A Light ballast PCB controls the current flow inside different lighting systems, helping the lamps work properly while protecting them from too much power. Without a proper light ballast PCB, many lamps would either flicker all the time or fail before reaching their normal lifespan. Today, most lighting projects, whether for homes or factories, depend on some form of light ballast PCB to make sure lamps work smoothly. Since more people want brighter, longer-lasting, and energy-saving lights, the design and quality of light ballast PCB become even more important. In this blog, we will explain what a light ballast PCB is, how it works, and its wiring steps. We will also cover technical details, diagrams, and real-world uses to give you a better understanding. Let’s start by understanding the basics.
What is a light ballast pcb?
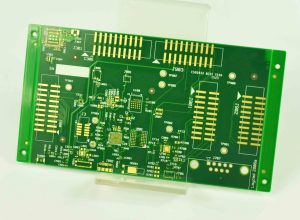
A light ballast PCB is a printed circuit board that manages the voltage and current delivered to lamps, mainly fluorescent, HID and some LED lamps. It controls the power flow to prevent too much electricity from reaching the lamp, which helps the light stay stable while avoiding flickering or overheating.

In traditional systems, light ballasts were heavy metal boxes with coils and transformers. Now, with modern PCB technology, most ballasts are smaller boards with electronic components. These boards offer better control, longer lifespan, and smaller size, which helps in compact lighting systems.
At its core, a light ballast PCB acts like a smart power gate, adjusting the electric supply to fit the lamp’s needs. For fluorescent lights, it also gives an initial high voltage to ignite the lamp before reducing the power to a safer level.
At Best Technology, we are able to provide you with One-stop solution from light ballast PCBs design to production and final assembly with fast delivery and competitive price, because Best Technology have 16 experience years in high-quality PCB solutions and PCBA service for all lighting applications. Whether you need standard or custom solutions, Best Technology is your go-to partner for all your PCB needs. Welcome to inquiry us sales@bestpcbs.com if you have any needs for lighting pcb.
What is wiring tips of light ballast PCB?
- Layered wiring: Separate the power supply and load parts to avoid mutual interference and improve the stability and performance of the circuit.
- Reasonable selection of power supply path: Ensure that the power supply path is clear and avoid unnecessary interference, especially when processing high-frequency signals, pay attention to the layout and direction of the signal line.
- Top layer priority principle: Try to wire on the top layer to reduce signal interference.
- Thickening the power line: Thickening the power line is conducive to the flow of current on the main road to ensure the stability of the circuit.
- Travel direction control: The wires at the input and output ends should avoid being adjacent and parallel to reduce interference.
- Chamfer rule: The corners of the trace should avoid being designed as sharp angles and right angles to reduce radiation.
- Device decoupling: Add necessary decoupling capacitors to filter out interference signals on the power supply and stabilize the power supply signal.
- Impedance matching: The width of the same network wiring should be kept consistent, or the effective length of the inconsistent part should be minimized.
- Ground wire loop rule: The loop area formed by the signal line and its loop should be as small as possible to reduce electromagnetic interference.
- Shielding protection: Consider using a copper-axis cable shielding structure design to isolate the ground wires up and down, left and right with ground wires, and effectively combine the shielding ground with the actual ground plane.
How does light ballast work on PCB?
A pcb ballast works by regulating the electrical current that flows through the light fixture. When the light is turned on, the ballast provides an initial surge of voltage to start the lamp. Once the lamp is lit, the ballast continues to regulate the current to maintain steady light output.
