What is an Amplifier Board?
An amplifier board is an electronic circuit designed to amplify audio signals. It takes a low-power input signal, such as the sound from a music player, and increases its strength to a level that can drive speakers or other audio output devices effectively. This amplification process ensures that the sound is louder and clearer when played through the speakers.
Amplifier boards are commonly used in various audio applications, including home theater systems, car audio setups, and professional sound equipment. They are essential for delivering high-quality audio performance, especially in environments where louder sound output is needed. Amplifier boards come in different types, each suited for specific applications, and are designed to handle various power levels and sound quality requirements.
What Does an Amplifier Board Do?
An amplifier board serves the crucial function of boosting the power of audio signals. In any audio system, the original signal generated by a source, such as a smartphone, MP3 player, or microphone, is usually weak. This weak signal is insufficient to drive speakers or produce audible sound at a volume that is satisfactory. The amplifier board steps in to enhance this signal, increasing its power so that it can drive speakers effectively.
Beyond simply making the sound louder, a well-designed amplifier board ensures that the audio signal remains clear and free from distortion throughout the amplification process. This means that whether you’re listening to music, watching a movie, or using a public address system, the sound you hear is rich, clear, and true to the original input.
Amplifier boards are versatile and can be found in various settings, from home audio systems and portable Bluetooth speakers to car audio systems and professional sound equipment. Each of these applications demands different levels of power and sound quality, and amplifier boards are designed to meet these specific needs.
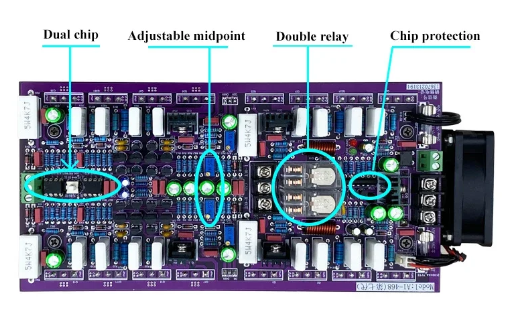
Types of Amplifier Boards
- Wiring Harness
- 2 Channel Stereo Amp
- Battery & Power
- 1 Channel Mono Amp
- 2.1 Channel Amp
- Interface
- Preamp
- 4 Channel Amp
- Bluetooth / Wi-Fi Receiver
- Panels & Mounting Acc.
- Panels & Mounting Acc.-Wiring Harness
- 10 Channel Amp
- 3 Channel Amp
- 6 Channel Amp
What Is the Function of the Amplifier?
The primary function of an amplifier is to increase the amplitude of an audio signal, making it strong enough to drive loudspeakers and other audio output devices. An amplifier takes in a low-power audio signal, processes it, and outputs a much stronger signal without significantly altering the original sound’s characteristics.
This function is crucial in ensuring that the sound produced by the speakers is loud enough to fill a room, stadium, or outdoor space, depending on the application. For example, in a home theater system, the amplifier ensures that the dialogue, music, and sound effects are all heard clearly, even during quieter scenes or moments of intense action.
In addition to boosting the signal, amplifiers often have other functions, such as controlling volume, adjusting equalization (bass, treble, midrange), and managing different audio inputs. This makes the amplifier a central component in any audio system, responsible for not just increasing volume but also enhancing overall sound quality.
What Kind of Amplifier Do I Need for Speakers?
Choosing the right amplifier for your speakers involves considering several factors, including the power rating of the speakers, their impedance, and the environment in which they’ll be used. The goal is to find an amplifier that can provide sufficient power to drive the speakers without overpowering them.
1. Matching Power Rating
The amplifier’s power output should generally match the speaker’s power handling capacity. For instance, if your speakers are rated at 100 watts, you’ll want an amplifier that can deliver 100 to 150 watts per channel. This ensures that the amplifier can drive the speakers efficiently without causing distortion or damage.
2. Impedance Compatibility
Speakers have an impedance rating, usually measured in ohms, that the amplifier must match. Common impedance values are 4, 6, or 8 ohms. The amplifier should be capable of driving the speaker’s impedance; otherwise, it may overheat or fail to deliver optimal sound quality.
