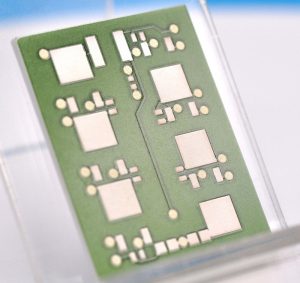
Ceramic substrate PCB is a printed circuit board with ceramic material as substrate. With its excellent performance and unique technical advantages, it occupies an important position in today’s rapidly developing electronics industry. Its high thermal conductivity, high insulation, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance and other characteristics enable it to be widely used in many fields.
What is a ceramic substrate?
Ceramic substrate is a special process board in which copper foil is directly bonded to the surface (single or double sides) of alumina (Al2O3) or aluminum nitride (AlN) ceramic substrate at high temperature.

This ultra-thin composite substrate has excellent electrical insulation properties, high thermal conductivity, excellent soft solderability and high adhesion strength, and can be etched with various patterns like PCB boards, with great current carrying capacity.
Therefore, ceramic substrate has become the basic material for high-power power electronic circuit structure technology and interconnection technology.
It has a wide range of applications, including but not limited to semiconductor modules, integrated circuits and electronic ceramics, among which alumina is one of the most commonly used ceramic substrate materials.
The characteristics of ceramic substrates include strong mechanical stress, shape stability, high strength, high thermal conductivity, high insulation, strong bonding, corrosion resistance, and good thermal cycling performance, with a cycle number of up to 50,000 times and high reliability.
In addition, the operating temperature range of ceramic substrates is wide, from -55°C to 850°C, and its thermal expansion coefficient is close to that of silicon, which simplifies the production process of power modules.
How thick is a ceramic substrate?
The thickness of ceramic substrates is generally between tens and hundreds of microns. This material usually has a flat surface for connecting and supporting microelectronic components.
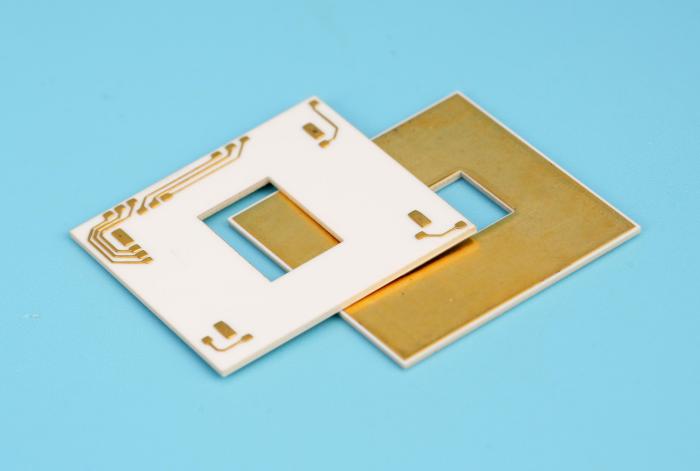
The thickness of ceramic substrates can be precisely processed according to specific needs to meet different application scenarios.
The thickness of alumina ceramic substrates can be adjusted between 0.2-1.5mm, which shows that the thickness range of ceramic substrates is quite wide and can be customized according to specific application needs.
What is a ceramic PCB used for?
Due to its unique performance and functions, ceramic PCB is widely used in many fields, including but not limited to LED lighting, semiconductor coolers, high-power semiconductor modules, power control circuits, electronic heaters, intelligent power devices, power hybrid circuits, high-frequency switching power supplies, automotive electronics, solid-state relays, military electronics, aerospace, communications, etc.

The requirements for electronic products in these application fields are to become thinner, smaller, and have more functions. As a new type of circuit material, ceramic PCB effectively provides a solution for the miniaturization of modern electronic products. Its advantages are:
- Heat dissipation performance and current carrying capacity: The heat dissipation performance, current carrying capacity, insulation, thermal expansion coefficient, etc. of ceramic substrates are better than those of ordinary glass fiber PCB boards, and are particularly suitable for high-power power electronic modules, aerospace, military electronics and other products.
- Thermal conductivity: Ceramic PCB has excellent thermal conductivity and can effectively dissipate the heat generated by components, making it the first choice for applications that generate a lot of heat and require efficient thermal management.
- Electrical performance: The excellent electrical performance of ceramic materials at high frequencies makes ceramic PCBs particularly suitable for radio frequency (RF) and microwave applications, which can maintain signal integrity and minimize signal loss.