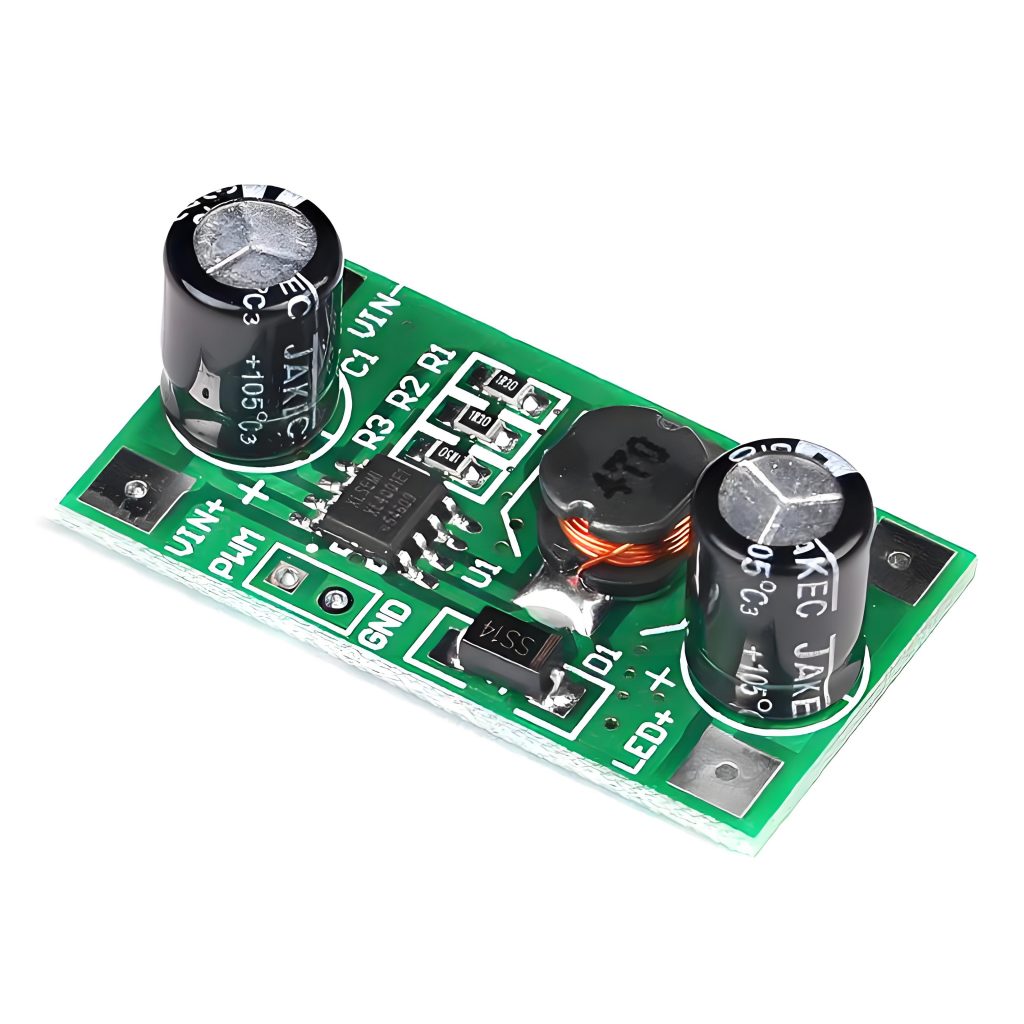

Here’s how it works in a bit more detail:
Startup Phase: The ballast delivers a high voltage to the lamp to start it up. Fluorescent lights, in particular, require this surge of power to get started.
Current Regulation: Once the light is on, the ballast regulates the current to keep it at a constant level. This ensures that the lamp doesn’t overheat or flicker, contributing to better light quality.
Energy Efficiency: In electronic ballasts, the high-frequency switching of MOSFETs and capacitors allows for energy-efficient operation. This reduces power consumption while maintaining optimal lighting levels.
What is technical parameters of light ballast PCB?
- Input voltage range: The driver board needs to be able to accept AC input within a certain range, usually the mains voltage (such as 100V-240V).
- Output current and voltage: The driver board provides stable DC output. The current and voltage need to be adjusted according to the requirements of the LED lamp, usually constant current or constant voltage output.
- Power factor: Indicates the effective utilization of electrical energy. A high power factor means high efficiency in power conversion.
- Efficiency: Indicates the ratio of output power to input power. Efficient conversion helps reduce energy waste.
