What is the Standard Thickness of a PCB?
The standard thickness of a PCB is often 1.6 mm. This has become the go-to thickness in the industry because it balances flexibility, cost, and performance for most applications. However, depending on the requirements of the design, PCB thickness can vary widely.
Manufacturers offer various thicknesses to accommodate specific designs, from 0.4 mm (0.016 inches) for ultra-thin, flexible boards, up to 3.2 mm or even thicker for high-current, rugged applications. The choice of thickness largely depends on the type of application and the mechanical strength needed.
How is PCB Thickness Measured?
Measuring PCB thickness accurately is crucial for ensuring the board meets design specifications and performs optimally in its application. The thickness of a PCB refers to the total height of the board, including all its layersâcopper, dielectric, and solder mask. This thickness plays a role in many factors, from electrical performance to mechanical stability, and must be precisely controlled. The tools and methods used to measure PCB thickness include:
1. Micrometers
A micrometer is the most common tool for measuring PCB thickness. It allows precise measurements down to fractions of a millimeter, making it ideal for multilayer PCBs where small deviations can affect performance. The micrometer is placed at various points across the board to ensure uniform thickness.
2. Calipers
Digital or analog calipers are also used to measure the thickness of PCBs. They are particularly useful for quickly gauging thickness across different sections of the board.
3. Cross-Sectioning
In cases where even more precision is required, manufacturers may opt to cross-section the board. This involves cutting a sample of the PCB and measuring it under a microscope to analyze each layer’s contribution to the overall thickness.
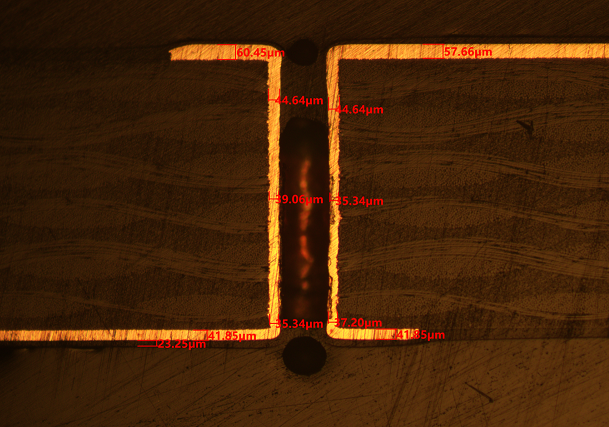
PCB thickness is typically measured in mils (1 mil = 0.001 inches) or millimeters, depending on the region and industry. Standard PCB thicknesses usually fall between 0.4 mm (0.016 inches) and 3.2 mm (0.125 inches), but custom designs may require other dimensions.
In mass production, quality control procedures are in place to ensure that the boards maintain a consistent thickness across large batches. Thickness tolerances range from ±10% to ±20%, depending on the manufacturer and materials used.
How Thick is a 2-Layer PCB Board?
A standard 2-layer PCB is typically 1.6 mm thick, but this can vary based on specific requirements. The board consists of two copper layers, one on each side of the insulating core.
Core Thickness: The thickness of the insulating material between the two copper layers is generally around 1.4 mm.
Copper Thickness: Standard copper thickness is 35 μm (1 oz copper), though this can be adjusted for higher current-carrying capacity.
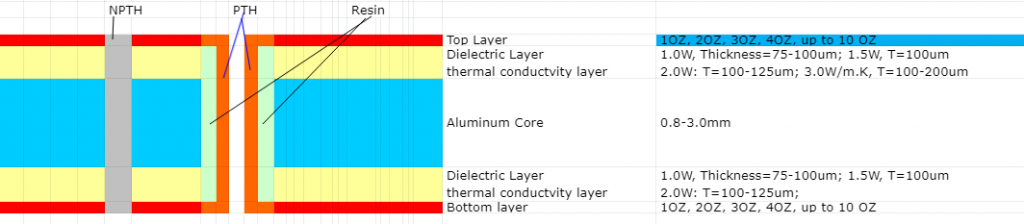
For lighter applications, such as compact consumer electronics, a thinner board of 0.8 mm may be used, providing more flexibility and space-saving. Meanwhile, more robust applications may demand thicknesses exceeding 2.4 mm.
How Thick is a Standard 8-Layer PCB?
When it comes to multilayer PCBs like the 8-layer variant, thicknesses usually range from 1.4 mm to 2.4 mm, depending on the design requirements. With multiple layers of copper and insulating material stacked together, manufacturers must optimize thickness while considering electrical performance and mechanical rigidity.
