Flux is usually a mixture of rosin as the main component and is an auxiliary material to ensure the smooth progress of the PCB soldering process. Soldering is the main process of PCB assembly, flux is the auxiliary material used in soldering. The main function of flux is to remove the oxide of the solder and the base metal surface to be welded, so that the metal surface to achieve the necessary cleanliness.
Flux prevents the reoxidation of the surface during welding, reduces the surface tension of the solder, and improves the welding performance. The performance of flux directly affects the quality of electronic products. There are different types of solder paste flux, including rosin-based, water-soluble, and no-clean flux. Each has its specific applications and cleaning methods.

Types of Flux
- Rosin Flux
This is one of the most commonly used fluxes in soldering. It includes activated rosin flux (RMA), which contains additional chemicals for enhanced cleaning of oxides, and non-activated rosin flux (RA), which offers basic cleaning for general purposes. Rosin flux is effective at preventing oxidation and improving solder flow, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic soldering applications.
- Water-Soluble Flux
This type of flux uses water-soluble chemicals to provide strong cleaning action. It is easily removed with water, making it ideal for applications where thorough residue removal is necessary. Water-soluble flux is often used in automated soldering processes where post-soldering cleanup is a key concern.
- No-Clean Flux
Designed to leave minimal, non-corrosive residue, no-clean flux does not require cleaning after soldering. This type of flux is beneficial in situations where cleaning is difficult or impractical, as it reduces post-soldering processing time while ensuring that the residue does not affect the performance of the PCB.
- Organic Acid Flux
Contains organic acids like citric or formic acid, providing effective cleaning and fluxing. While it offers strong fluxing action, it is more corrosive compared to rosin fluxes. Organic acid flux is used in applications requiring robust cleaning, with careful consideration of the corrosion risk.
- Solder Paste Flux
This flux is a combination of flux and solder powder, used in reflow soldering processes. It is commonly employed in surface-mount technology (SMT), where the paste is applied to PCB pads before component placement and reflow. Solder paste flux streamlines the soldering process by integrating fluxing and soldering into one step.

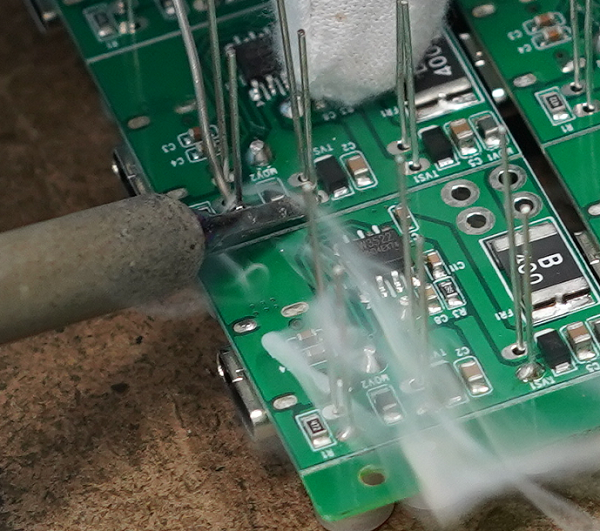
Is it Bad to Leave Flux on PCB?
There is obvious that leaving flux residue on a PCB surface can lead to several issues. Flux residues can attract moisture, resulting in corrosion of metal traces and component leads, which can compromise the integrity of the PCB over time. Some flux residues are conductive, potentially causing short circuits and affecting signal integrity, especially in high-frequency applications. Even no-clean flux can leave residues that impact sensitive components. Cleaning flux off the PCB can make sure the optimal performance and reliability of the overall product.
How to Remove Flux After Soldering?
We know leaving the flux on the PCBA surface is not a good thing, so how to remove it? Here we listing some common methods that manufacturers will used after soldering. Hope this information is helpful for you!
- Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA)
Use high-purity IPA (90% or higher). Apply it to the flux residue with a brush or cotton swab, gently scrubbing the area to dissolve the flux. IPA evaporates quickly and is effective for most flux types.
- Water Washing
Water washing is a common and straightforward cleaning method. It uses pure or deionized water to remove flux residues. This technique is simple, cost-effective, and easy to implement. However, water washing can potentially harm some PCBs and components if moisture accumulates on pads and pins, leading to short circuits or corrosion.
- Solvent Cleaning
Solvent cleaning is an efficient method that dissolves flux residues using chemical solvents. The solvent is then rinsed or sprayed off to clear the flux. While this method provides rapid and effective cleaning, solvents can be costly and require careful handling due to their chemical properties and safety considerations.
- Ion Cleaning
Ion cleaning is a high-tech approach that uses ion beams to clean the surface of PCBs. The high-energy and high-speed ion beams effectively remove contaminants and flux residues without damaging the PCB or components. However, ion cleaning equipment is expensive and requires specialized technology and support.
- Oxidation Cleaning
Oxidation cleaning is a physical cleaning method where oxidizing agents convert flux residues into easily removable substances. This technique is suitable for PCBs and components that are not compatible with water or solvent cleaning. The cost of oxidizing agents can be high, and safety precautions are necessary due to their reactive nature.
- Dry Ice Cleaning
Dry ice cleaning uses CO2 dry ice pellets as the cleaning medium. This method is efficient, environmentally friendly, and does not produce secondary pollution. During cleaning, high-speed CO2 dry ice pellets impact the flux residues on the PCB surface. The extremely low temperature of the dry ice causes the flux residues to become brittle, allowing them to be easily removed without damaging the PCB. This method offers a thorough cleaning solution while preserving the integrity of the circuit board.
FAQs
1. Can I use vinegar to clean flux off a PCB?
Vinegar can be used to clean certain types of flux, but it’s not as effective as IPA or specialized flux removers. It’s best to use a solvent designed for flux removal.
2. How often should I clean my PCB?
Clean your PCB after every soldering session to prevent residue buildup and ensure optimal performance.
3. Is it safe to use a hairdryer to dry a PCB after cleaning?
Yes, but use the lowest heat setting to avoid damaging sensitive components. Ensure the PCB is completely dry before powering it on.
4. Can I use a toothbrush for cleaning flux?
A toothbrush can be used, but a brush with anti-static properties is recommended to prevent static damage to the PCB.
5. Is no-clean flux really safe to leave on a PCB?
While designed to be left on, no-clean flux can still leave residues that may affect sensitive components. It’s best to clean it off for maximum reliability.
All in all, cleaning flux off your PCB is a crucial step to keep the reliability of your product. Remember, a clean PCB is a reliable PCB. Choose the right solvent, follow proper cleaning techniques, and your electronics will thank you with years of flawless performance.
For high-quality PCB & PCBA solutions and expert advice, choose Best Technology. We have more than 18 years in this field. Our commitment to excellence ensures your projects are in good hands. Contact us today to learn more about our products and services.
Tags: Solder paste, soldering