Antenna plays a vital role in wireless devices, and ceramic antenna and PCB antenna have their own characteristics. Ceramic antenna is small, low cost, easy to use, and has good anti-interference, waterproof, dustproof, lightning protection and other properties. PCB antenna is an important RF component and is also indispensable in wireless communication equipment.
What is a ceramic antenna?
Ceramic antenna is a miniaturized antenna suitable for Bluetooth devices. It uses a ceramic shell and has anti-interference, lightning resistance, waterproof and dustproof capabilities.
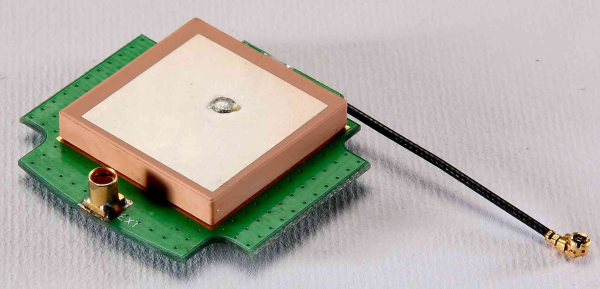
It mainly uses GPS satellites to achieve navigation and positioning. It is divided into block ceramic antenna and multilayer ceramic antenna. Block antenna uses high temperature to sinter the entire ceramic body once and then prints the metal part of the antenna on the surface of the ceramic block.
Multilayer antenna firing uses low temperature co-firing to stack and align multiple layers of ceramics and then sinter at high temperature. The metal conductor of the antenna can be printed on each layer of ceramic dielectric layer according to design requirements, which can effectively reduce the size of the antenna and achieve the purpose of hiding the antenna.
Since the dielectric constant of ceramic itself is higher than that of PCB circuit board, and the dielectric loss is also smaller than that of PCB circuit board, the use of ceramic antenna can effectively reduce the size of antenna while ensuring antenna performance, and is more suitable for use in low-power Bluetooth modules.
Ceramic antennas are widely used in Bluetooth devices, such as Bluetooth headsets, smart watches, Bluetooth e-cigarettes, smart small appliances, smart medical, smart home products, etc. Its gain is generally 2dbi, and the reading distance can reach 2 meters. It is an industrial-grade product for indoor use, with an external size of 78mm×78mm×5mm.
What is a PCB antenna?
PCB antenna refers to the part on the PCB used for wireless reception and transmission.
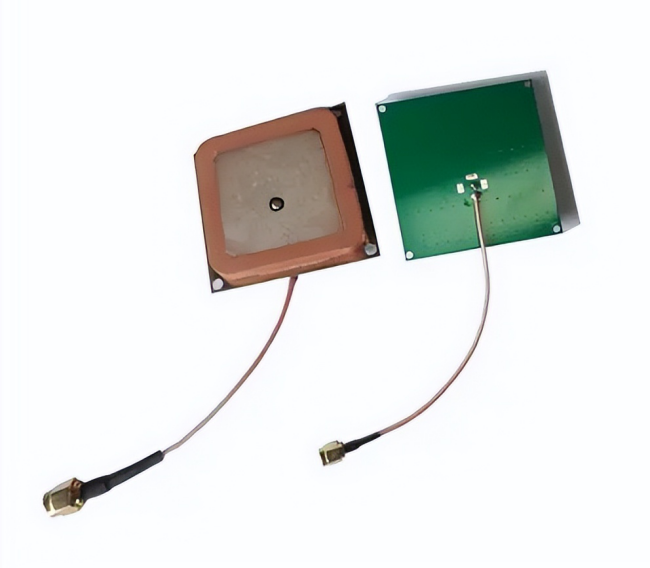
When transmitting, it converts the high-frequency current of the transmitter into electromagnetic waves in space; when receiving, it converts the electromagnetic waves intercepted from space into high-frequency current and sends them to the receiver. Usually set on Bluetooth or wireless transmission modules. For example, PCB antennas play an important role in ZM602 series Wi-Fi modules, achieving performance indicators such as gain > 2.0dBi, working bandwidth > 150MHz, S11 within bandwidth < -10dB, input impedance 50Ω, and standing wave ratio < 2.0.
The most common structure of PCB antenna is the inverted F antenna. The length of the antenna needs to meet the quarter free space wavelength of the transmitted signal. In actual design, it is often designed as a serpentine trace to reduce the occupied space.
The advantages of PCB antennas are small space occupation, low cost, no need to assemble the antenna separately, not easy to touch and damage, and convenient assembly of the whole machine; the disadvantages are that it is difficult to make a single antenna field round, the insertion loss is high, the efficiency is relatively low, and it is easy to be interfered by the motherboard.
What are the differences between ceramic antennas and PCB antennas?
- (I) Difference in dielectric constant:
In terms of dielectric constant, ceramic antennas have obvious advantages. The dielectric constant of ceramic antennas is higher than that of PCB antennas, which enables ceramic antennas to gather and transmit electromagnetic wave signals more effectively.
