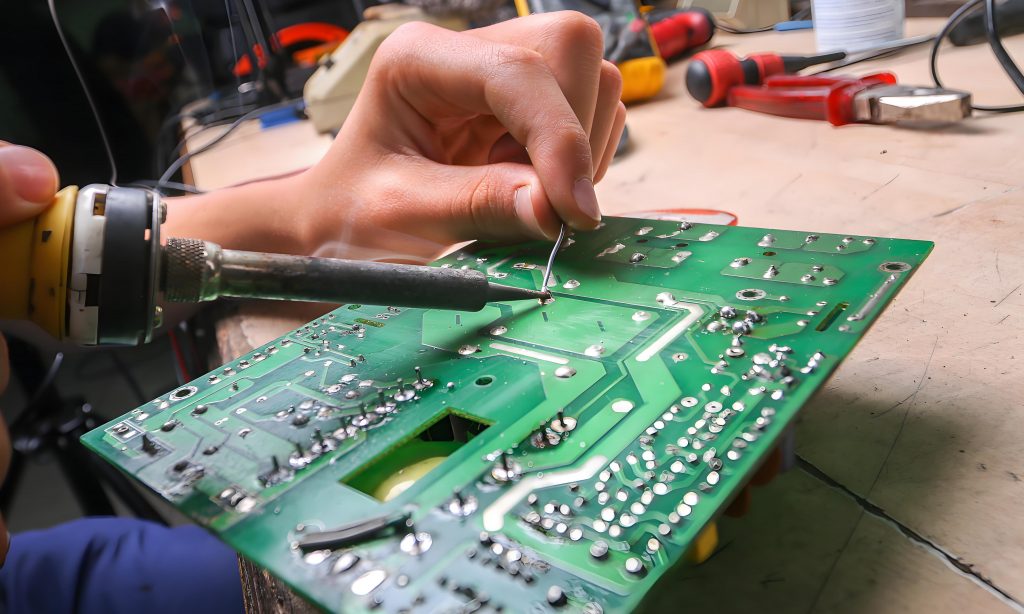
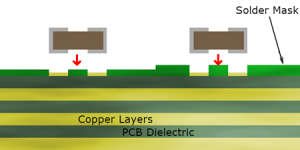
What is flux in soldering? Soldering is a vital process in electronics manufacturing. It ensures secure connections between components, creating a stable and efficient circuit.
One crucial element in soldering is flux. This chemical agent plays an essential role in improving solder adhesion, preventing oxidation, and ensuring a clean joint.
Without flux, achieving strong and long-lasting soldered connections would be difficult. It eliminates contaminants and promotes smooth solder flow.
What is flux in soldering?
Flux is a chemical substance used in soldering to remove oxidation from metal surfaces and improve solderability. It helps solder flow smoothly, creating strong and conductive joints. Without flux, metal surfaces would oxidize, making it difficult for solder to bond properly.
In PCB assembly, flux ensures that solder adheres well to components and circuit traces. It plays a critical role in maintaining the reliability of electronic devices.
Whether working with through-hole or surface-mount technology (SMT), using flux improves the overall soldering process.
What is the purpose of flux in soldering?
Flux serves multiple purposes in the soldering process:
- Removes oxidation – Eliminates surface oxides that hinder solder adhesion.
- Prevents re-oxidation – Forms a protective layer to keep metal surfaces clean.
- Improves solder wetting – Helps solder spread evenly, ensuring a strong bond.
- Enhances conductivity – Ensures a clean and stable electrical connection.
By using flux, soldering becomes more efficient and produces high-quality, durable joints. It is an essential component in both manual and automated soldering processes.
Is flux necessary for soldering?
Yes, flux is essential for effective soldering. Without it, solder may not properly bond to metal surfaces, leading to weak joints and poor conductivity.
The oxidation that forms on metal surfaces prevents proper adhesion, making flux a necessary step in the process.
For PCB assembly, flux is particularly important. It ensures that tiny solder joints remain clean and reliable. Some solder wires contain flux within their core, but additional flux may be required for complex soldering tasks.
What is flux made of?
Flux is composed of various chemical agents designed to clean metal surfaces and improve solder flow. The primary ingredients include:
- Rosin or synthetic resin – Helps remove oxidation and enhances solder adhesion.
- Activators – Chemically break down oxides and contaminants.
- Solvents – Keep the flux in liquid or paste form for easy application.
Different formulations exist depending on the type of soldering process. Selecting the right flux ensures optimal results and long-term solder joint reliability.
How to use solder flux?
Using solder flux correctly ensures clean and strong joints. Follow these steps for proper application:
- Apply flux – Use a brush, pen, or syringe to apply a thin layer to the joint.
- Heat the joint – Use a soldering iron to warm the metal surfaces.
- Add solder – Introduce solder to the heated joint, allowing it to flow evenly.
- Let it cool – Allow the joint to solidify naturally for a strong bond.
- Clean excess flux – Remove residue to prevent corrosion or contamination.
Following these steps ensures better soldering results and long-lasting electrical connections.
What are the types of flux?
Flux comes in different forms, each designed for specific soldering applications:
- Rosin flux – Commonly used in electronics; provides strong cleaning properties.
- Water-soluble flux – Easy to clean; ideal for high-precision soldering.
- No-clean flux – Leaves minimal residue, eliminating the need for post-cleaning.
- Acid flux – Used for plumbing and metalwork; not suitable for electronics.
Selecting the right flux depends on the soldering environment and the type of components being assembled.
What is the difference between solder flux and solder paste?
Although both are used in soldering, they serve different purposes:
- Solder flux – A cleaning agent that removes oxidation and improves solder flow.
- Solder paste – A mixture of flux and solder particles used in SMT assembly.
Flux is often applied separately in manual and wave soldering, while solder paste is essential in automated PCB manufacturing. Both materials play a critical role in ensuring high-quality solder joints.
Conclusion:
Flux is a fundamental component in soldering, playing a key role in achieving strong, clean, and conductive connections.Choosing the right flux and applying it correctly ensures reliable performance in electronic assemblies.
For high-quality PCB assembly with professional soldering techniques, contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com