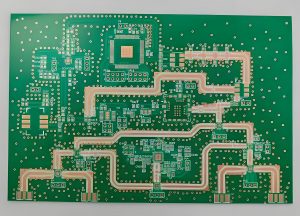
PCB Assembly plays a crucial role in modern electronics, turning bare circuit boards into functional devices. Without proper assembly, even the most advanced PCB designs cannot perform as expected. Whether for consumer electronics, automotive applications, or aerospace systems, high-quality PCBA ensures reliability and performance. In this guide, we explore everything about PCB assembly, from types and materials to design considerations and industry applications. By the end, you’ll understand why Best Technology is the right partner for your PCB assembly needs.
At Best Technology, we specialize in precision-driven PCB assembly services, offering turnkey PCBA solutions, rigorous quality control, and advanced manufacturing capabilities to meet diverse industry needs. With over 18 years of experience, Best Technology provide cost-effective, high-accuracy printed circuit board assembly solutions tailored to your requirements. Feel free to contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com for any doubts or queries you might have.

What is a PCB Assembly?
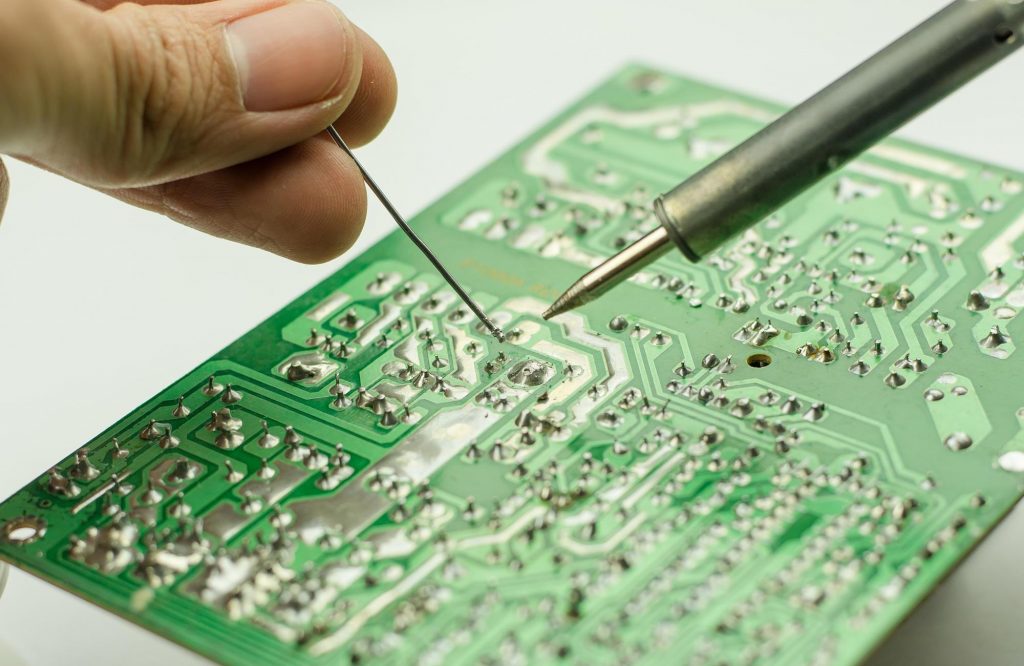
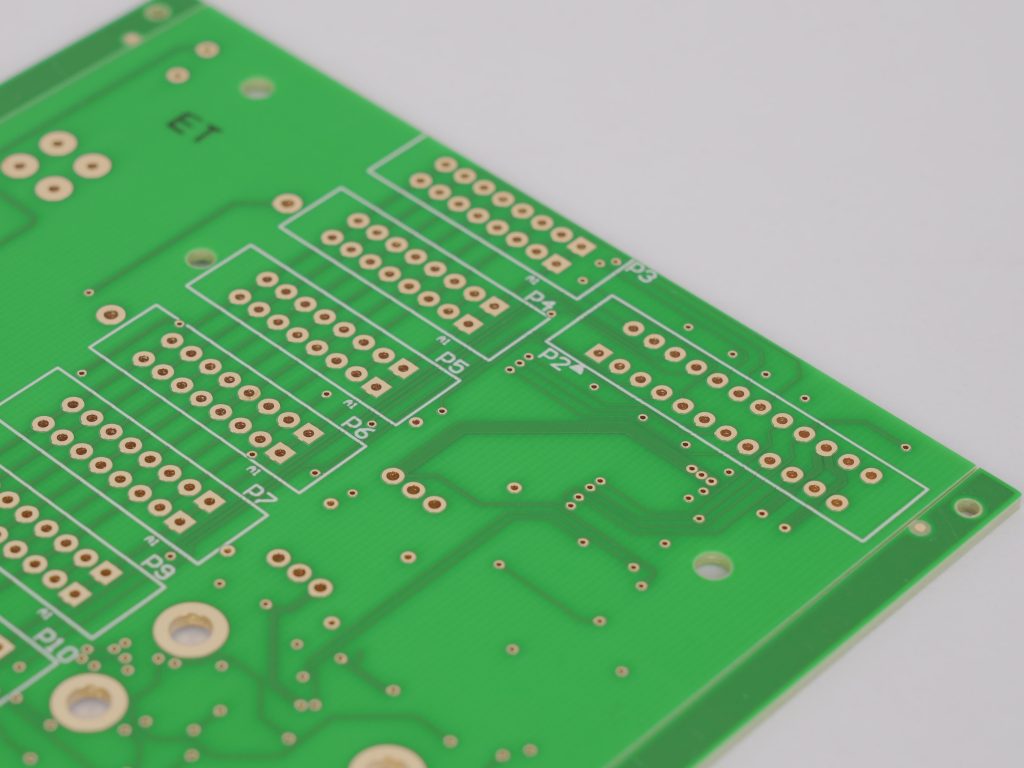
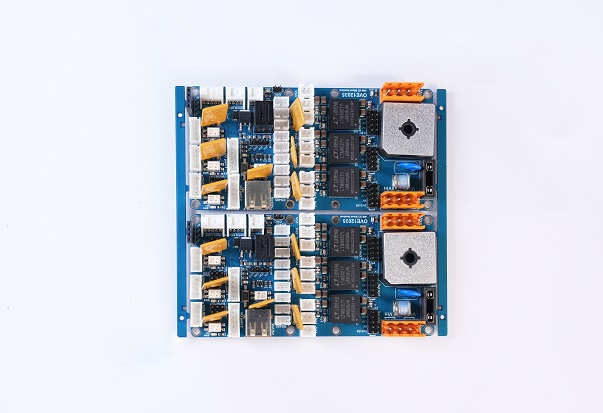
PCB assembly (PCBA) is the process of placing and soldering electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB) to create a functional electronic device. The assembly process involves multiple steps, including surface-mount technology (SMT), through-hole technology (THT), soldering, and quality inspections. Unlike a bare PCB, a fully assembled PCB has all the necessary components installed, making it ready for integration into electronic systems.
What Are the Different Types of PCB Assembly?
1. Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) Assembly – The most common assembly method, SMT involves mounting components directly onto the surface of the PCB. It allows for smaller, more compact designs and is ideal for high-density applications.
