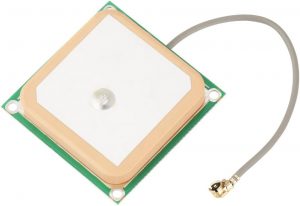
2.4 GHz antenna plays a key role in wireless communication today. From WiFi routers to smart home devices, they keep us connected without messy cables. Whether you need reliable coverage for short-range indoor use or long-range outdoor connections, the right 2.4 GHz antenna can improve your system’s performance. Best Technology handle both design and production for 2.4Ghz antenna PCB, we can optimize performance from the start. When you need reliable 2.4 GHz antenna PCB, Best Technology delivers top-quality solutions tailored to your project.

What is a 2.4 GHz Antenna?
A 2.4 GHz antenna is a specialized antenna that operates within the 2.4 GHz frequency band. This frequency is widely used for wireless technologies like WiFi, Bluetooth, and IoT devices.
Because 2.4 GHz antennas work within this popular band, they support many devices and systems. Whether for indoor use or longer outdoor coverage, they can send and receive signals efficiently. Their design focuses on matching frequency requirements while balancing gain, size, and range.
What Are the Different Types of 2.4 GHz Antennas?
There are several 2.4 GHz antenna types designed for different environments and needs. Each type offers distinct features to match specific wireless setups.
1. By Radiation Pattern
- Omnidirectional Antennas
Omnidirectional antennas send signals in all directions. Radiate signals in all directions horizontally, like ripples on water. They are ideal for indoor WiFi routers or small IoT devices where full-area coverage matters most. (e.g., Wi-Fi routers, smart speakers).
- Directional Antennas
Directional antennas focus energy in one direction to boost signal strength over longer distances. Focus energy like a flashlight beam. These are perfect for point-to-point outdoor links, long-distance links (e.g., outdoor cameras, wireless bridges).
2. By Integration Method
- PCB Antennas
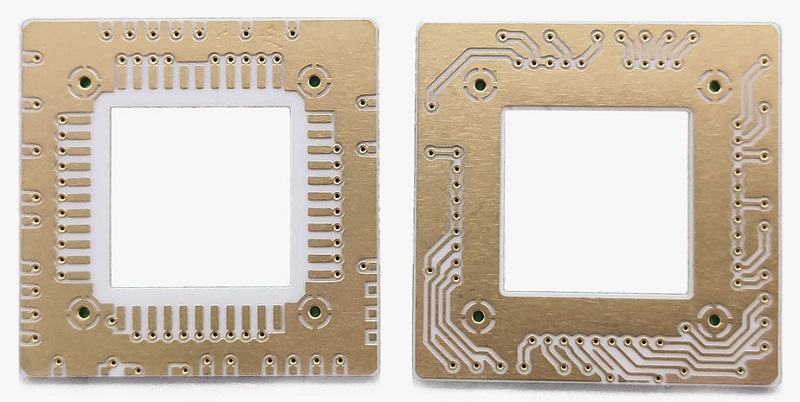
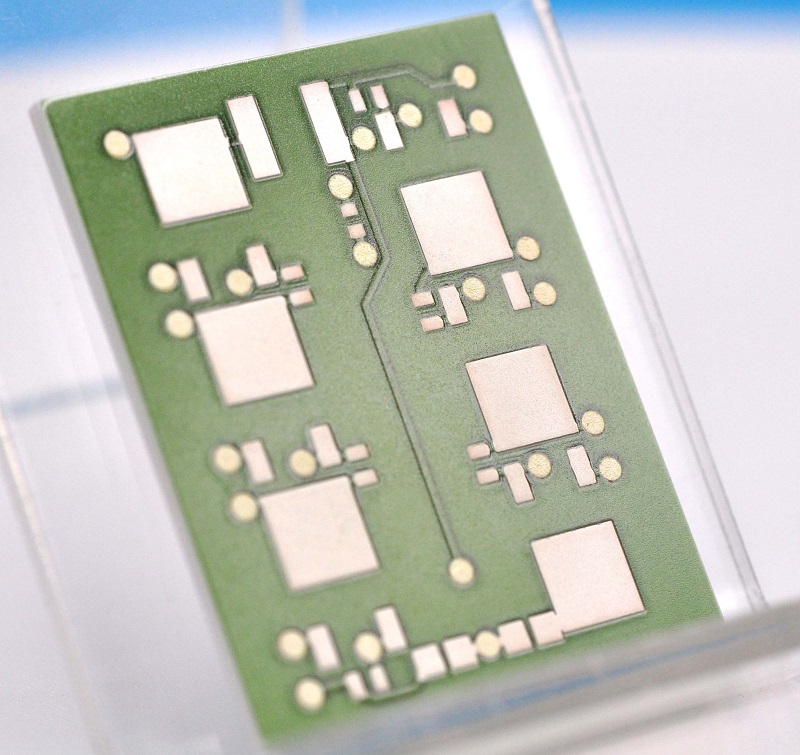
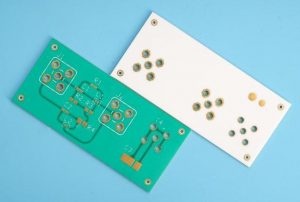
PCB Antennas are designed as copper traces embedded directly into circuit boards. Ideal for mass-produced devices due to low cost and space-saving design. Common in Bluetooth earphones, smart thermostats, and IoT sensors. Their performance depends on board material (e.g., FR4 for basic needs, Rogers substrates for high-frequency stability). Requires precise impedance matching to avoid signal loss.
