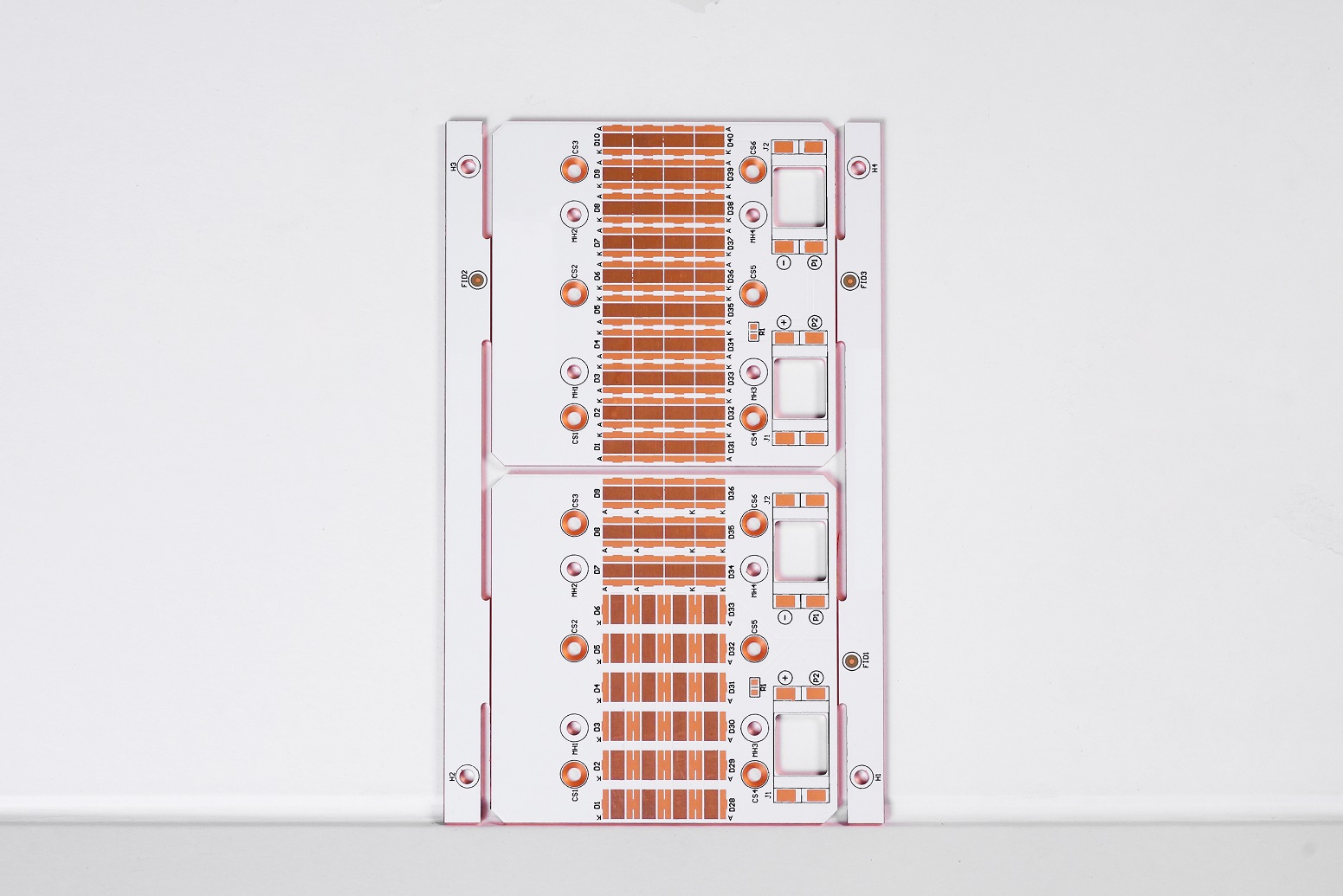
As electronic devices become increasingly miniaturized and high-performance, traditional circuit boards are no longer sufficient for certain high-demand applications. To address these challenges, the Thermal-Electric Separation Copper Substrate with Flexible PCB has emerged. This innovative composite circuit board combines the efficient heat dissipation characteristics of thermal-electric separation copper substrates with the flexibility of flexible PCBs (FPC). It is widely use for high-performance electronic products, which requires efficient heat dissipation and complex circuit.
What is Thermal-Electric Separation Copper Substrate with Flexible PCB?
The Thermal-Electric Separation Copper Substrate with Flexible PCB is a composite material that combines a rigid thermal-electric separation copper substrate with a flexible circuit board. It integrates the advantages of both, providing superior performance in high-power and high-density applications.
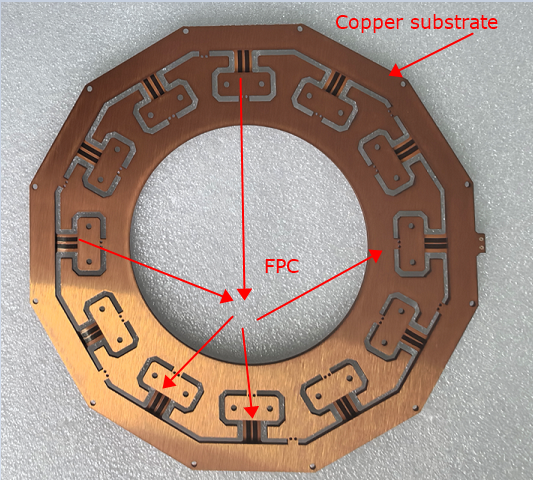
1. Thermal-Electric Separation Copper Substrate
The thermal-electric separation copper substrate is designed for high-power electronic devices, providing an efficient heat dissipation solution. It separates the paths of heat and electrical signals to avoid thermal interference with electrical performance. Its structure typically includes:
- Single-sided design: Electronic components are placed on one side of the copper substrate, while the other side is used for heat dissipation.