2. Through-Hole Technology (THT) Assembly – THT involves inserting component leads into pre-drilled holes on the PCB and soldering them in place. It provides strong mechanical connections and is used in applications requiring durability.
3. Mixed Assembly – A combination of SMT and THT, mixed assembly is used when a design requires both surface-mounted and through-hole components.
4. Single-Sided & Double-Sided Assembly – Single-sided assembly involves placing components on one side of the PCB, while double-sided assembly places components on both sides, maximizing space and functionality.
5. Box Build Assembly – This type of assembly goes beyond the PCB level, including wire harnesses, enclosures, and full system integration.
6. Turnkey PCB Assembly – A complete service where the manufacturer handles everything from PCB fabrication to component sourcing, assembly, and testing, providing a ready-to-use product.
7. Prototype PCB Assembly – Used for product development and testing before full-scale production.
What Materials Are Used to Make PCB Assembly?
Several materials are used in PCB assembly to ensure reliability and performance:
- PCB Substrate – The base material of the PCB, commonly made from FR4 (fiberglass epoxy), metal core, or ceramic for high-performance applications.
- Copper Traces – Thin layers of copper form the conductive pathways for electrical signals.
- Solder Mask – A protective layer applied over copper traces to prevent oxidation and short circuits.
- Silkscreen Layer – Used for labeling component positions and reference markings.
- Solder Paste – A mixture of flux and metal alloy used in SMT assembly to attach components before reflow soldering.
- Electronic Components – Resistors, capacitors, ICs, diodes, and other essential parts that enable the PCB to function.
- Solder Wire & Flux – Used in THT assembly to create strong electrical connections between components and the PCB.
How to Design PCB Assembly?