3. Application and Environment
Consider where and how the speakers will be used. For a small room, a lower-powered amplifier might be sufficient, while larger spaces or outdoor settings may require a more powerful amplifier. If you’re setting up a home theater system, you might need an amplifier that supports multiple channels to handle different speakers in a surround sound configuration.
4. Sound Quality Preferences
If you’re an audiophile or someone who values high-quality sound, you might opt for an amplifier that prioritizes sound fidelity, such as a Class A or Class AB amplifier. For more general purposes or where efficiency is key, a Class D amplifier might be more suitable.
What Is the Difference Between a Mixing Board and an Amplifier?
A mixing board, also known as an audio mixer, combines multiple audio signals into one or more outputs. It allows you to adjust levels, EQ, and other parameters for each input channel. On the other hand, an amplifier boosts the power of the audio signal to drive speakers. While a mixing board controls the audio mix, an amplifier ensures that the mix is loud enough for playback through speakers.

What Is the Main Advantage of an Amplifier?
The main advantage of an amplifier is its ability to enhance audio signals, allowing them to be played at higher volumes while maintaining sound clarity and fidelity. This is particularly important in situations where audio needs to be heard clearly over background noise or across large distances.
1. Loudness and Clarity: Amplifiers ensure that audio signals are strong enough to drive speakers and produce sound at desired volume levels. This is essential for ensuring that music, speech, and other audio content are heard clearly, whether in a small room, a large auditorium, or an outdoor event.
2. Improved Sound Quality: A well-designed amplifier can improve the overall sound quality of an audio system by minimizing distortion and noise, ensuring that the output remains true to the original recording.
3. Versatility and Control: Amplifiers often come with features that allow users to control various aspects of the audio signal, such as volume, balance, and equalization.
What Happens if an Amp is Too Powerful for Speakers?
Using an amplifier that is too powerful for your speakers can result in speaker damage. When an amplifier delivers more power than the speakers can handle, it can cause the speaker components to overheat or even blow out. It’s essential to match the amplifier’s power output to the speaker’s power rating to avoid such issues. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure compatibility.
How Many Watts is Good for a Speaker?
The appropriate wattage for a speaker depends on the intended use and the size of the space in which it will be used. For small rooms, speakers with a power rating of 20 to 50 watts per channel may suffice. For larger spaces or outdoor use, speakers rated at 100 watts or more per channel are recommended. It’s important to match the amplifier’s power output to the speaker’s rating to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What is the Basic Use of an Amplifier?
An amplifier’s basic use is to boost the power of audio signals so that they can drive loudspeakers effectively. Without amplification, the audio signal would be too weak to produce a meaningful sound output from the speakers. Amplifiers are used in various audio systems, including home theaters, car audio systems, and public address systems, to ensure that the sound is loud and clear.
Which Class Amplifier is Best for Sound Quality?
For sound quality, Class A amplifiers are often considered the best. They provide a consistent and high-quality output, making them ideal for high-fidelity audio systems. However, they are less efficient and generate more heat compared to other classes. For a balance between sound quality and efficiency, Class AB amplifiers are a popular choice, offering good sound quality while being more power-efficient than Class A.
Does an Amplifier Improve Sound Quality?
Yes, an amplifier can improve sound quality, especially when it’s well-matched to the speakers and the rest of the audio system. A good amplifier ensures that the audio signal is amplified without introducing distortion or noise. It also provides the necessary power to drive speakers, allowing them to perform at their best. However, it’s important to choose an amplifier that complements your audio setup to achieve the best sound quality.
Amplifier Board HS Code
The Harmonized System (HS) code for amplifier boards varies depending on the specific type and application. Generally, amplifier boards fall under the category of electronic integrated circuits or modules, which are typically classified under HS code 8542.90. However, it’s advisable to consult with a customs expert or refer to your country’s specific tariff schedule for precise classification.