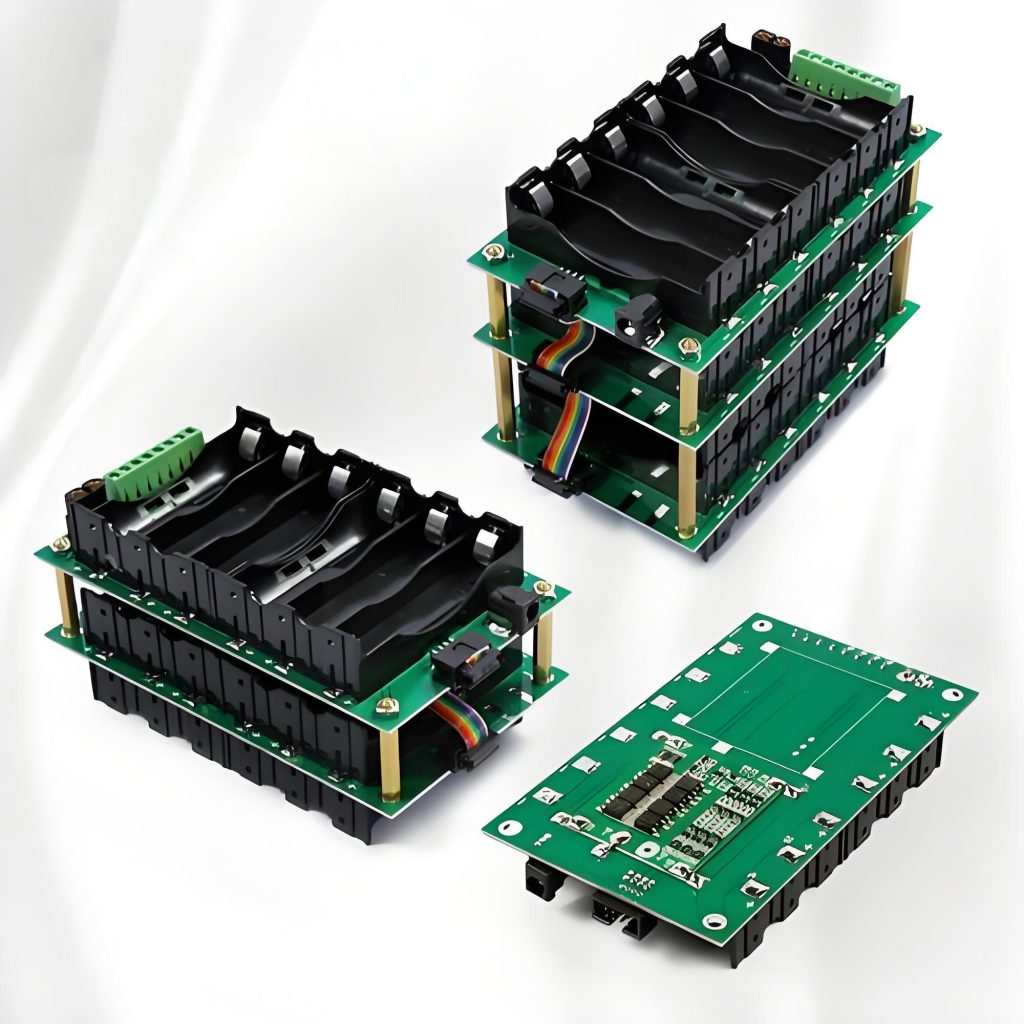
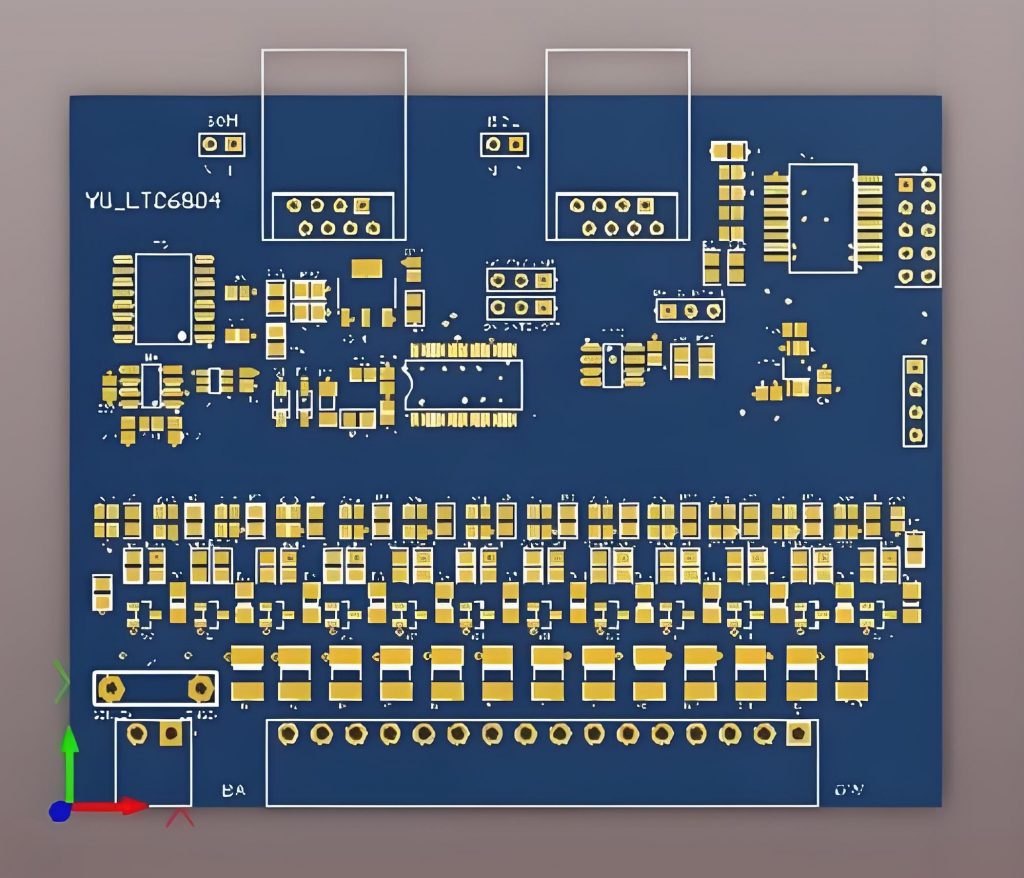
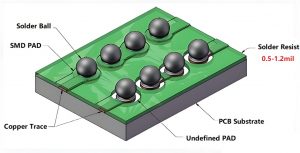
How to custom BMS PCB? To customize BMS PCB, you need to first clarify the functional requirements and environmental adaptability requirements, then carry out circuit design, layout and wiring, and thermal management planning, and select the appropriate materials and number of layers. During the manufacturing process, high-precision