Ceramic Antenna vs PCB Antenna, both two are popular types of antennas that are used in electronic devices. While they both serve the same fundamental purpose, they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. In the world of wireless communication, antennas play a crucial role in transmitting and receiving signals. In this blog, we will explore the differences between ceramic antennas and PCB antennas, their advantages, uses, and more.

What is a Ceramic Patch Antenna?
A ceramic patch antenna is another type of antenna that uses ceramic material as its substrate. These antennas are typically made from materials like zirconia, alumina, or other ceramic compounds that offer high dielectric properties. The ceramic material provides excellent performance, especially at higher frequencies, making it suitable for applications like GPS and satellite communication.
Ceramic patch antennas are designed with a patch (or conductor) on top of the ceramic material, which is usually mounted on a ground plane. These antennas are more robust and reliable than their PCB counterparts, especially when used in environments that require precision and high performance.
What is the Range of Ceramic Antenna?
Ceramic antennas are known for their excellent range, especially when used in GPS systems. Due to the high dielectric constant of ceramic materials, these antennas can transmit and receive signals over long distances with minimal loss. The range of a ceramic antenna depends on various factors, including the specific design, frequency, and environment in which it is used.
In general, ceramic antennas are effective for applications requiring longer-range communication, such as satellite communication, vehicle tracking, and high-performance wireless systems. Their ability to maintain a strong signal even at greater distances makes them ideal for outdoor and remote applications.
Why Are GPS Antennas Ceramic?
GPS antennas are commonly made from ceramic materials due to their superior dielectric properties. The ceramic material helps to maintain signal integrity, especially in environments with high levels of interference. GPS systems require precise, accurate signal reception, and ceramic antennas provide the reliability needed for such applications.
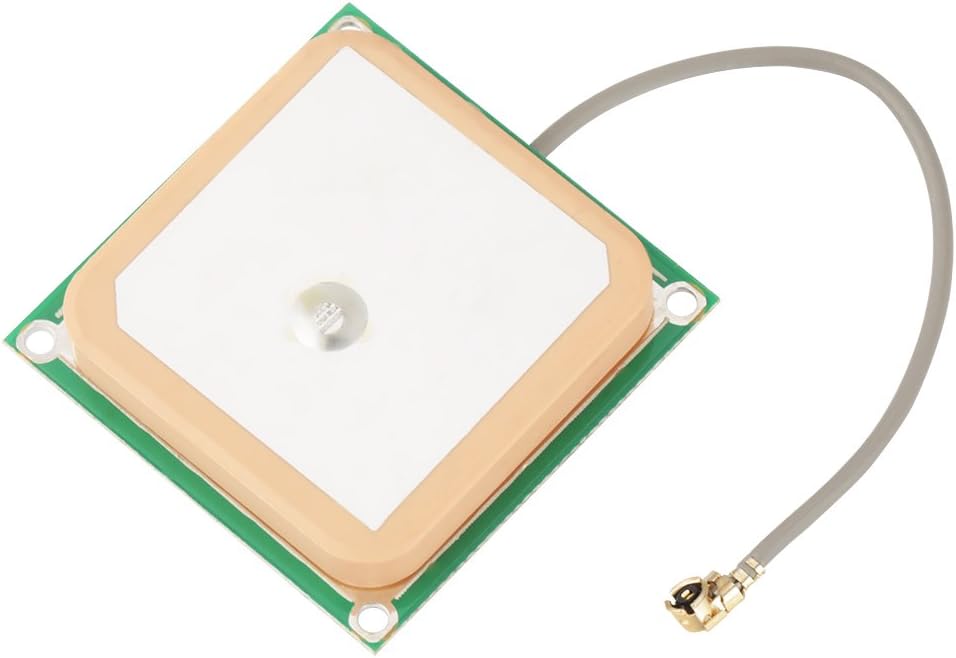
Additionally, ceramic antennas are compact and lightweight, which is essential for portable GPS devices like handheld GPS receivers and automotive navigation systems. Their ability to provide stable and consistent signal reception at various frequencies makes them the go-to choice for GPS technology.
How Does a Ceramic Antenna Work?
A ceramic antenna works by converting electrical signals into electromagnetic waves and vice versa. The process begins when an electrical current is passed through the antennaâs conductive elements, generating a fluctuating electromagnetic field. This electromagnetic field then radiates from the antenna in the form of radio waves.
In the case of a ceramic antenna, the high dielectric properties of the ceramic material enhance the efficiency of this process. The material helps to focus and direct the electromagnetic waves, allowing for better signal strength and range. Ceramic antennas are designed to operate at specific frequencies, and their performance is optimized to meet the requirements of various communication systems.
What is a PCB Antenna?
A PCB antenna is a type of antenna integrated into the PCB of an electronic device. These antennas are designed using the same materials and manufacturing processes used to produce the rest of the circuit board. PCB antennas are typically thin and can be designed in various shapes, depending on the needs of the device.
These antennas are often chosen for their low cost, ease of integration, and compact size. The simplicity of their design makes them suitable for a wide range of consumer electronics, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and IoT devices.