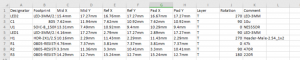
- Component Placement – Arrange components efficiently to optimize space, signal integrity, and heat dissipation.
- Layer Stack-Up – Define the number of PCB layers to meet electrical and mechanical requirements.
- Trace Routing – Ensure proper trace width, spacing, and routing strategies to minimize signal interference.
- Power & Ground Planes – Design stable power distribution and ground layers for noise reduction.
- Thermal Management – Use thermal vias, heat sinks, and copper pours to manage heat dissipation.
- DFM (Design for Manufacturability) – Optimize the PCB layout for efficient assembly, reducing potential defects and rework.
- DFT (Design for Testing) – Include test points and accessibility for automated testing.
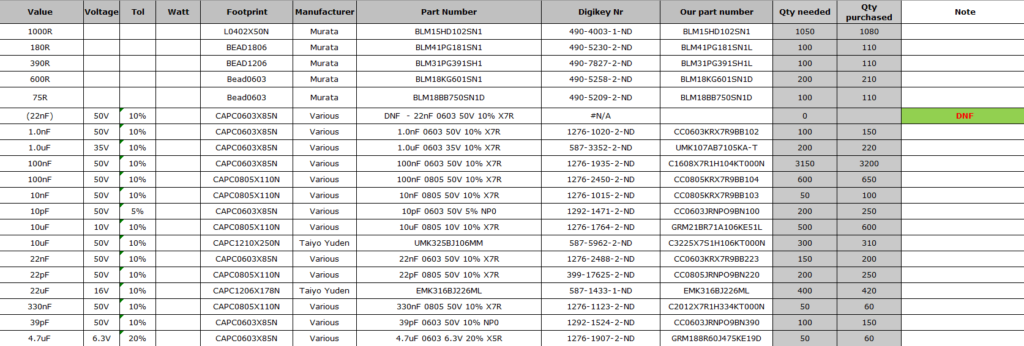
- Bill of Materials (BOM) Creation – List all required components, their specifications, and sourcing details.
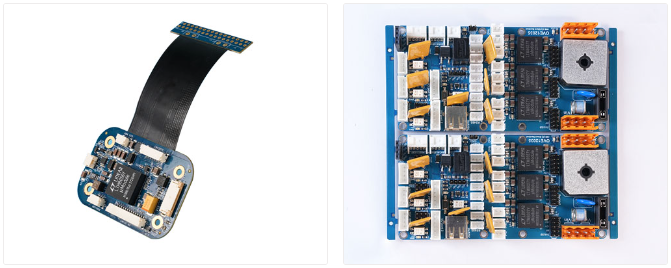
What Are the Benefits of PCB Assembly?
- Compact Design – Enables smaller, lightweight devices with high functionality.
- Cost-Effective Production – Automated assembly reduces labor costs and increases efficiency.
- High Reliability – Advanced soldering techniques and quality checks ensure long-lasting performance.
- Scalability – Suitable for both low-volume prototypes and high-volume manufacturing.
- Customization – Supports specialized requirements, such as high-speed, high-frequency, or high-temperature applications.
What Are the Applications of PCB Assembly?
- Consumer Electronics – Smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices.
- Automotive – Engine control units, infotainment systems, and safety sensors.
- Medical Devices – Patient monitoring systems, diagnostic tools, and imaging equipment.
- Aerospace & Defense – Avionics, communication systems, and radar technology.
- Industrial Automation – Robotics, control systems, and power electronics.
- Telecommunications – Networking equipment, signal processing, and wireless communication devices.
Why Choose Best Technology as Your PCB Assembly Manufacturer?
- Experience & Expertise – Over 18 years of experience in PCB manufacturing and PCB assembly. Best Technology is a leading PCB Assembly Manufacturer, providing manufacturing and sale service of various types of printed circuit boards and quality-focused PCBA Service.
- Comprehensive Services – Full turnkey, partial turnkey, and consignment assembly options. We provide one-stop service, including PCB assembly and component purchasing and all-around technical support before and after-sales.