printing and welding must be ensured, and its reliability must be verified through electrical testing, environmental testing, etc.
What is a BMS PCB?
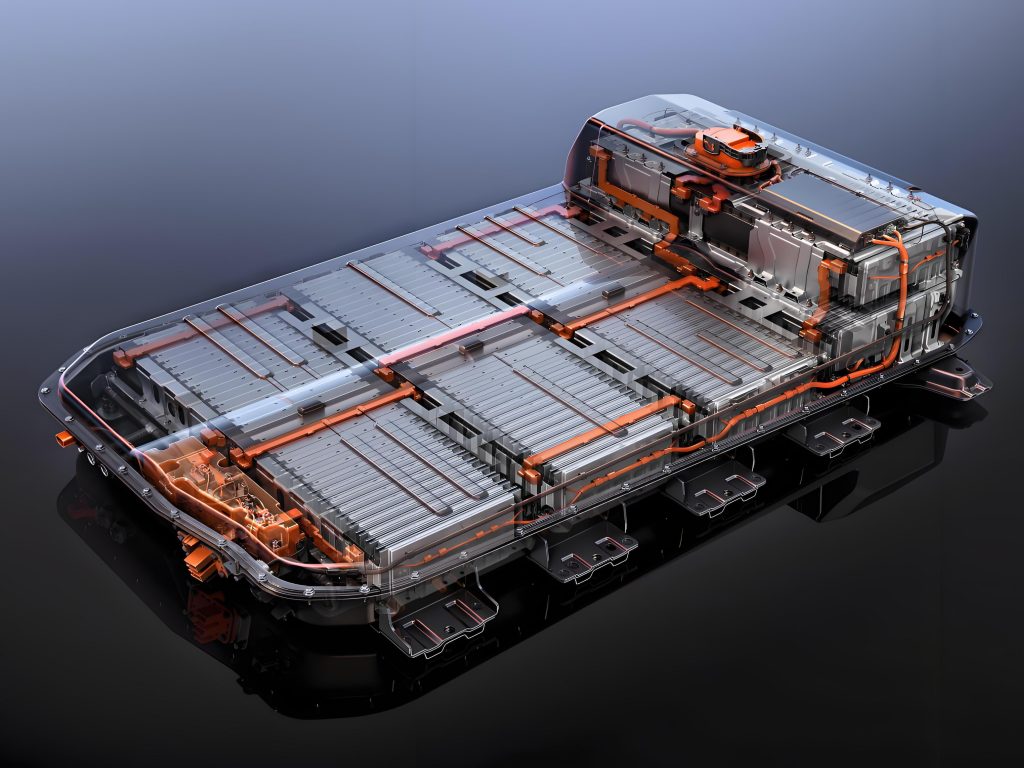
A BMS PCB is the heart of a Battery Management System, designed to monitor and control the performance of a battery pack. Itâs responsible for managing the charge and discharge cycles, balancing the cells, ensuring safety, and maximizing the life of the battery.
