What is an Assembly PCB? Assembling PCB refers to the process of installing electronic components on a printed circuit board. Through this process, various electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, chips, etc. are fixed on the PCB through welding technology to form a complete electronic circuit.
Assembling PCB is a key step in the manufacture of electronic equipment, which enables electronic components to be connected according to the designed circuit to achieve the functions and performance of electronic equipment.
What is the PCB Assembly Process?
PCB assembly is the process of attaching electronic components to a printed circuit board (PCB) to create a working electronic circuit. The primary goal is to ensure that all parts of the circuit are correctly connected and able to transmit electrical signals.
The PCB assembly process mainly includes the following steps:
- Solder paste printing: First, print the solder paste on the PCB, which is done by using a template to accurately apply the solder paste to the pads of the PCB.
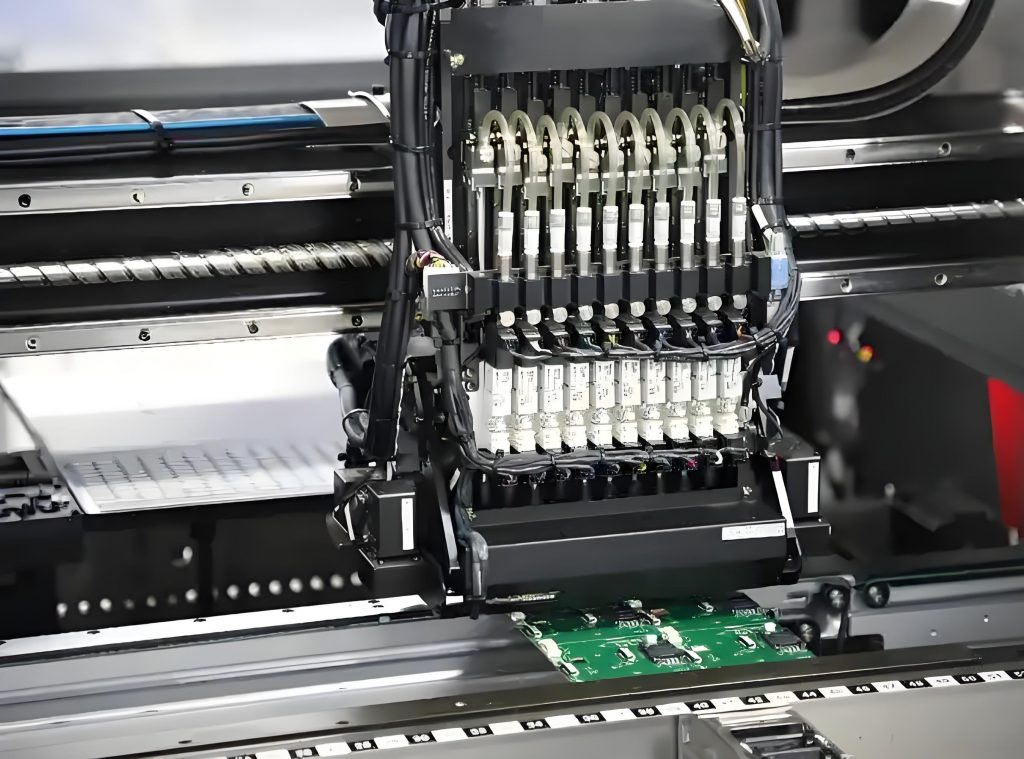
- Component placement: Use a high-speed, high-precision placement machine to place the components on the PCB. The placement machine accurately places the components at the predetermined position based on the coordinate information in the design file.
- Soldering: After the component placement is completed, the soldering process is carried out. For surface mount components, reflow soldering is usually used, and the PCB is sent into the reflow soldering oven, and the solder paste is melted by heating, so that the components are soldered to the PCB. For through-hole components, wave soldering is used.
- Inspection and testing: After the soldering is completed, inspection and testing are carried out to ensure the assembly quality. Automated optical inspection (AOI) equipment is usually used to check the soldering quality and the accuracy of component placement.