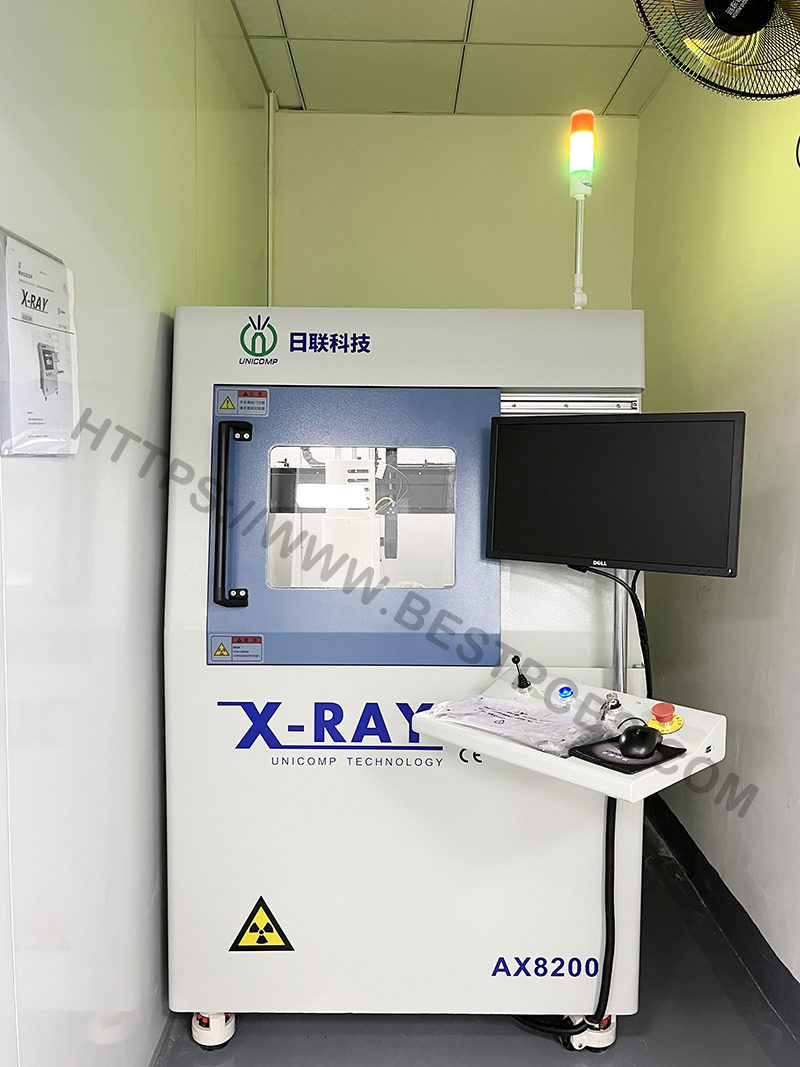
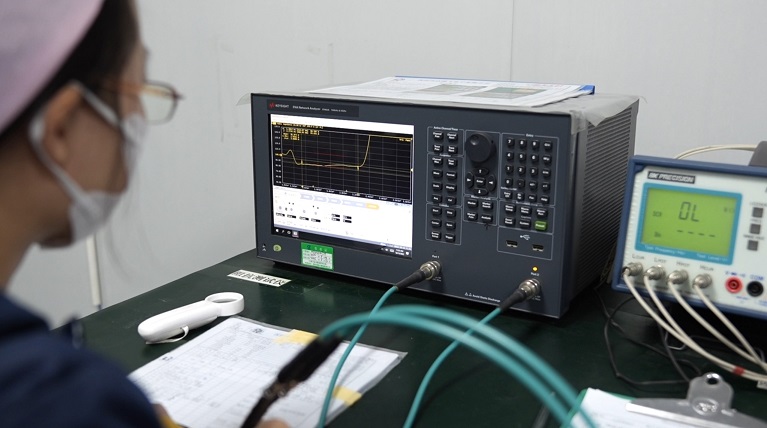
- Quality Assurance – Stringent IPC and industry-standard testing, including AOI, X-ray, and functional testing. The pursuit of quality and innovation is the driving force of Best Technology. Every stage, from sourcing raw materials to production, inspection, packaging, and even sales and marketing, strictly follows ISO quality standards to ensure consistency and reliability.
- Reliable Component Sourcing – Direct partnerships with trusted suppliers to prevent counterfeit parts. We procure all components exclusively from manufacturers or trusted distributors like Digikey, Mouser, Future, TTI, Avnet, and Arrow, ensuring authenticity.
