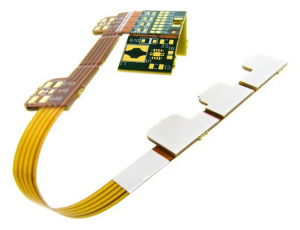
flex board are the only solution to meet the requirements of miniaturization and mobility of electronic products. They can be bent, wound, and folded freely, and can withstand millions of dynamic bending without damaging the wires. They can be arranged according to the requirements of spatial layout, and can be freely moved and stretched in three-dimensional space to achieve the integration of component assembly and wire connection. Flexible circuit boards can greatly reduce the volume and weight of electronic products, and are suitable for the development of electronic products towards high density, miniaturization, and high reliability.
What is a flex board?
Flexible board is a printed circuit board made of flexible insulating substrate, also known as flexible printed circuit board (FPC). This circuit board has many advantages that rigid printed circuit boards do not have, such as it can be bent, wound, folded freely, and can withstand millions of dynamic bending without damaging the wires. Flexible circuit boards provide excellent electrical performance, meet the design needs of smaller and higher density installations, help reduce assembly processes and enhance reliability. It is the only solution to meet the requirements of miniaturization and mobility of electronic products, which can greatly reduce the volume and weight of electronic products and adapt to the needs of electronic products developing towards high density, miniaturization, and high reliability.

The main feature of the flexible board is that its substrate is usually polyimide or polyester film. This material has good elasticity and a certain degree of softness, which allows the flexible board to move and stretch arbitrarily in three-dimensional space, realizing the integration of component assembly and wire connection. In addition, the flexible board also has the characteristics of high wiring density, light weight, thin thickness and good bendability, making it the preferred choice in many application scenarios.
The application of flexible boards is very wide. For example, in new energy vehicles, the FPC solution has become the main choice for most new models. FPC is integrated with CCS (integrated busbar system) and is connected with copper and aluminum busbars and plastic structural parts to form electrical connection and signal detection structural components.
What is a Flexboard made of?
Flexible boards are made of polyimide or polyester film.
Flexible circuit board (FPC) is a printed circuit board with high reliability and excellent flexibility. Its substrate is mainly polyimide or polyester film. This material selection gives FPC a variety of superior properties, including high wiring density, light weight, thinness and good bendability. These characteristics of FPC enable it to meet the needs of electronic products to develop in the direction of high density, miniaturization and high reliability.
Specifically, the substrate characteristics of FPC include:
Polyimide: This is a high-performance polymer with excellent mechanical properties, electrical properties and thermal stability. It is often used to manufacture flexible circuit boards because it can provide excellent flexibility and durability.
Polyester film: As a lightweight material, the application of polyester film in FPC provides good insulation performance and certain mechanical strength while maintaining overall lightness and thinness.
The choice of these two materials together ensures that the application of FPC in electronic devices can provide excellent electrical performance, meet the design needs of smaller and higher density installation, and help reduce assembly processes and enhance reliability.
Which flex material is best?
The best material for flexible PCB boards is polyimide. Polyimide has extremely strong toughness and scalability, and can meet the requirements of bending, folding, twisting, etc. in various shapes, which makes polyimide an ideal material for flexible PCB boards. In addition, polyimide also has good impedance control and signal integrity, ensuring the high reliability and stability of flexible PCB boards. Therefore, for application scenarios that require high flexibility and reliability, polyimide is the preferred flexible PCB material.
How many types of flex board are there?
There are four main types of flexible boards:
Single-sided flexible board: This is the most basic type of flexible circuit board, in which only one side has conductive lines. It is usually used for low-density and low-complexity applications, such as printer inkjet cartridges and computer memory.

Double-sided flexible board: This type of circuit board has conductive lines on both sides, and the electrical connection between the two sides is achieved through metallized vias.
