The resistance and capacitance buried in multi layers PCB process is a process of burying resistors and capacitors inside the PCB board. Usually, the resistors and capacitors on the PCB are directly soldered on the board through mounting technology, while the buried resistor and capacitor process is to embed the resistors and capacitors into the internal layer of the PCB board.
This kind of printed circuit board consists of a first dielectric layer, a buried resistor, a circuit layer and a second dielectric layer in order from bottom to top. Among them, the part of the buried resistor without a circuit layer on the buried resistor is covered with a polymer isolation layer, and the surface of the polymer isolation layer is roughened, the surface roughness Rz is bigger than 0.01 ╬╝m, and the thickness of the polymer isolation layer at the corners is at least 0.1 ╬╝m.
The printed circuit board of the utility model covers a layer of polymer isolation layer on the surface of the buried resistor, thereby protecting the buried resistor from being attacked and corroded by chemical chemicals during subsequent wet processes such as browning and super-coarseness, and improving the efficiency of manufacturing buried resistors. Resistor plate process capabilities further promote the application of buried resistive plates to inner layer buried resistors.
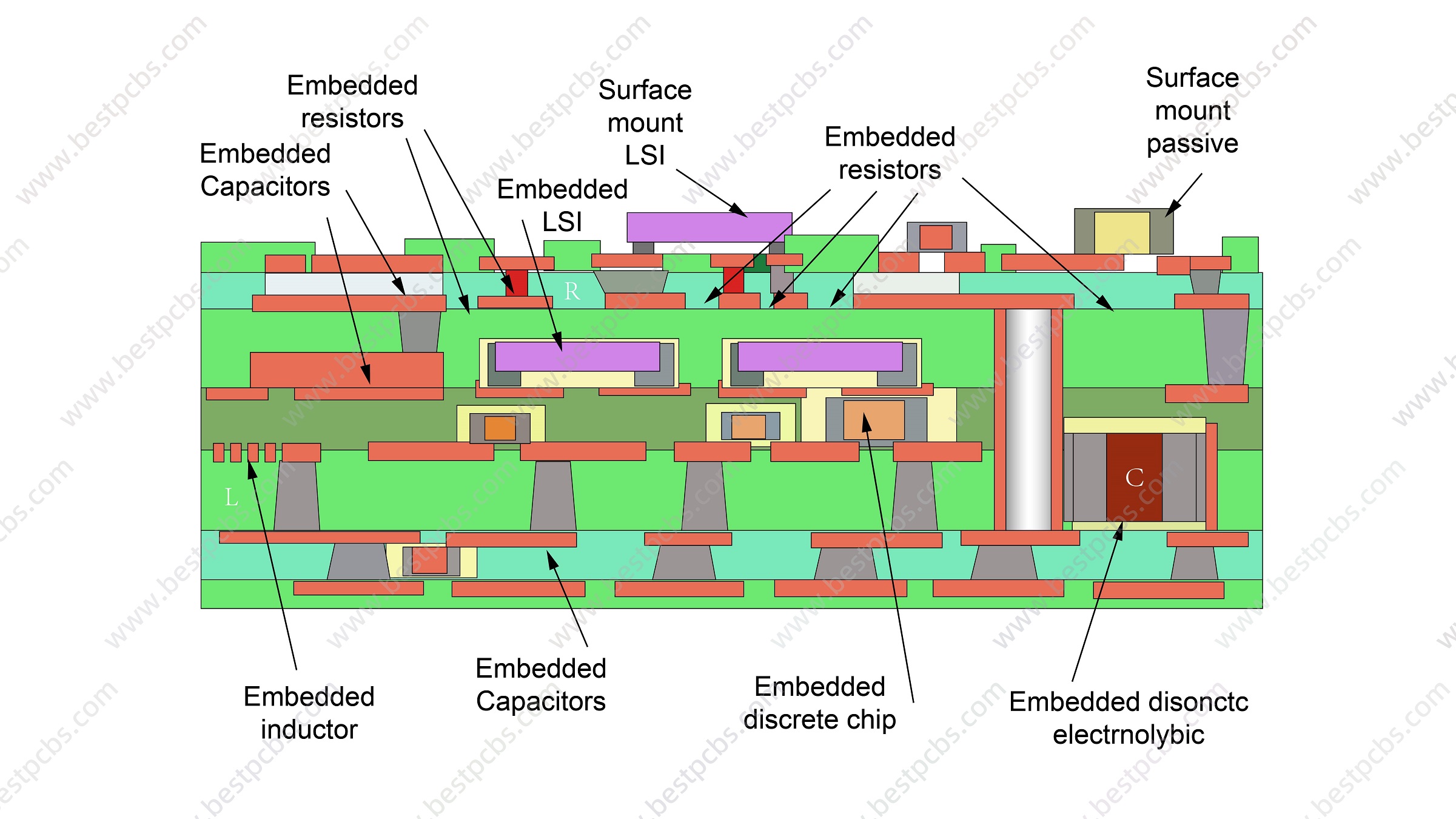
The advantages of the buried resistor and buried capacitor process include:
1. Space saving:
Since the resistors and capacitors are embedded directly into the internal layers of the board, space on the PCB board can be saved, making the entire circuit board more compact.
2. Reduce circuit noise:
Embedding resistors and capacitors into the internal layers of the board can reduce the electromagnetic interference and noise of the circuit and improve the stability and anti-interference capabilities of the circuit.
3. Improve signal integrity:
The buried resistance and buried capacitance process can reduce the transmission delay and reflection loss of circuit signals and improve the integrity and reliability of signal transmission.
4. Reduce the thickness of the PCB:
However, the buried resistor and buried capacitor process is relatively complicated in terms of manufacturing and repair, because the resistors and capacitors cannot be directly observed and replaced. In addition, the buried resistance and buried capacitance process is usually used in high-end electronic products, and the cost is relatively high.