- Flexible Antennas
Flexible Antennas are made with thin, bendable materials like polyimide film or flexible printed circuits (FPC). Withstands repeated bending, making them perfect for wearables (e.g., fitness bands) or devices with curved surfaces (e.g., medical patches). Some models survive 100,000+ bend cycles. Water-resistant options available for outdoor gear.
3. By Installation Location
- Internal Antennas
Integrated within the device housing, optimized for compact designs and aesthetic concealment. Common in consumer electronics (e.g., smartphones, smartwatches) where space and design are critical. Typically use PCB or flexible antennas for seamless integration
- External Antennas
Mounted outside the device via connectors (e.g., SMA) or cables, enabling flexible placement for optimal signal reception. Ideal for environments requiring tunable orientation or signal amplification (e.g., industrial routers, drones). High-gain directional variants (e.g., Yagi-Uda) are often external for long-range applications.
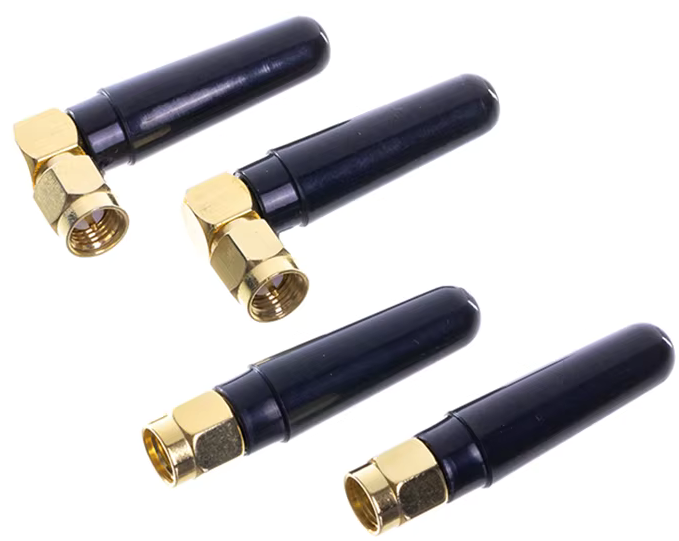

The reason 2.4GHz antennas widely adopt SMA connectors is threefold:
- Superior high-frequency performance – low loss (<0.1 dB @ 2.4GHz) and stable 50Ω impedance up to 18GHz;
- Robust mechanical design – compact threaded interface ensuring durability in space-constrained devices like drones;
- Regulatory compliance – standardized variants (e.g., RP-SMA) meet FCC/CE certifications for Wi-Fi routers and IoT equipment.
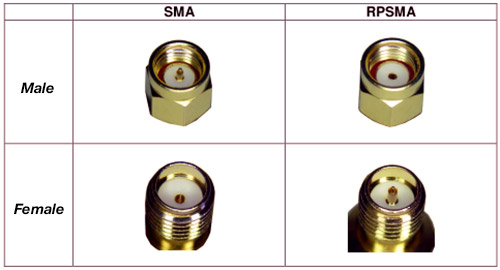
SMA Connector has gender identification. Most antennas use female SMA connectors (hole), while devices (e.g., routers) use male SMA ports (pin). SMA Connector Gender Identification:
- SMA Male (Plug): Features a center pin and inner threads.
- SMA Female (Jack): Has a center hole and outer threads.
Reverse-polarity SMA (RP-SMA) swaps genders, common in Wi-Fi gear. Pls always check device specs to avoid mismatches.