Each additional layer introduces more copper and insulation, increasing the overall thickness. For high-frequency applications or boards that must handle significant current, thicker boards may be necessary to ensure signal integrity and thermal management.
How Does PCB Thickness Affect Thermal Performance?
The influence of PCB thickness on thermal performance is mainly reflected in heat dissipation efficiency and heat capacity.
The thickness of the PCB directly affects its heat dissipation efficiency. Thicker PCBs have greater heat capacity and better heat conductivity, and are able to conduct the heat generated by electronic components more effectively. This is because copper has good thermal conductivity, and the thicker copper foil layer can more quickly transfer heat from the heating element to the cooling area or external radiator, helping to improve the overall thermal management efficiency and protect sensitive components from thermal damage.
In addition, the thickness of the PCB is also closely related to its mechanical strength and stiffness. Thicker PCB boards have higher flexural stiffness and impact toughness, can withstand greater mechanical stress and vibration, and ensure the stability and reliability of electronic equipment in harsh environments. This is equally important in thermal management, as it helps to maintain the stable operation of electronic equipment in high temperature environments and prevent performance degradation or damage due to overheating.
However, it is important to note that while thicker PCBs are good for heat dissipation, in high-frequency applications, excessively thick PCBs may increase the impedance and coupling of the signal, thus affecting electrical performance.
What Factors Influence PCB Thickness?
PCB board thickness is one of the key parameters to be considered in the design process, which has a great impact on the performance and reliability of the circuit board. When choosing plate thickness, the following factors need to be considered:
1. Signal speed
The thinner the plate, the faster the signal speed, and vice versa. However, when the board thickness is less than 0.8mm, the signal will have a great loss, will produce serious signal interference, affecting the normal work of the circuit board.
2. Heat conduction
The thinner the board thickness, the worse the heat dissipation ability, easy to produce hot spots and thermal runaway phenomenon, affecting the performance and reliability of the circuit board.
3. Mechanical strength
The greater the thickness of the plate, the higher the mechanical strength, the smoother the surface of the plate, and the greater the bending strength. However, too thick a board will affect the assembly and size of the board design.
4. Number of layers
More layers mean a thicker board. A single-layer PCB may be as thin as 0.4 mm, while multilayer boards like an 8-layer PCB may reach over 2 mm.
Taking the above factors into consideration, it is usually appropriate to choose the plate thickness between 1.6mm-2.0mm.
How to Decide PCB Thickness?
According to different applications and needs, PCB board can be divided into a variety of thicknesses, commonly used board thickness is 0.8mm, 1.0mm, 1.2mm, 1.6mm, 2.0mm and so on. When selecting PCB board thickness, it is necessary to make comprehensive consideration according to specific application scenarios and design requirements. Here are a few ways to choose plate thickness:
1. Determine according to the circuit complexity and working environment
When the circuit complexity is high, multiple components need to be connected at the same time, or the circuit board needs to work in a high temperature environment, you are advised to select a thicker board thickness to effectively improve the performance and reliability of the circuit board.
2. Determine the device size and type
If the device size is small and requires precision assembly, a thinner plate thickness is recommended. For large devices, such as power switches and high-power LED lights, it is recommended to choose a thicker board thickness.
3. Determined according to design requirements and cost control
In terms of cost control, the thinner the plate thickness, the higher the corresponding plate cost will be. Therefore, the cost and performance should be considered comprehensively in the design, and the most appropriate plate thickness should be selected.
In addition, as an 18+ years experienced PCB manufacturer, we summarized a small tip for choosing PCB thickness, hope this is help for you.
- The board thickness below 1.0mm is generally used for small electronic devices and mobile devices, such as smart watches, Bluetooth headsets and so on.
- 1.0mm-1.6mm PCB thickness is suitable for most common electronic devices, such as smart phones, tablets, digital cameras, etc.
- Thickness >1.6mm is generally used for industrial control equipment, power switches and other large electronic equipment.
Advanced PCB Manufacturer â Best Technology
At Best Technology, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality PCBs tailored to meet your exact design specifications. We offer custom thickness options for single-layer, double-layer, and multilayer boards.
We understand that PCB thickness is critical to performance, whether youâre working on high-current applications or compact designs. Our team of experts can guide you through the selection process, ensuring that your boards are not only optimized for electrical performance but also for thermal and mechanical stability.
Tags: pcb thickness, printed circuit board thickness standards