Fiducial marks may seem small, but their impact on PCB manufacturing is substantial. They act as reference points during the assembly process, ensuring precision in placing components. Without them, the accuracy of automated machines would drop, leading to potential misalignment. This guide covers everything you need to know about fiducial marks and their significance in PCB design.
What is the Fiducial Mark?
Fiducial marks are small, round copper pads on a PCB. They serve as reference points to guide automated assembly machines. Usually circular and made of copper, it serves as a visual cue that tells machines where the board is located on the assembly line. In the PCB manufacturing industry, fiducial marks play an important role in improving production efficiency and quality and reducing manual errors.

What is the Purpose of Fiducial Marks?
The fiducial marks on PCB plays a vital role in the manufacturing industry, mainly used to assist equipment or systems in the production process of PCB automatic positioning, alignment error detection, size measurement, lead inspection and other operations. Specifically, the role of fiducial marks includes the following:
- Accurate positioning
Fiducial marks can provide high-precision positioning information, so that the PCB components can be accurately aligned and installed.
- Automated assembly
Through the use of machine vision system, fiducial marks can be automatically identified and positioned to achieve automated PCB assembly process, improve production efficiency and reduce manual errors.
- Quality control
Fiducial marks can be used to detect the position and condition of PCB components for quality control and defect detection to ensure product compliance with specifications.
- Accurate calibration
Fiducial marks can be used to calibrate measuring equipment or machine vision systems to ensure their accuracy and stability.
- Design update and repair
Fiducial marks can be used as markers or reference points for positioning and adjusting the PCB during design iteration, troubleshooting, and repair.
What are the Different Types of Fiducial Marks in PCB?
Fiducial marks are not one-size-fits-all. Depending on the PCB design and complexity, different types of fiducials come into play:
- Global Fiducials: These marks are used to align the entire board. They’re usually placed on the corners or designated locations on the PCB to help machines recognize the board’s overall position.
- Local Fiducials: When certain areas of the PCB require high precision—especially spots with tight component layouts—local fiducials come into play. They’re placed near these critical sections to ensure parts like chips and connectors are placed with pinpoint accuracy.
- Panel Fiducials: If multiple PCBs are organized into a single panel for manufacturing, panel fiducials are added to align the entire panel. This ensures that each section of the panel stays in place during assembly.
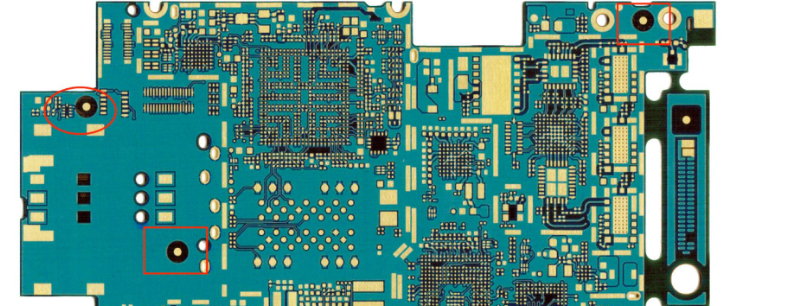
Each type of fiducial has its job, guiding machines from broad alignment down to component-specific positioning.
What is the Size of the Fiducial Marks on a PCB?
The dimensions of the optical points on the PCB are usually circular pads of 1mm to 3mm diameter, plus a solder shield of twice or more the pad size. Specifically, the size of the optical points can be adjusted according to different needs, and common sizes include:
- 1mm diameter round pad with a 0.6mm radius solder mask.
- 2mm diameter round pad with a 1mm radius solder mask.
These sizes are chosen to ensure that the optical points can be accurately identified and positioned by the mounter during the SMT production process, especially when dealing with dense pin components, improving the mounting accuracy.
In addition, the shape of the optical point is generally round, because the circular object is easier to be positioned by the machine, and the machine vision system can find the center of the reference point 2 more accurately.
What are Fiducial Marks Used For?
Fiducial marks have a straightforward yet essential purpose. They act as guideposts for automated assembly, ensuring the board is positioned and oriented correctly. Their main uses include:
- Aligning the Board: Fiducials tell the machines where the board starts and ends, helping them align it for each production step.
- Orientation Control: They guide machines to understand how the board is placed on the assembly line, preventing flipped or rotated placement.
- Component Precision: Especially with advanced and densely packed PCBs, fiducials ensure that each component is placed where it belongs.
Fiducial Marks vs. Positioning Holes
Fiducial marks and positioning holes are both used for alignment, but they serve different roles. Fiducial marks are visual reference points that automated machines read optically. They tell the machine where the board is and ensure accurate component placement. On the other hand, positioning holes are physical features. They’re used to mount the board securely onto a frame or machine bed, ensuring that it stays put during the assembly or manual handling.
Think of fiducial marks as the eyes of the process and positioning holes as the hands. Fiducial marks guide precision and accuracy, while positioning holes provide stability and physical anchoring.
Tags: fiducial marks pcb