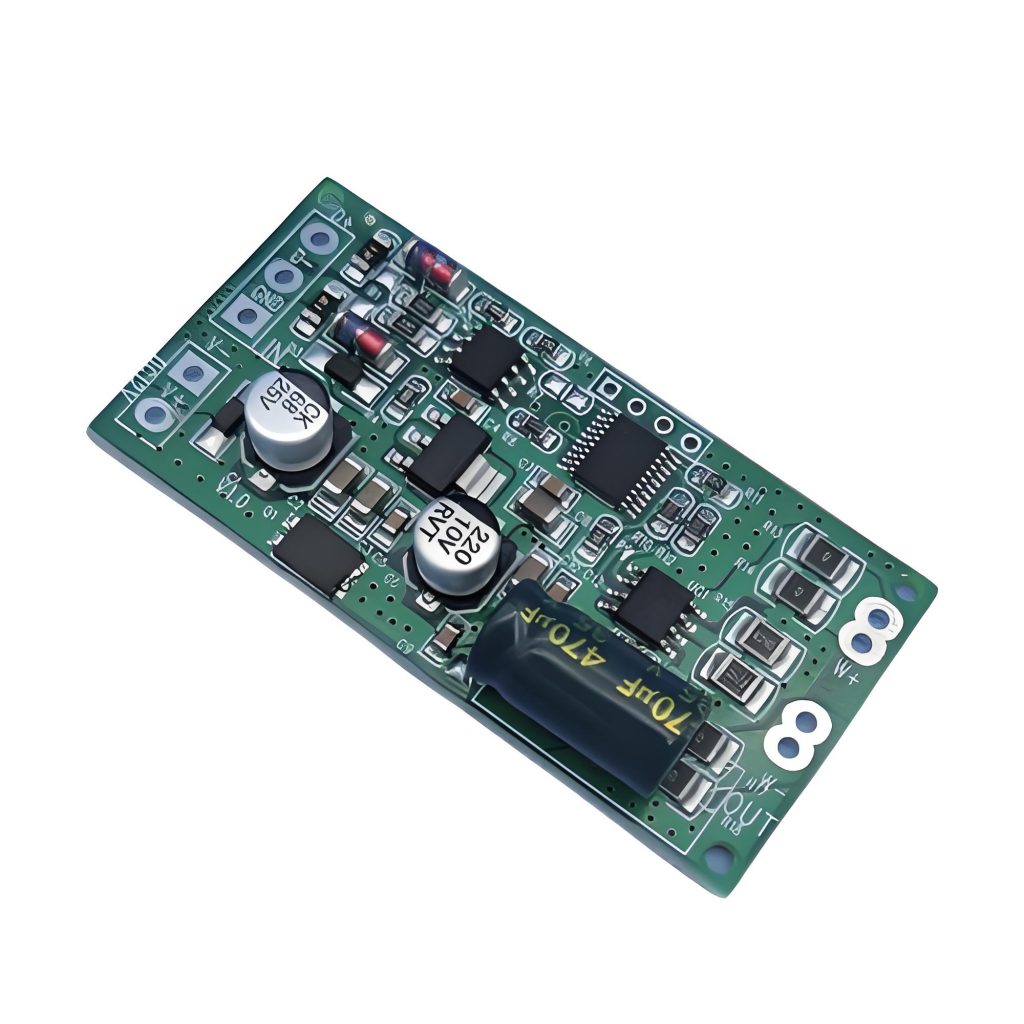
Through the design and selection of these technical parameters, the stable operation and long life of the LED lamp can be ensured, achieving the best lighting effect.
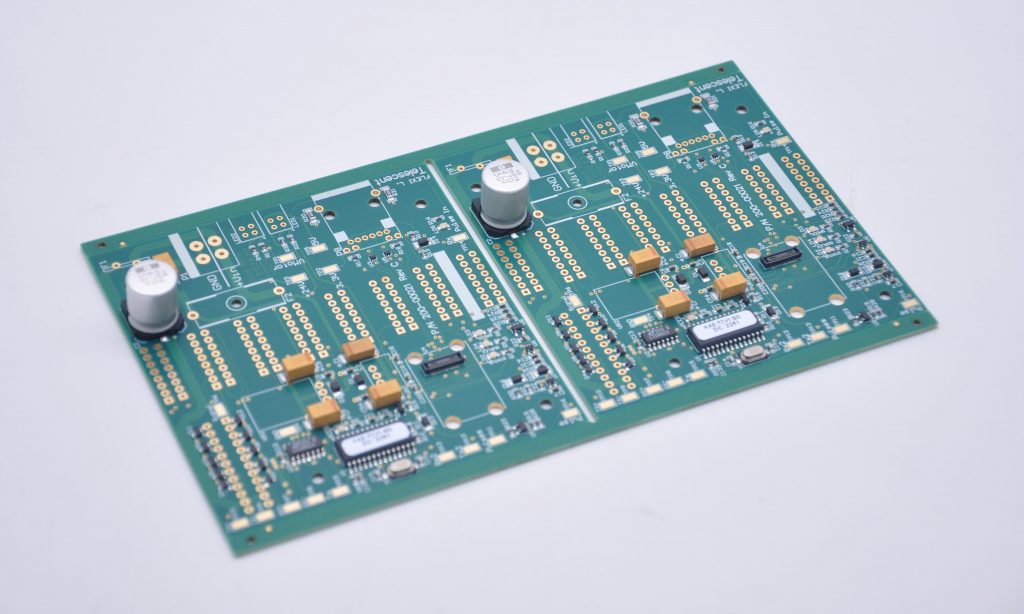
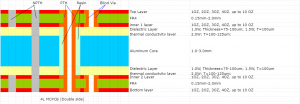
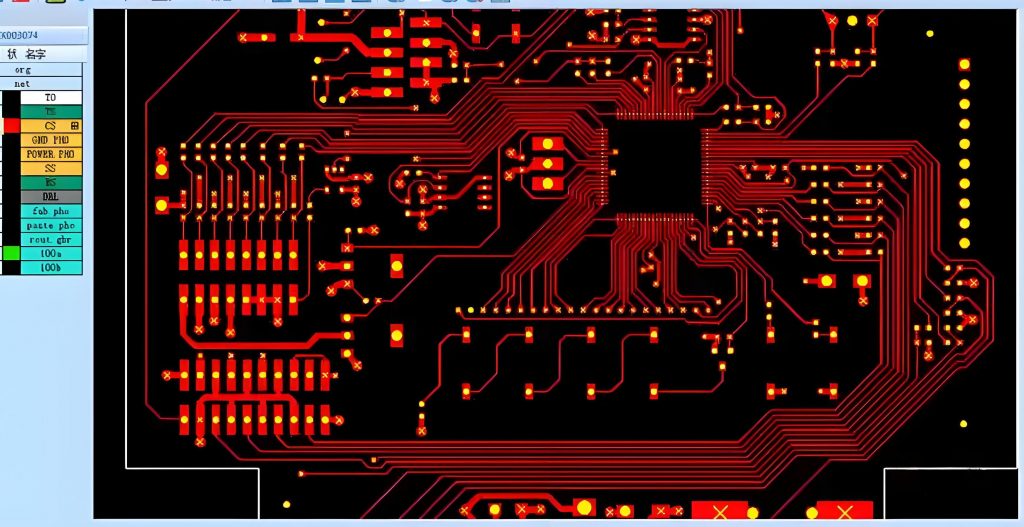
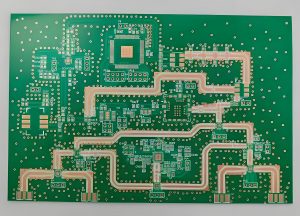
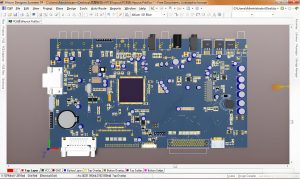
Explanation PCB diagram of ballast light