- High thermal conductivity materials: Such as copper or aluminum, which can quickly conduct heat, like copper is 400W/m.k, aluminum is 237W/m.k.
- Thermal vias: Vertical heat conduction paths that rapidly transfer heat to the dissipation layer.
2. Flexible PCB (FPC)
Flexible PCBs (Flexible Printed Circuits, FPC) use flexible materials like polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET) that can bend and fold to adapt to complex three-dimensional structures and dynamic application scenarios. Their advantages include:
- Lightweight: Reducing the overall weight of the device.
- High-density wiring: Achieving complex circuit designs in limited space.
- Flexibility: Meeting diverse design needs.
Structure and Characteristics
The structure of the Thermal-Electric Separation Copper Substrate with Flexible PCB includes rigid and flexible parts, connected together using conductive adhesives or other bonding materials to form a unified whole.
1. Rigid Part
The rigid part uses the thermal-electric separation copper substrate, responsible for efficient heat dissipation and mechanical support. This part usually carries high-power components to ensure rapid heat transfer and dissipation.
2. Flexible Part
The flexible part uses the flexible PCB, which can bend and fold to fit the complex internal structure of devices. This part is typically used to connect the rigid part with other modules that require flexible connections.
3. Bonding Method
The flexible and rigid parts are bonded together using conductive adhesives, welding, or mechanical connections. The design of the bonding area ensures stable electrical connections and reliability during bending and dynamic use.
Thermal-Electric Separation Copper Substrate with Flexible PCB Advantages
1. Efficient Heat Dissipation
The thermal-electric separation copper substrate provides excellent heat dissipation, effectively conducting away the heat generated by high-power components to maintain a reasonable operating temperature range. This is especially important for applications like high-power LEDs and power semiconductor devices.
2. Flexibility
The use of the flexible PCB offers great design freedom, allowing adaptation to the complex three-dimensional structures and dynamic application needs within devices. This enables designers to achieve more complex circuit designs in limited spaces, increasing device integration and functionality.
3. Reliability
The thermal-electric separation design and high thermal conductivity materials enhance the reliability of the circuit board, reducing the impact of heat on electrical performance. The flexible part reduces the number of connection points, lowering the risk of failure.
4. Space Saving
Combining the advantages of rigid and flexible circuit boards allows for efficient heat dissipation and complex circuit in limited space. This is crucial for modern miniaturized and high-density electronic product designs.
Where Thermal-Electric Separation Copper Substrate with Flexible PCB used?
1. High-Power LED Lighting
High-power LEDs generate a significant amount of heat during operation. The thermal-electric separation copper substrate provides an efficient heat dissipation solution, ensuring the stable operation and long lifespan of LEDs. The flexible part is used to connect different LED modules, accommodating diverse design requirements.
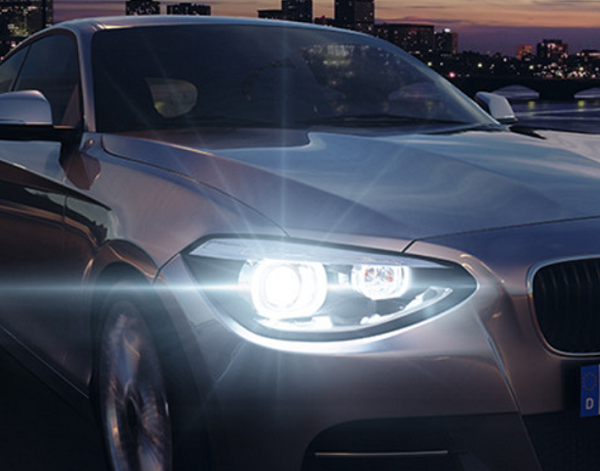
2. Automotive Electronics
In automotive electronics, such as in-vehicle cameras and sensor modules, efficient heat dissipation and compact design are required. The thermal-electric separation copper substrate with flexible PCB can meet these demands, enhancing device reliability and performance.

3. Consumer Electronics
Devices like smartphones and tablets require lightweight and miniaturized designs. The thermal-electric separation copper substrate with flexible PCB offers efficient heat dissipation and flexible circuit, optimizing device performance and user experience.
4. Medical Devices
In applications that require flexibility and reliability, such as portable diagnostic equipment and implantable medical devices, the thermal-electric separation copper substrate with flexible PCB can help to enhancing device performance and reliability.
How does Thermal-Electric Separation Copper Substrate with Flexible PCB manufactured?
The manufacturing process for the thermal-electric separation copper substrate with flexible PCB is complex, typically including the following steps:
- Material Preparation: Selecting appropriate rigid and flexible materials and performing pre-treatment.
- Circuit Printing: Printing circuit patterns on both rigid and flexible materials.
- Lamination and Bonding: Combining the flexible circuit board with the thermal-electric separation copper substrate, usually using conductive adhesives or other bonding materials.
- Drilling and Plating: Drilling holes and electroplating to form conductive paths on the combined board.
- Surface Treatment: Performing surface treatments such as pad coating on the circuit board.
- Testing and Inspection: Conducting electrical and mechanical performance tests to ensure the quality and reliability of the board.
The thermal-electric separation copper substrate with flexible PCB, as an innovative composite circuit board, combines the advantages of efficient heat dissipation and flexible wiring. It is widely used in high-performance and complex design electronic products. With continuous technological advancements and growing market demand, this composite circuit board will play an important role in more fields, driving the ongoing innovation of electronic manufacturing technology. Want know more about it, just feel your free to contact us.