What is copper oxydation pcb?Copper oxidation is the process of copper reacting chemically with oxygen in the air to form copper oxide. When PCB is exposed to humid air, moisture will be adsorbed on the copper surface. In the early stage of this oxidation process, only a very fine and imperceptible discoloration layer may be formed on the copper surface, but with the passage of time and the continuous action of oxidation conditions, the oxide layer will gradually thicken.
What is PCB Oxidation?
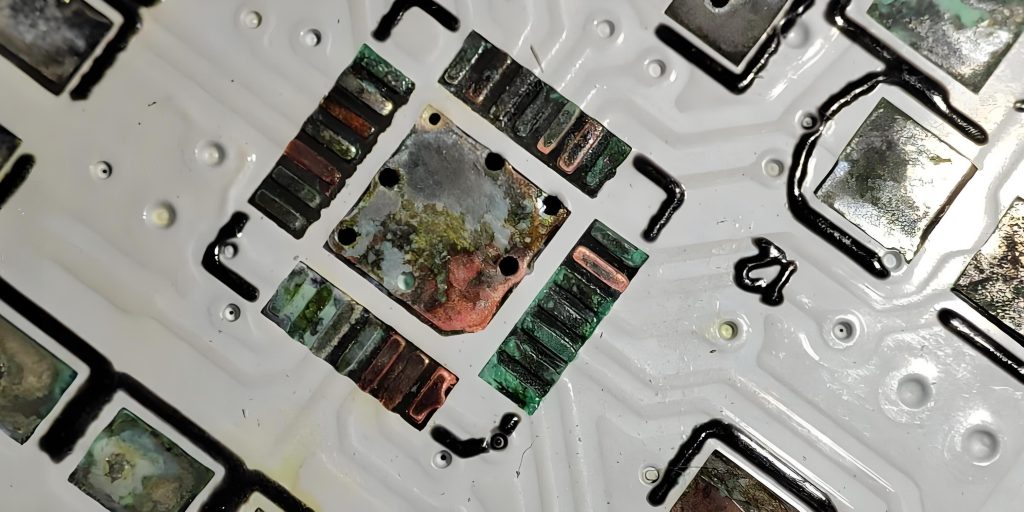
PCB oxidation refers to the phenomenon that the metal wire or pad surface on the PCB board reacts chemically with oxygen to form an oxide layer. This oxide layer is usually formed by oxides on copper materials, mainly including copper oxide (CuO) or cuprous oxide (Cu2O).
The reasons for PCB oxidation are varied, mainly including the following points:
- Environmental factors: high temperature and humidity, high pH or pollutant-containing environments will accelerate the oxidation process of PCB boards.
- Manufacturing and storage conditions: During the manufacturing and storage process, if the appropriate temperature and humidity are not maintained, or if the packaging is improper, causing the PCB to be exposed to moisture and corrosive gases, oxidation is likely to occur.
- Chemical reaction: The metal part on the PCB reacts with moisture and chemicals in the surrounding environment, which is also an important cause of oxidation.
What are the effects of PCB oxidation?
PCB oxidation will have many effects on the performance and reliability of electronic products. First, oxidation will lead to a decrease in conductivity, making the circuit board prone to poor contact, cross-connection and short circuit problems, thereby affecting the use effect and performance of electronic products.
Second, oxidation may cause short circuits and fires, because the oxide layer will form a conductive rust layer, which may cause safety accidents once a short circuit occurs. In addition, oxidation will also reduce the stability and reliability of the circuit board, because the oxide layer reduces the protective layer on the surface of the circuit board, making it more susceptible to interference and fluctuations during long-term operation.
To prevent PCB oxidation, the following measures can be taken:
- Control humidity and temperature: Store the PCB in a dry and ventilated environment, avoiding humidity and high temperature environments.
- Use high-quality materials: Choose a circuit board with a copper-plated protective layer, which can effectively reduce the degree of oxidation.
- Moisture-proof treatment: Use a moisture-proof treatment agent to treat the PCB with moisture to enhance its stability.
- Daily maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the PCB to detect and deal with surface corrosion in a timely manner.
What are the types of PCB corrosion?
The types of PCB corrosion mainly include the following:
- Atmospheric corrosion: This is the most common type of corrosion, usually caused by a chemical reaction between oxygen and moisture in the air and copper, resulting in the formation of copper oxide on the copper surface, reducing the conductivity of the circuit board, but the mechanical properties remain unchanged.
- Local corrosion: This type of corrosion mainly affects a limited or small area, usually due to exposure to an environment with excessive humidity. Local corrosion includes filiform corrosion, crevice corrosion, and pitting corrosion.
- Galvanic corrosion: occurs when two different metals (such as copper and another metal) are coupled in a corrosive electrolyte. Galvanic corrosion causes one metal to corrode faster than the other, usually when one end of the wire/cable is connected to the positive electrode and the other end is connected to the negative electrode.