The circuit structure of the ballast light is shown in the figure, which covers several key parts such as capacitor step-down circuit, rectifier circuit, LED light-emitting circuit and photoelectric control circuit. These circuits work together to ensure that the LED light can emit light stably and efficiently.
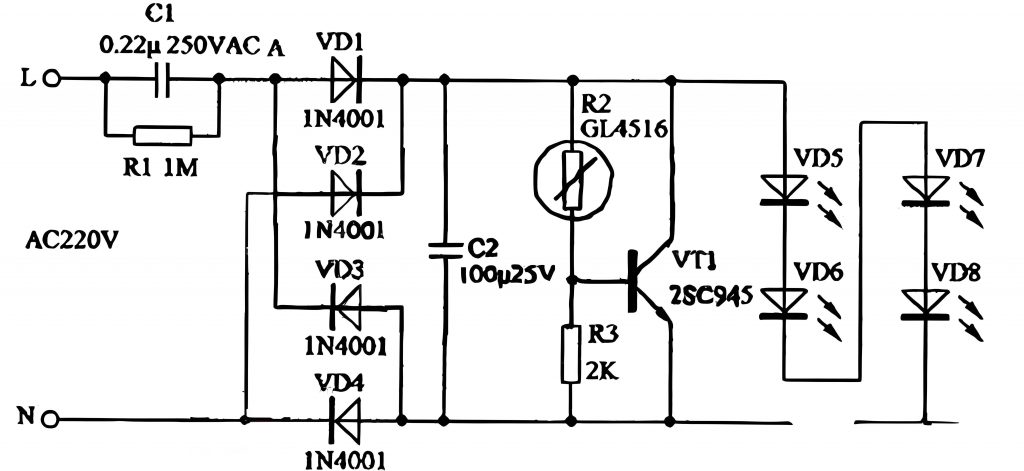
A typical light ballast PCB diagram shows both input and output sides, along with key components like capacitors, inductors, and switching transistors.
