last with an Inverter?
The lifespan of a 12V battery when used with an inverter largely depends on the wattage of the devices you’re powering. Inverters typically drain the battery at different rates based on the energy demand of the connected devices. For instance, if you’re running a light or small appliance, the battery can last for several hours. However, larger appliances like refrigerators or air conditioners will drain the battery much faster.
On average, a 12V battery can provide power for anywhere from 3 to 10 hours with an inverter, depending on the load. It’s essential to size your inverter and battery capacity properly to ensure your system works efficiently. By balancing energy use with battery life, you can maximize the performance of your inverter system.
How to Choose a DC AC Inverter?
Choosing the right DC to AC inverter involves considering several factors. First, determine the type of devices you’ll be powering. Consider the total wattage your devices require. Inverters come in various sizes and capacities, so it’s essential to match the inverter’s output with your needs.
Next, consider the efficiency of the inverter. More efficient models will waste less power and give you better performance, especially if you’re using renewable energy sources like solar power. You should also think about the inverter’s durability, features like surge protection, and whether it has any warranties or support.
The inverter’s voltage rating must also align with your power system. For example, in a 12V system, you should choose a 12V DC to AC inverter. Also, remember to check the inverter’s surge capacity, especially if you’re powering devices with a high initial startup load, like motors.
Why PCB is Important in DC and AC Inverters?
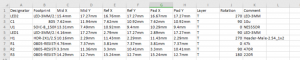
PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) play a crucial role in both DC and AC inverters by providing the necessary connections and support for various electrical components. Inverters rely on PCBs to ensure proper functionality, reliability, and safety. For DC to AC conversion, the PCB helps in routing the signals between critical components like transistors, diodes, and capacitors, ensuring the conversion process runs smoothly.
In both types of inverters, the PCB also helps dissipate heat, manage power efficiently, and prevent potential short circuits. High-quality PCBs are essential for maintaining the long-term durability and performance of inverters, particularly in energy-intensive applications like solar or backup power systems. The design, material quality, and structure of the PCB can directly affect the efficiency and lifespan of the inverter, making it a key component in any inverter system.

With over 18 years of experience in the PCB manufacturing industry, Best Technology is a trusted name in providing high-quality, reliable PCBs for various applications, including inverters. Our expertise and commitment to innovation allow us to create tailored solutions for both residential and industrial energy systems. Whether you’re looking for robust PCBs for solar inverters, backup power solutions, or any other inverter application, Best Technology ensures precision and durability in every product we deliver. For more information about PCB and PCB assembly, pls feel free to contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between a DC inverter and an AC inverter?
The main difference is that a DC inverter converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), while an AC inverter converts AC to DC.
2. Can an inverter work without a power source?
Yes, inverters can still function when connected to a backup power source, such as a battery or solar panel, even if there’s no grid electricity.
3. How do you size an inverter for your needs?
The inverter should be sized based on the wattage of the devices you want to power. Make sure the inverter’s output matches or exceeds the required load.
4. What are the typical applications of a DC to AC inverter?
DC to AC inverters are typically used in off-grid applications, renewable energy systems, and backup power solutions.
5. Do DC inverters have better energy efficiency than AC inverters?
Yes, DC inverters are generally more energy-efficient in solar and battery-based systems as they convert stored energy directly without much loss.
Tags: dc and ac inverters