- Electrolytic corrosion: occurs when an ionized substance (electrolyte) comes into contact with two electrodes and current passes through the PCB. The electrolyte speeds up the rate of electrochemical reactions, causing the corrosion process to accelerate.
- Fretting corrosion: Electrochemical corrosion occurs when two metal surfaces come into contact with each other and one of the metals is in a corrosive environment. Fretting corrosion usually occurs between two different metals, such as copper and steel or copper and aluminum, causing current to flow from copper to steel or aluminum, forming copper oxide.
- Electrolytic dendrite formation: When there is ion contamination in the moisture, dendrites are formed on the copper traces, causing short circuits between traces. This deformation causes metal strips to grow from adjacent copper traces with different voltages, ultimately leading to a short circuit.
How to remove oxidation from PCB?
The methods for removing oxides from PCBs mainly include physical removal, chemical reduction, surface treatment, and environmental control.
1. Physical removal method:
- Fine sandpaper wiping: For mild oxidation, fine sandpaper (non-iron sandpaper) can be used to gently wipe the oxide layer until the metallic luster is restored.
- Diluted acid soaking: For more serious oxidation, you can soak the circuit board in diluted sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid or white vinegar (acetic acid). After the oxide layer is corroded, clean it with alcohol.
2. Chemical reduction method:
- Dimethyl borane alkaline solution: Use alkaline solution mainly composed of dimethyl borane to reduce the oxidized surface of the inner layer copper foil to enhance acid resistance and adhesion.
- Sodium thiosulfate reduction solution: Use sodium thiosulfate reduction solution with a pH value of 3-3.5 to treat copper surface whiskers to form a coating layer of copper and cuprous oxide mixture to improve antioxidant capacity.
3. Surface treatment method:
- Tin plating: Tin plating on the surface of the PCB to form a protective layer, which effectively prevents oxidation and has a low cost.
- Gold plating: Gold plating can provide higher corrosion resistance, but the cost is higher.
- Coating anti-oxidation coating: Use anti-oxidation coating to form a strong, corrosion-resistant protective layer to isolate the PCB surface from contact with air.
4. Environmental control method:
- Control the ambient temperature and humidity: During the manufacturing, storage and transportation of PCBs, strictly control the temperature and humidity of the environment to avoid exposing the PCB to high temperature, high humidity or pollutant-containing environments.
- Choose appropriate packaging materials: such as moisture-proof bags, foam boxes, etc. to ensure the integrity and quality of the PCB.
How to protect PCB from oxidation?
The methods to protect PCBs from oxidation include the following aspects:
- Choose high-quality substrates: Select substrates with strong antioxidant properties, such as FR-4, high TG boards or aluminum substrates.
- Control the ambient humidity: During the manufacturing and storage process, maintain a low humidity environment to reduce the risk of oxidation, because high humidity will accelerate the occurrence of oxidation reactions.
- Use antioxidants: During the manufacturing or assembly of PCBs, antioxidants are applied to protect the circuit layer from oxidation, which can be implemented during the packaging and coating process.
- Surface treatment process: The use of metal plating with strong antioxidant properties, such as gold plating, silver plating, tin plating, etc., can form a protective film on the surface of the metal circuit to prevent the occurrence of oxidation reactions.
- Regular cleaning and maintenance: Use appropriate cleaning agents and regular cleaning methods to remove possible dirt and oxides and keep the PCB surface clean.
- Reasonable storage and use environment: Avoid exposure to humid, high temperature, and highly polluted environments. It is best to use sealed packaging and place it in a dry and cool place. During use, pay attention to keeping the electronic equipment clean and prevent dust, moisture and other pollutants from entering the PCB.
What chemical is used to clean PCB?
Common chemicals for cleaning PCBs include water-based cleaning agents, hydrocarbon cleaning agents, and organic solvents.
Water-based cleaning agents use water as the cleaning medium and improve the cleaning effect by adding a small amount of surfactants, detergent aids, and corrosion inhibitors. This cleaning agent has a good dissolving effect on water-soluble dirt and is suitable for batch cleaning.
Hydrocarbon cleaning agents are suitable for manual scrubbing and local surface treatment wiping, but the air in the working environment must be unobstructed. Hydrocarbon cleaning agents have weak cleaning power and are flammable and explosive safety risks.
The organic solvent cleaning process is relatively simple, and only the same solvent needs to be used for cleaning and rinsing. Common organic solvents include trichloroethylene, carbon tetrachloride, etc. These solvents have a good dissolving effect on dirt, but attention should be paid to their volatility and safety.
Copper oxidation PCB involves many links in electronic manufacturing, from design to manufacturing, from use to maintenance, and negligence at each stage may lead to this problem, thereby damaging the performance of the PCB. As a professional PCB manufacturer, BEST Technology blocks oxidation factors from cleaning to packaging. Once an oxidation problem occurs, special cleaning agents are used for minor treatments, and professional processes such as micro-etching and electroplating are used for repair.