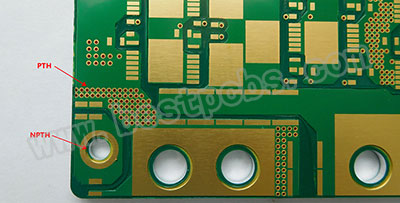
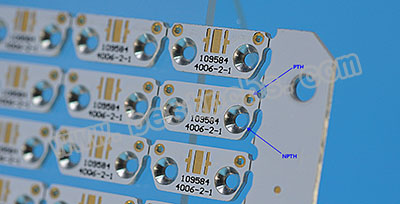
If you look closely at a MCPCB board, you will see holes of different sizes in the board, each hole was designed for a purpose. These holes can be divided into PTH (Plating Through holes) and NPTH (Non-Plating Through holes). Best Technology’s smallest drill tool is 0.5mm, so generally we require customers to design the minimum hole size of 0.5mm or more.
How to distinguish PTH and NPTH through holes?
In fact, it is very simple. Just look at the hole wall to see if there are bright plating traces (Copper). The holes with copper are PTH, and the holes without copper are NPTH.
What is the NPTH used for?
If you pay a little attention, you will find that the size of NPTH is usually larger than the PTH, because most of NPTH are for positioning purposes, it can be divided into the following four types.
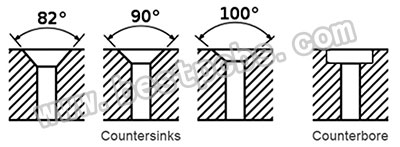
- 1) Countersink: It’s a cone-shaped hole that is cut into the PCB to allow the flat head of a socket cap screw to fit flush with the surface of the board.
- Counterbore: It’s a cylindrical flat-bottomed hole that is designed to house a hex head or socket head cap screw to be used to secure a PCB board.
- Screw hole: As shown as below.

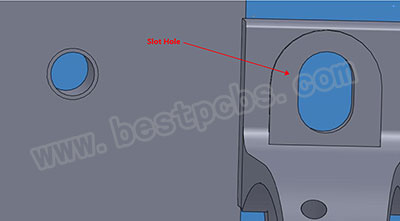
- Slot hole: Some components of the installation and positioning of the foot is rectangular or oval, we called this kind of irregular drilling as slot hole. During PCB machining, there are two types of drilling tools for plugins, one is called a drill cutter, which is used to drill round holes, and the other is called a routing bit, which is used to drill slot hole.
What is the PTH used for?
In order to connect the circuits between two or more layers, we need to design the PTH, which have following three main purposes.
- Used for conducting electricity.
- Used for heat dissipation.
- Used for plug-in components.
If you have other questions about MCPCB, welcome to contact us