What is High-Frequency Ceramic PCB for Antenna?
When people talk about high-frequency ceramic PCB for antenna, they often focus on two things: the material and the performance. This type of PCB uses ceramic-based substrates instead of standard materials like FR4. Ceramic materials handle high frequencies much better, which is why they are widely used in antennas, especially for advanced communication systems.
Ceramic PCBs are different because they have excellent thermal properties, stable performance across various temperatures, and a low dielectric loss. When designing antennas, stable signal transmission matters a lot. If the PCB can’t hold signals well, the antenna won’t perform as expected. That’s where ceramic PCBs shine. They can work reliably at frequencies over 1GHz, even reaching into the millimeter-wave range.
For antennas, precision and stability are key. High-frequency ceramic PCBs offer low signal loss, better impedance control, and excellent high-speed signal transmission. Compared to other materials, they help antennas work more efficiently, even in complex environments.

Raw Materials of High-Frequency Ceramic PCB
The materials used in high-frequency ceramic PCB for antenna directly impact performance. Ceramic PCBs rely on substrates like Alumina (Al2O3), Aluminum Nitride (AlN), and Beryllium Oxide (BeO). Each has special properties that match specific antenna needs.
- Alumina is popular for its balance between cost and performance. It has stable electrical properties, good thermal conductivity, and works well with various frequencies.
- Aluminum Nitride provides higher thermal conductivity than Alumina, which helps when antennas run in high-power or high-heat situations.
- Beryllium Oxide offers even better thermal properties, but it’s used less due to its handling restrictions.
Ceramic PCBs also use conductive materials like silver, gold, or copper, depending on the frequency and environment needs. The right combination of ceramic substrate and conductor helps antennas maintain low signal loss and high reliability, even under extreme conditions.
Advantages of Ceramic PCB Used in Antenna
Using high-frequency ceramic PCB for antenna provides many benefits, especially when high performance matters. These advantages help designers build better antennas that stay stable over time, make them in a smart choice for antennas in 5G, radar, GPS, and satellite communication systems.
- Low dielectric loss: Signals travel through ceramic with less loss, which helps antennas work better at high frequencies.
- Stable performance: Ceramic PCBs handle temperature changes, moisture, and mechanical stress well. That stability matters for outdoor antennas or systems working in tough environments.
- Excellent thermal management: Antennas, especially those handling strong signals, produce heat. Ceramic spreads heat faster than traditional materials, which helps antennas work longer without performance drops.
- Higher frequency support: Standard PCBs struggle with frequencies above a few GHz. Ceramic PCBs handle millimeter-wave frequencies better, making them ideal for advanced communication systems.
- Tighter tolerances: Ceramic PCBs can be made with more precise dimensions, which helps match the antenna’s electrical design closely. This precision supports better impedance control.
- Longer lifespan: Ceramic resists wear, corrosion, and aging better than many organic materials. That means antennas using ceramic PCBs tend to last longer.
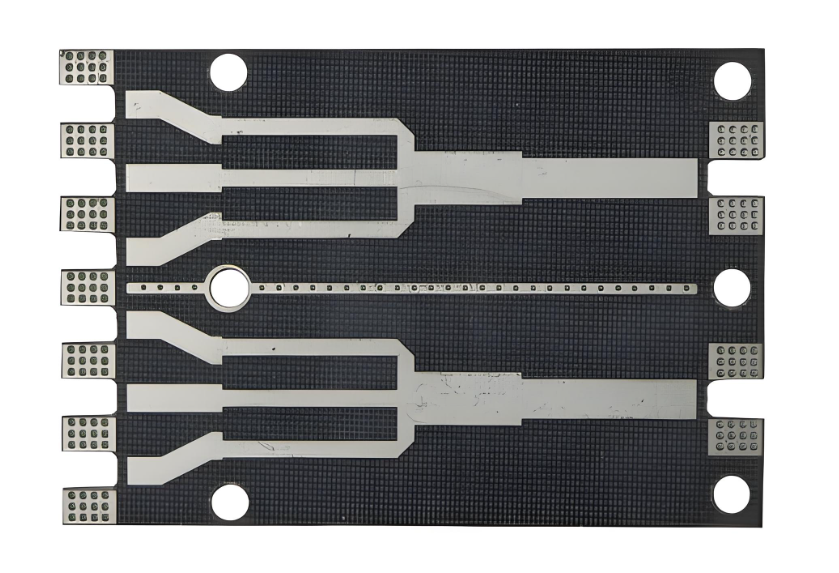
High-Frequency Ceramic PCB vs. High-Frequency PCB
It’s common to hear people compare high-frequency ceramic PCB for antenna with standard high-frequency PCB. Both support high-speed signals, but they serve different purposes.