The higher dielectric constant allows ceramic antennas to be more compact in design, effectively reducing the size of the antenna. In some miniaturized Bluetooth devices, such as smart watches and Bluetooth headsets, the high dielectric constant characteristics of ceramic antennas can meet the strict space requirements of the device, leaving more design space for other electronic components.
- (II) Difference in dielectric loss:
Ceramic dielectrics also perform well in dielectric loss. Compared with PCB circuit boards, ceramic dielectrics have lower dielectric losses, which means that in low-power Bluetooth modules, ceramic antennas can transmit signals more efficiently while reducing energy loss.
The use of ceramic antennas in low-power Bluetooth modules is significantly better than PCB antennas, which can effectively extend the battery life of Bluetooth devices. The low dielectric loss characteristics of ceramic antennas can ensure that the device still maintains stable signal transmission when running for a long time.
- (III) Difference in size and effect:
The size of ceramic antennas is generally comparable to that of 1210 packages. In practical applications, antennas of this size can well meet the design requirements of various miniaturized electronic devices. At the same time, the effect of ceramic antennas is stronger than that of PCB antennas. This is because the special structure and material properties of ceramic antennas make them more efficient and stable in signal reception and transmission.
In some Bluetooth audio devices with high signal quality requirements, ceramic antennas can provide clearer and more stable audio transmission effects, reducing signal interference and distortion. However, due to the limitations of its design and manufacturing, PCB antennas are often not as good as ceramic antennas in signal transmission effects.
What are the benefits of ceramic antennas?
Advantages:
Ceramic antennas take up little space, which makes them very advantageous in miniaturized electronic devices. For example, in wearable devices such as smart watches and Bluetooth headsets, more space can be left for other electronic components, making the design of the device more compact.
Its performance is good, and it can effectively reduce power consumption while ensuring signal strength. For example, in some low-power Bluetooth devices, ceramic antennas can extend the battery life of the device.
Ceramic antennas can also effectively improve the integration of the motherboard, reduce the antenna’s restrictions on ID, and introduce the design in the early stage of product design, so that it can be better integrated with the motherboard and improve the overall performance of the product.
Disadvantages:
The bandwidth of ceramic antennas is narrow, and it is difficult to achieve multi-band. This means that in some application scenarios that need to support multiple frequency bands at the same time, ceramic antennas may not meet the needs.
In some multifunctional wireless communication devices, it is necessary to support multiple frequency bands such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS, etc. at the same time. Ceramic antennas may need to be used in conjunction with other antennas, which increases the complexity and cost of the design.
What are the benefits of PCB antennas?
Advantages:
PCB antennas take up less space and are especially suitable for electronic devices that have strict space requirements. For example, in some ultra-thin smartphones and laptops, PCB antennas can be directly integrated on the circuit board without taking up additional space.
Low cost is also an important advantage of PCB antennas. Since it can be made directly on the PCB board, no additional assembly process is required, which reduces production costs.
PCB antennas do not need to be assembled separately, are not easily damaged by touch, and are easy to assemble as a whole, which improves production efficiency.
Disadvantages:
It is difficult to make a single antenna field of a PCB antenna round, which will affect the coverage and stability of the signal.
High insertion loss means that the signal is lost more during transmission, reducing the strength and quality of the signal.
PCB antennas are easily interfered by other electronic components on the motherboard, which requires careful consideration and optimization during design and layout to reduce the impact of interference on the signal.
Application scenarios and selection of ceramic antennas and PCB antennas
According to different needs, PCB onboard antennas can be selected in environments without metal coverage, IPEX external antennas can be selected with metal coverage, and ceramic antennas can be selected if the space is not large.
In actual applications, different usage environments and needs determine the choice of antenna type. If it is in an environment without metal coverage, PCB onboard antennas are an economical and convenient choice. PCB onboard antennas have the advantages of low cost, no need to assemble antennas separately, not easy to touch and damage, and easy assembly.
When in an environment with metal coverage, IPEX external antennas are more suitable. IPEX external antennas have good directional directivity, high efficiency, strong anti-interference ability, and can stay away from interference on the motherboard. Although it is costly and difficult to assemble, it can ensure stable signal transmission in a metal environment.
If the PCB board space is not large, ceramic antennas are an ideal choice. Ceramic antennas can effectively reduce the size of the antenna to achieve the purpose of hiding the antenna. At the same time, since the dielectric constant of ceramic itself is higher than that of PCB circuit board, it can better adapt to the design requirements of small space while ensuring performance.
In summary, when choosing an antenna, we need to comprehensively consider the specific use environment and needs and choose the most suitable antenna type to ensure that the device can achieve stable and efficient wireless communication.
Conclusion:
Ceramic antennas and PCB antennas each have their own characteristics and advantages. Understanding their differences will help you make the most appropriate decision when choosing wireless devices.
BEST Technology has many years of experience in manufacturing ceramic circuit boards. Its products can provide stable and reliable signal transmission in the fields of GPS navigation, Bluetooth devices, wireless LAN, and the Internet of Things.
Tags: antenna, ceramic PCB, PCB