- Durability and mechanical strength: Ceramic PCBs have impressive mechanical strength and durability, and can withstand challenging mechanical stress and vibration, while having good chemical resistance and the ability to withstand harsh environments.
In summary, ceramic PCBs occupy an important position in high-performance electronic applications due to their excellent physical and electrical properties, as well as high reliability and stability, and are an important part of the development of modern electronic technology.
What is the difference between ceramic substrate and FR-4?
The main differences between ceramic substrates and FR-4 are their physical and electrical properties, cost, production cycle, application areas, and high-frequency performance.
Physical and electrical properties:
- Ceramic substrates use ceramic substrates, such as alumina ceramic substrates, aluminum nitride ceramic substrates, silicon nitride ceramic substrates, etc., with good heat dissipation and insulation, thermal conductivity between 25w and 230w, and insulation resistance greater than or equal to 10 to the 14th power.
- In contrast, FR-4 is made of glass fiber, which has poor heat dissipation performance and no insulation performance. It needs to add an insulation layer to transfer heat, and its heat dissipation performance is only a few watts.
Cost and production cycle:
- The production cost of ceramic substrates is high, and the production cycle is usually 10~15 days.
- In contrast, the production cost of FR-4 substrates is lower, and the production cycle is shorter. Some can be shipped in 24 hours.
Application areas:
- Ceramic substrates are widely used in high thermal conductivity, high current, high insulation, high frequency and other fields due to their high thermal conductivity, excellent insulation, high frequency performance, high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance.
- FR-4 substrates are more widely used and in high demand due to their low cost and short production cycle.
High frequency performance:
- The dielectric constant of ceramic substrates is relatively stable and low, generally around 7~10, with high high frequency performance and low dielectric loss, faster and more stable signal transmission, so it is suitable for high frequency communication.
- In contrast, the high frequency performance of FR-4 is not as good as that of ceramic substrates.
In summary, there are significant differences between ceramic substrates and FR-4 in terms of physical and electrical properties, cost, production cycle, and application areas.
What is a ceramic substrate for power electronics?
The ceramic substrate for power electronics is a special process board made by directly bonding copper foil to the surface (single or double sides) of an alumina (Al2O3) or aluminum nitride (AlN) ceramic substrate at high temperature.
This ultra-thin composite substrate has excellent electrical insulation properties, high thermal conductivity, excellent soft solderability and high adhesion strength, and can be etched with various patterns like a PCB board, with a large current carrying capacity.
Therefore, ceramic substrates have become the basic materials for high-power power electronic circuit structure technology and interconnection technology.
The characteristics of ceramic substrates include strong mechanical stress, stable shape, high strength, high thermal conductivity, high insulation, strong bonding, corrosion resistance, good thermal cycle performance (cycle times up to 50,000 times, high reliability), no pollution, no pollution, wide operating temperature (-55℃~850℃), thermal expansion coefficient close to silicon, and simplified production process of power modules.
These characteristics make ceramic substrates widely used in the field of power electronics, especially in application scenarios that require high heat dissipation, low thermal resistance, long life, and voltage resistance, such as home appliance indicator lights, car lights, street lights, and large outdoor billboards.
In addition, the market for ceramic substrates is expected to increase by 94.27% in the next three years, showing a strong demand for localization. With the improvement of production technology and equipment, product prices have accelerated rationalization, further expanding its application areas in the LED industry.
The development trend of diversification and structural integration of ceramic substrates has put forward higher requirements on the performance of packaging substrates. They have been widely used in electronic device packaging, such as thin film ceramic substrates, thick film printed ceramic substrates, and direct bonding ceramic substrates. These substrates have high thermal conductivity, good heat resistance, low thermal expansion coefficient, high mechanical strength, good insulation, corrosion resistance, and radiation resistance.
Conclusion:
Ceramic substrate PCB has shown great value in the electronics industry with its excellent performance and wide range of uses. With the continuous advancement of science and technology, ceramic substrate PCB will surely be more deeply applied and developed in more fields, contributing to the innovation and progress of electronic technology.
As a professional ceramic circuit board manufacturer, BEST Technology has advanced production technology and a strict quality control system. It is always committed to providing customers with high-quality products and professional services, and continuously promoting the development of the ceramic circuit board industry.
Tags: ceramic PCB, PCB, pcb design