When it comes to high-density circuit design, PCB buried resistance and buried capacitance technology has become a very useful technology. In traditional PCB layout, resistors and capacitors are usually soldered on the PCB surface in the form of patches. However, this layout method causes the PCB board to take up more space and may cause noise and interference on the surface.
The buried resistance and buried capacitance process solves the above problems by embedding resistors and capacitors directly into the internal layer of the PCB board.
The following are the detailed steps of the PCB buried resistor and buried capacitor process:
1. Make the inner layer:
When making a PCB board, in addition to the conventional layers (such as outer layer and inner layer), it is also necessary to make a separate inner layer specifically for buried resistance and buried capacitance. These internal layers will contain areas for buried resistors and capacitors. The inner layers are usually made using the same techniques as regular PCB manufacturing, such as electroplating, etching, etc.
2. Resistor/capacitor footprint:
Resistors and capacitors are packaged in a special package in the buried resistor and capacitor process so that they can be embedded into the internal layer of the PCB. These packages are usually thinned to accommodate the thickness of the PCB board and have good thermal conductivity.
3. Buried resistor/capacitor:
In the process of making the inner layer, the buried resistor and capacitor process is completed by embedding resistors and capacitors into the inner layer of the PCB board. This can be achieved through a variety of methods, such as using special pressing techniques to embed resistors and capacitors between inner layers of material, or using laser technology to etch holes in the inner layer material and then fill them with resistors and capacitors.
4. Connection layer:
After completing the inner layer of the buried resistor and buried capacitor, connect it to other regular layers (such as the outer layer). This can be achieved through conventional PCB manufacturing techniques such as lamination, drilling, etc.
In general, the buried resistance and buried capacitance process is a highly integrated technology that embeds resistors and capacitors in the internal layer of the PCB board. It can save space, reduce noise, improve signal integrity, and make PCB boards thinner and lighter. However, due to the complexity, the buried resistor and buried capacitor process is usually used in high-end electronic products with higher performance requirements.