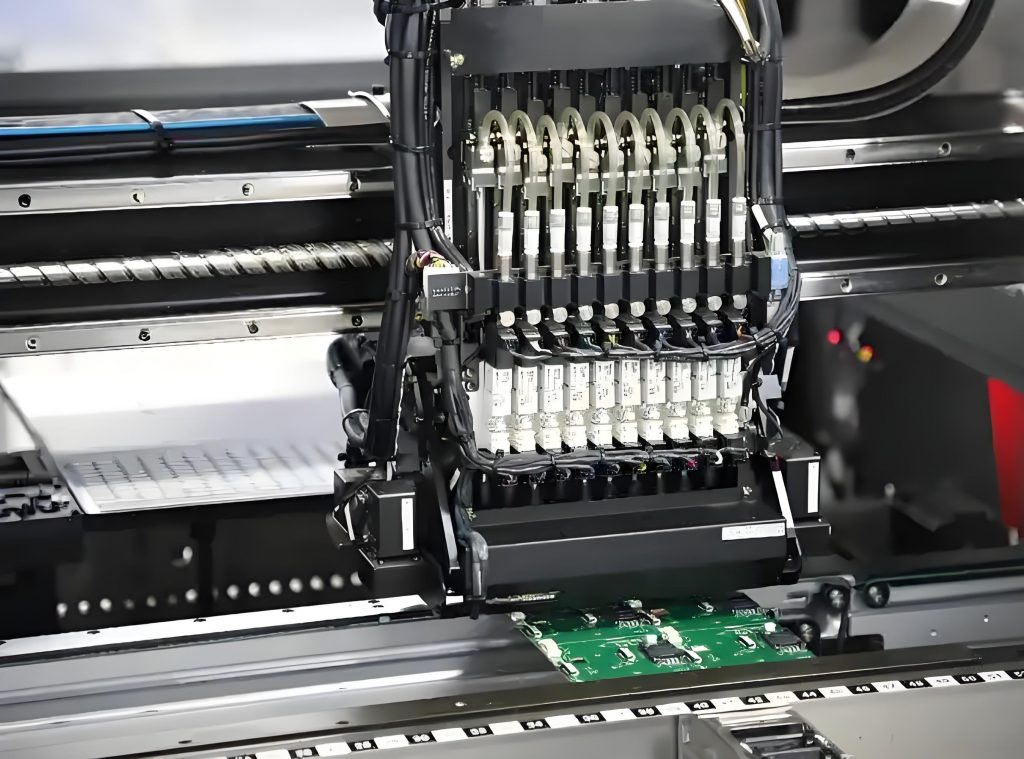
- State-of-the-Art Equipment – Advanced assembly machines ensure precision and efficiency. By leveraging cutting-edge technology and advanced PCB assembly equipment, we constantly refine our manufacturing processes, enhance testing and measurement techniques, and optimize our quality management system.
- On-Time Delivery – Expedited services available for urgent orders. No matter where you are, we guarantee on-time delivery for every order.
- Competitive Pricing – Cost-effective solutions without compromising quality.
- Customer Support – Dedicated one-on-one sales assistance for a smooth collaboration. With exceptional team, Best Technology ensures prompt responses within 12 hours.
In conclusion, choosing the right PCB assembly manufacturer ensures product reliability, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery. Best Technology offers expert solutions for various industries with a focus on quality and efficiency. Whether you need a simple prototype or a high-volume production run, our team is ready to support your project. Just feel free to reach out to us at sales@bestpcbs.com to discuss your PCB assembly needs!
FAQs of PCB Assembly
1. What is the difference between PCB and PCB assembly?
- A PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is the bare board with copper traces, while a PCB Assembly (PCBA) includes all the necessary electronic components soldered onto the board, making it a fully functional unit ready for use.
2. What is the purpose of a pick and place drawing in the SMT process?
- A pick and place drawing provides detailed guidance for automated SMT machines, specifying component placement, orientation, and reference designators on the PCB. It ensures accurate positioning (including polarity indicators for diodes and capacitors) and facilitates post-assembly inspection.
3. What are counterbores and countersinks?
- Counterbore: A cylindrical recess with a flat bottom, designed to allow a screw head to sit flush with the PCB surface. Commonly used with flat-head screws to ensure secure mounting, such as for attaching heatsinks or connectors.
- Countersink: A conical recess that matches the angle of a tapered screw head, such as self-tapping screws. Helps create a smooth, low-profile surface, often used when securing PCBs within enclosures.
The key difference is that counterbore provides a level surface by embedding the screw head within the material. Countersink features a tapered design that aligns the screw and evenly distributes stress.
4. How to distinguish the PTH & NPTH?
- PTH is PLATING Through Hole, it has copper in the holes inside, which can be conductive. NPTH is Non PLATING Through Hole, which don’t have copper inside the holes. Through holes means through the top and bottom on the PCB, it could be PTH and NPTH.