What Materials Are 2.4 GHz Antennas Made Of?
The materials used to build a 2.4 GHz antenna directly affect how well it performs, how long it lasts, and how easy it is to fit into different devices. Choosing the right materials helps balance conductivity, weight, cost, and durability. Let’s break down the most common material choices and where they fit best.
1. Conductive Metals for High Signal Efficiency
The main goal of any 2.4 GHz antenna is to efficiently radiate and receive signals, so the core material must conduct electricity well.
- Copper is one of the top choices. Its excellent conductivity helps signals pass through with minimal loss, which directly improves antenna efficiency. Copper is widely used in both external and internal antennas, particularly in applications where high performance is critical.
- Aluminum offers another option, especially for larger antennas where weight savings are important. Although aluminum’s conductivity is lower than copper’s, it’s still good enough for many 2.4 GHz antenna applications, especially directional designs like Yagi antennas or outdoor panels.
These metals form the main radiating elements in most antennas, whether they’re external, internal, or PCB-based.
2. Ceramic for Compact Embedded Designs
When devices shrink, so do their antennas. Many modern devices rely on ceramic antennas, especially for built-in 2.4 GHz antenna PCB layouts.
Ceramic materials allow antennas to stay small without losing too much performance.
They handle higher frequencies like 2.4 GHz well, making them perfect for compact gadgets such as IoT sensors, smart home devices, fitness trackers, and smartphones.
Ceramic antennas are often printed directly onto the PCB or mounted as small components. Their high dielectric constant helps keep the physical size small while still maintaining reasonable performance.
3. Protective Coatings and Weatherproof Materials
For outdoor applications, 2.4 GHz antennas face a different challenge—exposure to sun, rain, and extreme temperatures. Materials used in these antennas need to survive tough conditions without affecting performance.
Many outdoor antennas use weather-resistant plastics to cover the metal radiators. This plastic shielding blocks moisture and dirt but allows radio signals to pass through with minimal interference.
In harsher industrial or marine settings, UV-resistant coatings and corrosion-resistant metals add extra protection, keeping antennas working reliably for years.
These protective materials make sure outdoor antennas can handle long-term exposure while still providing stable connections, even in challenging environments.
2.4 GHz Antenna Design
How to design a 2.4 GHz antenna? Designing a 2.4 GHz antenna may look simple on the surface, but every step directly affects how well the antenna performs. Engineers focus on balancing frequency, size, gain, and impedance matching to get the best signal strength and stable connection. Below is a clear step-by-step breakdown of the key stages.
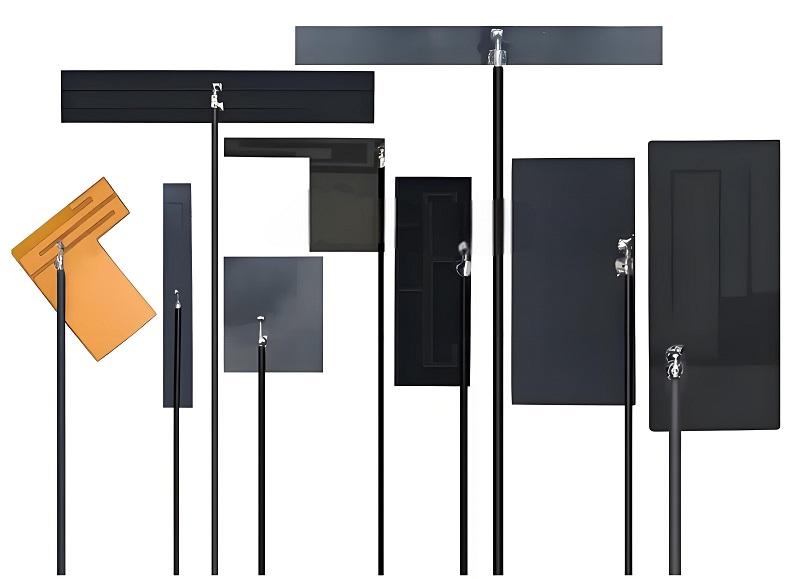

1. Selecting the Right Antenna Type and Length
The first step in the design process is deciding which 2.4 GHz antenna type works best for the device and its application. Common options include omnidirectional antennas, directional antennas, and PCB-integrated antennas.
- Omnidirectional antennas radiate signals evenly in all directions, which suits routers, smart home devices, and wireless cameras.
- Directional antennas focus the signal in one direction, which helps with long-range connections or point-to-point communication.