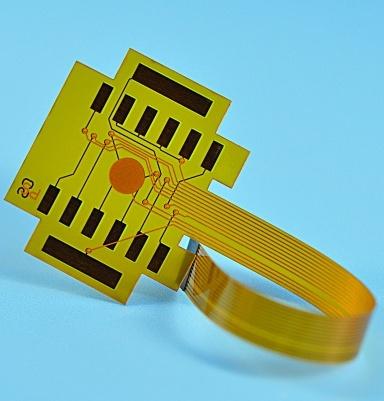
Multi-layer flexible board: Multi-layer FPC consists of several layers of conductive lines and insulating materials, and the electrical connection between the layers is achieved through blind holes, buried holes or through holes.
Rigid-flex combination flexible board: This type combines a rigid substrate and a flexible substrate, and a conductive connection is formed through metallized holes. Rigid-flexible combined flexible boards meet the needs of electronic products to develop in the direction of miniaturization, high frequency, high speed and multi-function.
These different types of flexible boards are widely used in consumer electronics, automotive electronics, medical equipment, aerospace and defense, etc. according to their specific application requirements and design complexity.
What is the thickness of a flex board?
The thickness of a flexible circuit board (FPC) usually ranges from 0.1mm to 0.2mm. This thickness range applies to single-layer and double-layer flexible circuit boards. For multi-layer flexible circuit boards, due to their complex manufacturing process and high cost, the thickness is uncertain.
The thickness range of the reinforcement board is wider, from 0.05mm to 0.1mm for thin reinforcement boards to 0.2mm to 0.5mm for thick reinforcement boards, and even ultra-thick reinforcement boards with a thickness of more than 0.5mm. The thickness selection of these reinforcement boards depends on the design requirements, the use environment and the required mechanical strength.
The material of flexible circuit boards usually includes polyimide (PI), and its thickness generally ranges from 12.5um (0.5mil) to 125um (5mil), and common specifications include 25um (1mil) and 12.5um (0.5mil). This information shows that the thickness of flexible circuit boards can be adjusted according to specific application requirements and designs, from thin to thick reinforcement boards, to meet different mechanical strength and stability requirements.
In general, the thickness selection of flexible circuit boards is very flexible and can be customized according to specific application scenarios and design requirements. Whether it is a single-layer, double-layer or multi-layer flexible circuit board, its thickness can be adjusted as needed to ensure the best electrical performance and mechanical strength.
Why are Flex PCBs so expensive?
The high price of flexible PCBs (flexible circuit boards) is mainly caused by factors such as its material cost, the complexity of the manufacturing process, and technical requirements.
Material cost: The main substrates of flexible PCBs include polyimide (PI) and polyester (PET). Polyimide has excellent heat resistance and electrical properties, but the price is higher; polyester has lower cost, but the performance is slightly inferior. In addition, the conductive layer is usually composed of copper foil, and factors such as foil thickness, copper purity and quality will also affect the cost.
Manufacturing process: The manufacturing process of flexible PCB is complex, including multiple links such as exposure, development, etching, lamination and testing. The process accuracy and equipment level of each link will affect the production cost.
Technical requirements: The design complexity, special requirements and gold finger surface treatment methods of flexible PCB in the production process will affect the cost. Complex circuit design requires more design time and process control, while special requirements such as high temperature resistance, moisture resistance, and bending resistance require different processes and difficulties, which increase the manufacturing cost.
Size and circuit structure: The cost of flexible PCB is also affected by size and circuit structure. Larger size and complex circuit structure will increase manufacturing cost.
In summary, the high cost of flexible PCB is mainly due to the combined effect of factors such as high material cost, complex manufacturing process, high technical requirements, and complexity of size and circuit structure.
Conclusion:
Compared with traditional hard boards, flexible boards have higher flexibility and bendability, adapt to various complex shapes and spatial layouts, and make circuit board design more flexible and diverse. With the advantages of small size and light weight, it greatly reduces the size and weight of the device, making it more convenient to carry electronic equipment. For the design and manufacture of various flexible circuit boards, you can contact BEST Technology, and we will provide you with comprehensive and best quality services.
Tags: flex board, Flexible board, fpc, PCB