1. Material difference:
High-frequency PCBs often use PTFE, hydrocarbon, or special composite materials. Ceramic PCBs use Rogers Alumina, Aluminum Nitride, or similar ceramics.
2. Thermal performance:
Ceramic spreads heat much faster than PTFE or composites, helping antennas in high-power systems.
3. Dielectric loss:
Ceramic PCBs generally have lower dielectric loss at high frequencies, which helps antennas maintain signal clarity.
4. Mechanical stability:
Ceramic is rigid and doesn’t change shape much with temperature or moisture. Some high-frequency laminates can swell or shrink, which affects signal paths.
5. Frequency range:
While both support GHz-level signals, ceramic handles higher frequencies more easily, including millimeter-wave bands.
In short, high-frequency ceramic PCBs work best when both thermal performance and high-frequency stability matter. Standard high-frequency PCBs work well for simpler systems, but antennas pushing into higher frequencies often rely on ceramic for better results.
Design Considerations for High-Frequency Ceramic PCB
Designing a high-frequency ceramic PCB for antenna involves more than choosing the right materials. Several factors impact performance, so careful attention at the design stage helps prevent later problems.
1. Substrate choice: Picking the right ceramic type depends on frequency, heat load, and physical size. Higher frequencies need materials with lower dielectric loss, while high-power antennas need better thermal conductivity.
2. Avoid crosstalk: It is best to use a straight line or 45degree traces to reduce the transmission of high frequency signals and mutual coupling. Parallel routing in a close distance may cause crosstalk.
3. Impedance control: Maintaining accurate impedance across the whole PCB keeps signals clean. Ceramic’s stable properties help, but the design must account for it too.
4. Via design: For multi-layer designs, vias must maintain low loss and good grounding. Plated vias, filled vias, or even embedded vias help control high-frequency signals.
5. Grounding strategy: Good grounding keeps signals clean and reduces unwanted noise. Ground planes should be carefully placed and connected to avoid signal interference.
6. Thermal management: Heat buildup changes performance over time. Even though ceramic handles heat better than FR4, the layout should still allow heat to spread efficiently.
When all these factors work together, the final antenna performs better, holds signal quality longer, and operates reliably under real-world conditions.

Antenna Ceramic PCB Manufacturer – Best Technology
When choosing a high-frequency ceramic PCB for antenna, working with an experienced manufacturer makes a real difference. Best Technology, with more than 18 years of PCB manufacturing experience, specializes in high-frequency ceramic PCBs designed for antennas in various industries.
We work with top-grade ceramic materials like Dupont, Rogers, Isola, etc. to meet the demands of advanced communication systems. Our team works closely with customers to match the right material and design to each antenna’s frequency range, power level, and environment.
We also offer precision manufacturing processes to keep line widths, spacing, and via placements within the tight tolerances high-frequency designs need. Whether your antenna supports 5G, satellite communications, or radar systems, we deliver reliable, high-performance ceramic PCBs that keep signals clean and strong.
With advanced testing, rigid quality control, and a customer-first approach, we help companies build better antennas faster. Contact Best Technology today to explore how our high-frequency ceramic PCBs can improve your next antenna project.
FAQs of High Frequency Ceramic PCB
Q1: Why use ceramic PCBs for high-frequency antennas?
Ceramic PCBs offer lower signal loss, better thermal management, and more stable performance at high frequencies than traditional materials.
Q2: Which ceramic materials work best for antenna PCBs?
Alumina, Aluminum, Nitride are popular choices. Each supports different frequencies and heat loads.
Q3: Are ceramic PCBs suitable for 5G antennas?
Yes, they support the millimeter-wave frequencies used in 5G networks, along with excellent signal integrity.
Q4: Do ceramic PCBs cost more than regular high-frequency PCBs?
They often cost more initially, but their longer lifespan and better performance provide good value.
Q5: Can ceramic PCBs handle outdoor conditions?
Yes, ceramic resists moisture, temperature changes, and mechanical stress better than many organic materials.
Tags: High-Frequency Ceramic PCB for Antenna, pcb antenna manufacturer