- PCB antennas fit directly onto the circuit board, making them perfect for compact gadgets like wearables and IoT devices.
Once the type is clear, the 2.4 GHz antenna length becomes critical. For 2.4 GHz signals, a quarter-wavelength antenna is roughly 31 mm, while half-wavelength antennas are about 62 mm. These values shift slightly depending on the design and placement, especially in small or embedded products. Keeping the length correct ensures the antenna resonates properly at 2.4 GHz, which directly impacts performance.
2. Shaping the Antenna and Optimizing Radiation Pattern
The next important part is choosing the antenna shape since it directly affects how the antenna radiates signals. Different shapes suit different needs:
- Helical antennas (coiled wire designs) work well when space is extremely limited. Despite the compact form, they still deliver usable performance.
- Patch antennas, often seen in routers and access points, offer reliable coverage with a relatively small footprint.
- Monopole or dipole antennas strike a balance between size and performance, making them versatile for indoor and outdoor devices.
Once the shape is selected, engineers use simulation software to model how the antenna radiates at 2.4 GHz. These simulations reveal weak points, dead zones, or unexpected reflections that could weaken signal strength. The design can be adjusted to boost coverage, reduce interference, and fine-tune the antenna’s radiation pattern.
3. Ensuring Proper Impedance Matching and Minimizing Interference
With the physical design in place, attention shifts to impedance matching—a critical factor for signal transfer efficiency. The 2.4 GHz antenna must match the output impedance of the connected device, typically 50 ohms. A mismatch causes signal reflections, which lower efficiency and reduce range.
The antenna materials, trace width, and even the 2.4 GHz antenna PCB layout all affect impedance. Engineers adjust these factors during prototyping to get the cleanest match possible.
Finally, interference checks are essential. The 2.4 GHz band is crowded, with Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and countless smart devices all sharing the same space. Good antenna designs use filtering techniques, proper shielding, and smart placement to reduce noise from nearby electronics. By minimizing interference, the antenna delivers cleaner signals and better reliability, especially in busy environments like homes and offices.
Best Technology offers a full range of high-quality antenna PCBs, customized to match the unique requirements of each customer. With competitive ODM & OEM pricing, we deliver reliable 2.4 GHz antenna solutions to support your projects from initial design to final production.
What Are the Benefits of 2.4 GHz Antennas?
The 2.4 GHz antenna stands out in the wireless world thanks to its strong performance across various devices and environments. Its advantages explain why it plays such a key role in modern communication systems. Let’s break down some of the key benefits.
1. Compatibility Across Multiple Technologies
One of the biggest benefits of a 2.4 GHz antenna is its broad compatibility. It works smoothly with popular wireless standards like WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and proprietary RF systems.
This flexibility allows engineers to create devices that communicate across homes, offices, factories, and even outdoor spaces—all using the same frequency band. Because so many devices operate at 2.4 GHz, businesses and designers can standardize around this frequency, reducing complexity when building connected systems.
2. Longer Range Compared to Higher Frequencies
Another key advantage is range. Compared to higher bands like 5 GHz, the 2.4 GHz antenna supports better signal penetration and wider coverage.
Signals at 2.4 GHz travel farther, especially indoors where walls, furniture, and other obstacles can block higher frequencies. This longer range is valuable for applications like smart homes, industrial sensors, and outdoor IoT systems where stable connections matter more than speed.
This is why 2.4 GHz antennas remain so popular, even though faster frequencies exist.
3. Flexible Designs for Every Application
The 2.4 GHz antenna can be designed to match almost any requirement.
- For compact devices like wearables or sensors, tiny PCB antennas fit directly onto circuit boards without adding bulk.
- For outdoor or long-distance uses, larger high-gain directional antennas focus signals in a specific direction to improve coverage and signal strength.
This range of options—from small embedded antennas to large external ones—gives designers freedom to choose the perfect antenna for each product.
What Are the Applications of 2.4 GHz Antennas?
Because the 2.4 GHz antenna combines wide compatibility, reliable range, and flexible designs, it fits into countless industries and use cases. From home networks to industrial automation, this frequency keeps devices connected in every corner of life.
1. Smart Homes and Consumer Electronics
In residential settings, 2.4 GHz antennas power the everyday devices people rely on.
- WiFi routers use 2.4 GHz to provide whole-home coverage, especially in multi-story homes where walls and floors block higher frequencies.
- Smart TVs, security cameras, smart plugs, and speakers also connect using this band, ensuring devices stay linked to home networks without constant dropouts.