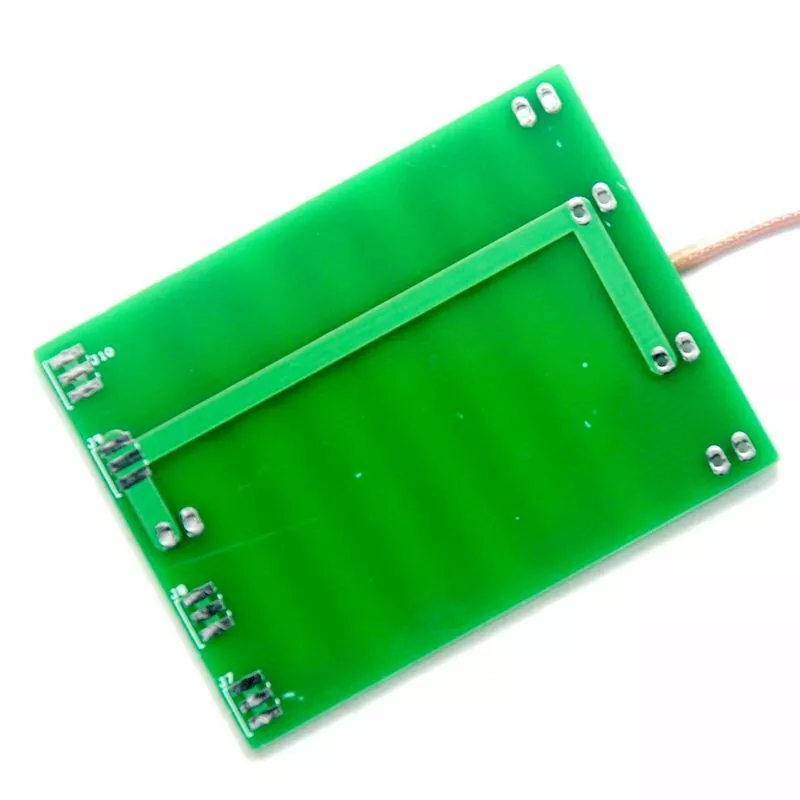
What is a PCB Trace Antenna?
A PCB trace antenna is a specific type of PCB antenna, where the antennaâs design is embedded directly into the PCB as a copper trace. This design allows the antenna to be integrated seamlessly into the PCB without requiring additional components or external parts. PCB trace antennas are usually smaller, lightweight, and cost-effective, making them ideal for compact devices that require space-saving solutions.
They are commonly used in small form-factor devices, such as wireless routers, Bluetooth devices, and GPS receivers. Due to their simplicity, they are often chosen for consumer-grade products.
What are the Advantages of PCB Antenna?
PCB antennas offer several advantages that make them a popular choice in modern electronic devices. Here are some key benefits:
Compact Size: PCB antennas are integrated directly into the PCB, saving space within the device. This is crucial for compact and portable devices.
Cost-Effective: Since they are part of the PCB, the cost of manufacturing is lower than traditional antennas that require separate components or assembly processes.
Simplicity: PCB antennas are easy to design and integrate into existing PCB layouts. Their simplicity reduces the complexity of the overall design and assembly process.
Customization: PCB antennas can be customized to fit the specific needs of a device, with various shapes and sizes available to accommodate different designs.
Reliability: PCB antennas are highly reliable due to their integration into the PCB, making them resistant to external factors like environmental damage.
What are PCB Antennas Used For?
PCB antennas are used in a variety of applications, especially in devices where size and cost are critical factors. Some common uses include:
IoT Devices: PCB antennas are widely used in IoT devices such as smart home systems, sensors, and wearables. Their compact size and efficiency make them perfect for these types of devices.
Mobile Devices: Smartphones, tablets, and other portable electronics often incorporate PCB antennas due to their low-profile design and cost-effectiveness.
Wireless Communication Systems: PCB antennas are used in wireless routers, Bluetooth devices, and Wi-Fi systems for communication and signal transmission.
Consumer Electronics: From gaming consoles to digital cameras, many consumer electronic products rely on PCB antennas to support wireless capabilities.
In conclusion, both ceramic and PCB antennas have their own unique strengths and applications. Ceramic antennas excel in performance, range, and reliability, making them perfect for high-performance applications like GPS and satellite communication. PCB antennas, on the other hand, offer cost-effectiveness, compactness, and ease of integration, making them ideal for a wide range of consumer electronic devices and IoT systems.
The choice between ceramic and PCB antennas depends on the specific requirements of the device, including factors like size, cost, signal range, and performance. By understanding the differences between these two types of antennas, you can make an informed decision on which one best suits your needs.
For companies looking to explore the benefits of both antenna types, it’s important to work with a trusted manufacturer who can offer tailored solutions. At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we provide high-quality Ceramic and PCB antennas’ components to meet the diverse needs of our customers. Whether you need a compact PCB antenna or a high-performance ceramic antenna, we have the expertise to help you achieve the best solution for your project.
Tags: Ceramic Antenna vs PCB Antenna, ceramic PCB, PCB, PCBA, printed circuit board