The PCB is the physical platform that interconnects all the components of the BMS, including sensors, controllers, and power management circuitry.
The BMS PCB typically includes several critical elements such as:
- Voltage and current sensing components to monitor the batteryâs health.
- MOSFETs to manage the flow of current during charging and discharging.
- Microcontrollers to process data and execute commands.
- Protection circuits to prevent overcharging, deep discharging, and short circuits.
This PCB ensures that the battery operates safely and efficiently, which is why customizing it to meet specific needs is so important.
How to customize BMS PCBï¼
Customizing a BMS PCB involves a detailed process that addresses various factors such as power requirements, battery specifications, and safety features.
- Define the Requirements: Understand the application, battery specifications, and power requirements.
- Select the Components: Based on the requirements, choose the right components, such as MOSFETs, capacitors, resistors, and microcontrollers.
- Design the PCB Layout: The PCB layout should be designed for efficient current flow, heat dissipation, and compactness. Make sure to include clear routing for power and signal paths.
- Safety Features: Include protection circuits for over-voltage, under-voltage, over-current, and thermal protection. These features help prevent damage to both the battery and the device.
- Prototyping and Testing: After the design is complete, build a prototype and test the PCB for performance, safety, and reliability. Test for thermal performance and ensure the BMS can handle the expected load.
- Refinement and Finalization: After testing and debugging, finalize the design, and prepare for mass production if needed.
What is a PCM in BMS?
PCM stands for Protection Circuit Module, a critical component of the BMS. Itâs designed to monitor the batteryâs voltage, current, and temperature to protect the cells from operating outside safe limits.
If the batteryâs voltage drops too low, or if it overheats, the PCM will disconnect the load or charge source, preventing potential damage.
PCMs are typically used in simpler battery packs or in scenarios where a full-fledged BMS might not be necessary. While PCMs offer basic protection, they may not include more advanced features like cell balancing or communication capabilities.
What does MOS mean on BMS?
MOS stands for Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor, commonly referred to as MOSFETs.
MOSFETs are crucial components in the BMS because they control the current flow between the battery cells and the deviceâs power system.
MOSFETs are used in BMS to switch the charging and discharging processes on and off. They regulate the voltage and current to ensure the battery operates safely. In most BMS designs, youâll find both P-channel and N-channel MOSFETs, each serving a different purpose for controlling the charge and discharge cycles.
How many types of BMS are there?
There are primarily three types of Battery Management Systems:
- Centralized BMS: All the components, including sensors and control units, are located in a central hub.
- Distributed BMS: Each module of the battery pack has its own BMS, which communicates with a central controller.
- Modular BMS: Similar to distributed BMS but with a more flexible, modular approach. Each module can operate independently but can be combined with other modules for larger systems.
The type of BMS you choose depends on the size and complexity of the battery pack, as well as the specific requirements of your application.
Do all lithium batteries need a BMS?
While not every lithium battery needs a BMS, most modern lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries do require one for safety and longevity.
A BMS ensures that each cell is monitored and protected, preventing issues such as overcharging, over-discharging, and thermal runaway.
For smaller battery packs used in devices like smartphones or laptops, a simple PCM may be sufficient.
However, for larger battery systems, such as those used in electric vehicles, solar power storage, and large-scale energy systems, a full-featured BMS is essential for safe and reliable operation.
What is the difference between BMS and PCB?
While both a BMS and a PCB are integral to battery-powered systems, they serve different purposes.
A BMS is a system that manages the battery, including monitoring the cells, balancing the charge, and protecting against unsafe conditions.
A PCB, on the other hand, is the physical board that holds all the electronic components together, providing the connections and pathways needed for the BMS to function.
Essentially, a BMS may include a PCB, but a PCB by itself isnât a complete BMS.
What is p+ and p on BMS?
The P+ and P markings on a BMS typically refer to the positive terminal connections for the battery. These terminals are crucial for connecting the battery pack to the BMS and ensuring proper charge and discharge processes.
The P+ is usually the main positive terminal, while P might be used to denote a secondary or more specific positive terminal, such as the one for a particular cell.
What is b in BMS?
The B in BMS stands for Battery. It often refers to the negative terminal connection of the battery. Just like the positive terminals (P+ and P), the B terminals are used to manage the flow of current and monitor the batteryâs condition. In some cases, B- refers to the common ground or negative connection in the system.
What does s mean in BMS?
The S in BMS refers to Sense. This is typically associated with the voltage or current sensing points on the BMS. These sensors allow the BMS to measure the voltage across individual cells and ensure that each one operates within safe limits.
By sensing the voltage, the BMS can determine if the battery is overcharged or undercharged, providing valuable data to help manage the overall health of the battery pack.
Conclusion:
At Best Technology, we specialize in the design and manufacture of high-quality PCBs, including custom BMS PCBs tailored to meet the specific needs of your application. Whether youâre designing a BMS for a small consumer device or a large-scale electric vehicle, contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com