- Even smaller gadgets like smart thermostats, light switches, and door sensors all benefit from the reliability of 2.4 GHz antennas.
2. Industrial and Agricultural Systems
Beyond homes, 2.4 GHz antennas support critical wireless links in factories, warehouses, and farms.
- In industrial automation, machines rely on 2.4 GHz wireless connections to report performance data and receive remote commands.
- In smart agriculture, wireless soil sensors, irrigation controllers, and livestock trackers all depend on 2.4 GHz antennas to transmit data across fields and greenhouses.
These industries value 2.4 GHz for its range, penetration, and low power requirements, making it ideal for sprawling facilities and remote locations.

3. Automotive and Healthcare Technologies
The automotive and medical sectors also take advantage of 2.4 GHz antennas in innovative ways.
- Connected vehicles use them to communicate with roadside sensors, smart traffic lights, or other vehicles nearby.
- In healthcare, patient monitors, wearable health trackers, and wireless diagnostic tools rely on 2.4 GHz to continuously transmit data to caregivers without using wired connections.
Because 2.4 GHz antennas balance reliable performance and compact size, they work perfectly in cars and medical devices where space and reliability matter most.
2.4 GHz Antenna PCB Manufacturer
Why choose Best Technology as your trusted 2.4 GHz antenna PCB manufacturer? When choosing a 2.4 GHz antenna PCB manufacturer, you want more than just a product — you need a partner who understands your industry, your project requirements, and your timeline. At Best Technology, we deliver all that and more. Here’s why companies worldwide trust us for their 2.4 GHz antenna needs:
1. Full Turn-key Antenna PCB Solutions
At Best Technology, we do more than supply antennas PCB — we work alongside you from initial design all the way to final delivery. Whether you need a standard design or something fully customized to match your device size, operating environment, and signal requirements, we’ve got you covered.
2. 18 Years PCB Manufacturing Experience
With over 18 years of hands-on experience in PCB manufacturing, our engineering team ensures your antenna’s performance is fine-tuned from the start. By handling both design and production under one roof, we make sure every detail — from material selection to layout optimization — works in harmony to maximize performance.
3. No MOQ Requirement
We also provide flexible order sizes, whether you need a small prototype batch for testing or high-volume production for mass deployment. With no MOQ restrictions, we ensure rapid turnaround times and dedicated support for projects of any scale.
4. 2-3 Weeks Fast Delivery Time
With delivery times as fast as 2-3 weeks, we help you hit your project milestones without compromising on quality. Our streamlined production process and dedicated team ensure timely delivery to keep your projects on track.
5. High Quality Ensured
Reliability matters, especially for wireless communication. Every PCB of 2.4 GHz antenna from Best Technology undergoes thorough performance checks to ensure it meets frequency accuracy, gain, and long-term durability requirements.
6. ISO13485, IATF16949 & AS9100D Compliant
Our production facilities operate under globally recognized quality systems, including ISO13485 for medical, IATF16949 for automotive, and AS9100D for aerospace applications.
7. Customer-Oriented Support
Whether you’re developing antennas for IoT devices, medical equipment, automotive systems, or industrial applications, our team deeply understands the unique wireless challenges across these industries and delivers tailored solutions. Our professional PCB engineers are here offering 24/7 consultation and rapid response. As an professional 2.4 GHz antenna PCB manufacturer, Best Technology feel pleasure to give customers the expert advice on 2.4GHz antenna PCB design. Just feel free to reach out to us at sales@bestpcbs.com with any questions or for additional information.
FAQ Of 2.4GHz Antenna
- Will a 2.4 GHz antenna work for 5 GHz?
No, 2.4 GHz antennas are designed for 2.4 GHz signals. They cannot efficiently handle 5 GHz frequencies due to size and impedance differences.
- What is the difference between 2.4G and 5G antennas?
2.4G antennas focus on longer range and better penetration, while 5G antennas prioritize faster speeds but with shorter range.
- Do longer WiFi antennas work better?
Not always. Length should match signal wavelength. Longer antennas can add gain, but only if properly matched.
- What is the best length for a 2.4 GHz antenna?
A quarter wavelength around 31 mm works well for most designs.
- How far can a 2.4 GHz antenna reach?
It depends on gain and environment. Indoors, 30 meters is common. Outdoors, high-gain directional antennas can achieve over 5 kilometers in ideal line-of-sight environments.
- How does a 2.4 GHz antenna work?
It converts electrical signals into 2.4 GHz electromagnetic waves for transmission and vice versa for reception, enabling wireless communication through resonant frequency matching.