Learn everything about aluminum backed PCBs, including their advantages, limitations, and how they handle heat.
Aluminum-backed PCBs, also known as aluminum PCBs or aluminum core PCBs. These PCBs offer a unique combination of excellent thermal conductivity and structural strength, making them ideal for applications like LED lighting, power electronics, and automotive circuits.
What Is Aluminum Backed PCB?
An aluminum-backed PCB is a type of printed circuit board (PCB) where the base layer is made of aluminum rather than the traditional fiberglass or other materials. The key difference is the metal core, which significantly enhances the thermal conductivity of the PCB. The aluminum core is typically covered with a dielectric layer that isolates the conductive circuit from the metal base, allowing the PCB to maintain its electrical properties while providing better heat dissipation.
The combination of the aluminum base and the dielectric layer makes these PCBs ideal for high-power applications where heat management is essential. The aluminum core helps quickly dissipate heat away from sensitive components, thus improving the overall efficiency and lifespan of the device.

What Temperature Can Aluminum PCB Withstand?
Aluminum PCBs are designed to withstand high temperatures, but the exact temperature tolerance depends on several factors, including the thickness of the aluminum substrate and the quality of the dielectric layer. In general, aluminum-backed PCBs can handle temperatures up to about 130°C. However, it’s important to note that the temperature tolerance also depends on the specific materials used in the construction of the PCB and the environmental conditions in which it operates.
For high-power applications like LEDs, where heat is generated during operation, aluminum PCBs are a great choice because they help maintain lower temperatures. By dissipating heat effectively, they prevent components from overheating, which could otherwise damage the circuits.
How Thick Is the Dielectric Layer of Aluminum PCB?
The dielectric layer of an aluminum PCB plays a crucial role in providing electrical insulation while also allowing heat to be transferred away from sensitive components. The thickness of the dielectric layer typically ranges from 50µm to 200µm, depending on the application and the desired thermal performance.
Thicker dielectric layers are used in high-power applications where enhanced electrical insulation and thermal management are required.
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum PCB?
Aluminum PCBs offer several advantages, which make them an attractive choice for many industries. Here are some of the most notable benefits:
1. Superior Heat Dissipation: One of the key advantages of aluminum-backed PCBs is their excellent thermal conductivity. The metal base helps quickly dissipate heat away from the components, reducing the risk of overheating and prolonging the lifespan of the device. This makes them ideal for applications like LED lighting, power supplies, and high-power electronic devices.
2. Lightweight and Durable: Despite being made from metal, aluminum PCBs are lightweight yet durable. The metal core provides structural integrity without adding unnecessary weight, which is especially important in industries like automotive and aerospace.
3. Enhanced Performance: The combination of a high-quality dielectric layer and the aluminum substrate leads to better electrical performance, especially in high-current applications. Aluminum PCBs provide a stable platform for components to function optimally, minimizing electrical noise and interference.
4. Cost-Effective: Compared to other types of dissipation heat materials, aluminum-backed PCBs can be more cost-effective, especially for applications where heat dissipation is critical. Their lower manufacturing costs combined with higher production efficiency can reduce overall production costs, making them a preferred option for many applications.
5. Widely Applications: Aluminum-backed PCBs are primarily used in applications where heat dissipation is a concern. They are excellent for high-power applications, audio device, Communication electronics, Office automation equipment, automobile, computer, and etc. As a chief manufacturer partner for aluminum PCB, Best Technology provides custom service and full turn-key solutions. For more information or any inquiry, warm welcome to reach out to us via sales@bestpcbs.com.

What Are the Disadvantages of Aluminum PCB?
While aluminum-backed PCBs offer numerous benefits, there are some drawbacks to consider. However, these limitations are generally outweighed by their advantages in many applications. Letâs look at a few of the challenges:
1. More Complex Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process for aluminum-backed PCBs can be more complex compared to traditional PCBs. This complexity can increase the production time and cost, especially for custom designs.
2. Mechanical Stress: Aluminum is a relatively soft metal, which means it can be prone to deformation or bending under mechanical stress. This makes it unsuitable for applications where the PCB will be subject to harsh physical conditions or mechanical pressure.
3. Conductive Issues: The surface of aluminum PCB is prone to oxidation. Besides, The heat conductivity coefficient of aluminum is relatively low. Thus the metal core of aluminum PCBs can sometimes create challenges in terms of electrical grounding. Proper design and careful manufacturing are essential to ensure that the electrical properties of the PCB are maintained.
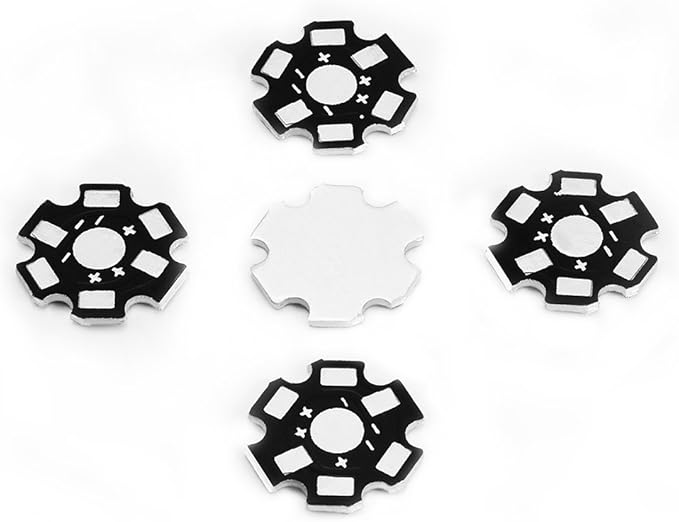

Why Is Aluminum No Longer Used in Integrated Circuits?
While aluminum used to be a common material for integrated circuits (ICs), it has largely been replaced by copper and other materials in modern IC manufacturing. There are several reasons for this shift:
1. Better Electrical Conductivity of Copper: Copper has better electrical conductivity than aluminum, making it the material of choice for interconnects in integrated circuits. Copperâs lower resistance allows for faster signal transmission and better overall performance.
2. Miniaturization of ICs: As ICs have become smaller and more complex, aluminumâs larger size and weaker electrical properties no longer meet the demands of modern integrated circuit design. Copper allows for the miniaturization of ICs without sacrificing performance.
3. Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum is more prone to oxidation compared to copper, which can affect the long-term reliability of integrated circuits. Copper, on the other hand, is more resistant to corrosion and offers better durability.
Despite these factors, aluminum still plays a crucial role in specific applications, particularly in PCBs where heat dissipation is the primary concern. Its ability to manage heat effectively makes it a valuable material in the realm of power electronics and LED technology. At Best Technology, quality is the priority. With 18 years manufacturing experience, we can provide high-quality Aluminum Backed PCBs solutions with fast delivery. Pls feel free to contact us to get more information and personalized solutions.
In a nutshell, aluminum-backed PCBs offer an effective solution for managing heat in high-power applications, making them a popular choice in industries like LED lighting, automotive electronics, and power supply systems. With advantages like superior thermal conductivity and lightweight durability, aluminum PCBs are a top choice for projects that require efficient heat dissipation.
However, they do come with some challenges, including more complex manufacturing processes and potential mechanical stress. Understanding these limitations is key to determining whether an aluminum PCB is the right choice for your specific needs. Whether you’re designing a custom aluminum PCB for LED lighting or exploring its benefits for power electronics, these PCBs offer unique advantages that make them a valuable asset in modern electronic design.
Tags: Aluminum Backed PCBs, aluminum pcb, PCB