At the input stage, a fuse and filter block unwanted noise from the power source. Next, a rectifier converts AC to DC, which passes through smoothing capacitors to create stable voltage. The control section uses a micro-controller or driver IC to regulate switching transistors. These transistors adjust voltage and frequency, ensuring the lamp gets the right current flow. The output stage includes the final filter and connections to the lamp. In fluorescent lamps, this stage also includes a high-voltage starter circuit.
Overall, the diagram reflects a balance between power conversion, current control, and protection, all packed into a compact PCB layout.
Application of light ballast on PCB
Light ballast PCBs appear in many everyday products and systems.
- Kitchen lights, bathroom fixtures, and under-cabinet fluorescent lamps at home.
- Ceiling panels, emergency lights, and retail display lamps in offices.
- High-output lighting systems used for work areas, safety zones, and storage spaces in factories and warehouses.
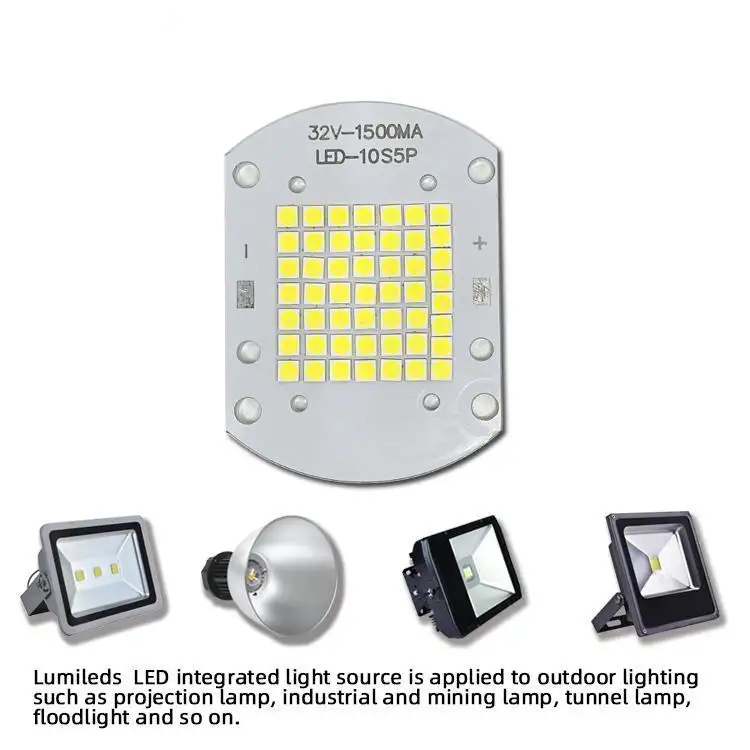
- Streetlights, parking lot lamps, stadium floodlights, and more. As outdoor lighting shifts to LED, many ballasts also act as LED drivers, offering advanced dimming and color control.
- Growing application relates to recycling programs. Old ballasts, especially PCB fluorescent light ballasts, need careful handling due to environmental rules. Proper pcbs ballast recycling helps recover valuable metals while safely disposing of any hazardous materials.
FAQ light ballast PCB
- Aging of electronic components: Electronic components in light ballast power supplies, such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, etc., may age due to open circuits, short circuits, burnouts, leakage, functional failures, etc. during long-term use.
- PCB quality impact: The quality of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and printed circuit board assemblies (PCBA) directly affects the reliability of LED driver power supplies. Problems such as poor wetting, board explosion, delamination, CAF (anode foil fiberization), open circuits, short circuits, etc. may cause power supply failure.
- Heat dissipation problem: The electronic components in the light ballast PCB are very sensitive to temperature changes, especially the electrolytic capacitors. Poor heat dissipation may shorten the life of the components, thus affecting the stability of the LED lamps.
- Solder joint failure: Solder joints are the key connection between electronic components and PCB boards, and their quality directly affects the reliability of the power supply. Solder joint failure may be caused by welding problems during the production process, or thermal stress fatigue caused by differences in thermal expansion coefficients.
- Other issues: If the substrate hole is too large, the solder furnace temperature is too low, the board surface is poorly solderable, the solder mask is invalid, the board surface is contaminated, etc., it will also cause PCB problems.
Conclusion
The light ballast PCB plays a quiet but critical role in modern lighting systems. By delivering stable, efficient power, it protects lamps, saves energy, and supports advanced lighting controls. Whether you need simple fluorescent support or advanced smart lighting, the right light ballast PCB keeps your system running smoothly.