- Rework and packaging: For defective products found during the inspection, rework is carried out. Qualified PCB assembly boards are packaged for transportation and storage.
The entire PCB assembly process requires a high degree of automation and precise control to ensure the quality and reliability of the final product.
What is the Standard for PCB Assembly?
The standard for PCB assembly depends on several industry-specific certifications and guidelines. However, some of the most widely recognized standards include:
- IPC-2221: This standard provides the generic requirements for designing and manufacturing PCBs, including assembly considerations.
- IPC-A-610: Often referred to as the “Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies,” this standard covers the acceptability criteria for soldering, component placement, and the quality of assembly in general.
- ISO 9001: Many PCB assembly manufacturers are certified to this standard, which ensures that they follow consistent quality management practices in their processes.
These standards help ensure that the PCB assembly process is carried out in a controlled and quality-assured manner.
What Files are Needed for PCB Assembly?
A successful PCB assembly requires the right files to communicate the design and specifications to the manufacturer. Some of the essential files include:
- Gerber Files: These files provide the detailed design of the PCB, including copper traces, pads, and other essential information for PCB fabrication.
- Bill of Materials (BOM): The BOM lists all the components that will be used in the assembly, such as resistors, capacitors, and ICs.
- Pick-and-Place Files: These files contain the specific information about where each component will be placed on the PCB, which is essential for automated placement machines.
- Stencil File: This file is used for creating the solder paste stencil, which is used to apply solder paste to the PCB during the soldering process.
These files ensure that the PCB board assembly is accurate and matches the original design specifications.
What Are the Materials Used in PCB Assembly?
The materials used in PCB board assembly are crucial to the functionality and performance of the finished product. Some of the most commonly used materials include:
- PCB Substrate: The most common material is FR4 (fiberglass resin), but for high-performance applications, materials like aluminum or ceramic may be used.
- Solder Paste: A mixture of metal solder and flux, solder paste is used to attach components to the PCB during the soldering process.
- Soldering Materials: Lead-based or lead-free solder is used to create permanent connections between the PCB and components.
- Components: Resistors, capacitors, ICs, and other components are soldered onto the PCB. These can be sourced from various manufacturers and come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Each material is selected based on the needs of the specific application. For example, ceramic PCBs are chosen for high-temperature environments, while aluminum-backed PCBs are selected for heat dissipation.
What is the Difference Between PCB Fabrication and PCB Assembly?
Many people confuse PCB fabrication with PCB assembly, but the two are distinct steps in the PCB manufacturing process.
PCB Fabrication refers to the process of creating the physical PCB from raw materials. This includes the creation of the PCBâs layers, the copper traces, drilling holes for vias, and etching the patterns that connect the components. In simple terms, PCB fabrication is the creation of the “bare” board.
PCB Assembly, on the other hand, refers to the process of attaching electronic components to the fabricated PCB. This involves placing and soldering the components to form a functional circuit.
So, PCB fabrication is all about making the PCB, and PCB assembly is about making it functional by adding components.
What is the Difference Between SMD and SMT in PCB?
The terms SMD (Surface-Mounted Device) and SMT (Surface-Mount Technology) are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different aspects of the assembly process.
SMD refers to the actual components used in the assembly process. These components are designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB rather than through-hole components, which are inserted into holes drilled into the board.
SMT, on the other hand, refers to the technology and process used to assemble SMDs onto the PCB. SMT involves automated machines that place components onto the PCB and then solder them into place, typically using reflow soldering.
In summary, SMD refers to the components, and SMT refers to the method of attaching those components.
Conclusionï¼
PCB assembly is a critical step in creating functional electronic circuits. From the placement of components to the soldering process and final testing, every aspect of assembly must be carefully executed to ensure a reliable and high-performance product. If you have any PCB assembly needs, feel free to contact BEST Technology at sales@bestpcbs.com.
Tags: assembly PCB, PCB Assembly