The debate between 1.6t vs 1.2 PCB is a common one for those designing or customizing mechanical keyboards. The thickness of a PCB affects not only the overall durability but also the typing experience. Whether you prioritize a solid feel with a 1.6 mm PCB or prefer the lighter, more flexible nature of a 1.2 mm PCB, understanding these differences can help you make the right choice. In this blog, we’ll break down the key distinctions, and show you how the thickness of your PCB can influence the performance and comfort of your keyboard.

What is the difference between 1.2 and 1.6 PCB?
The primary difference between a 1.2 PCB and a 1.6 PCB is the thickness of the board itself. A 1.2 PCB is 1.2 millimeters thick, while a 1.6 PCB measures 1.6 millimeters. The thickness of a PCB impacts its durability, rigidity, and overall feel in applications such as mechanical keyboards.
A 1.2 mm PCB is often used in keyboards that require a more flexible, lighter feel. It’s commonly chosen for lightweight builds or when aiming for a slim profile. On the other hand, a 1.6 mm PCB is thicker, providing greater rigidity, which results in a more solid, firm keypress experience. This thickness is favored in high-end mechanical keyboards, where stability and a more premium feel are prioritized.
Why are PCBs 1.6 mm thick?
PCBs are typically 1.6 mm thick because this thickness offers an excellent balance between durability and flexibility for most applications. At 1.6 mm, the board is sturdy enough to support complex circuit designs and ensure reliable performance, yet it remains thin enough to fit comfortably within most electronic devices, including keyboards.
The 1.6 mm thickness is the industry standard for many consumer electronics, as it can accommodate a variety of components without compromising the integrity of the circuit. It’s also an ideal thickness for creating a uniform look in keyboards, ensuring that all components fit together neatly while still maintaining high-quality performance.
What is the thickness tolerance of a 1.6 mm PCB?
The thickness tolerance of a 1.6 mm PCB generally falls within a range of ±0.1 mm. This means that the actual thickness of the PCB can vary slightly, typically between 1.5 mm and 1.7 mm, depending on the manufacturing process. Tolerance is an important factor because even slight variations in thickness can affect the fitting and performance of components, especially in high-precision builds like mechanical keyboards.
However, manufacturers ensure that the tolerance level is within an acceptable range to prevent any significant issues when assembling the keyboard. This makes it easier to work with PCBs of this thickness, as the components are more likely to fit correctly and perform optimally.
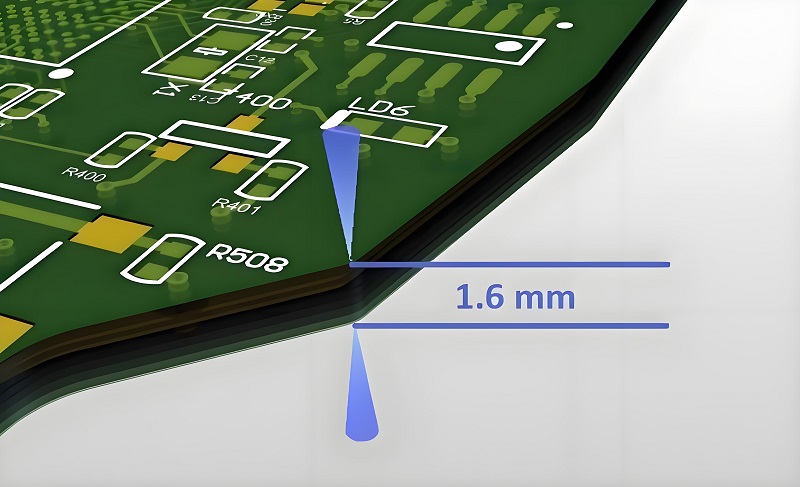
What is the most common PCB thickness?
The most common PCB thickness is 1.6 mm, particularly for consumer electronics, including keyboards, smartphones, and other portable devices. This thickness strikes the perfect balance between strength and flexibility, making it the default choice for many applications. Whether you are designing a simple circuit or a more advanced mechanical keyboard, the 1.6 mm PCB provides the reliability and durability needed for long-term use.
In keyboards, this thickness is widely used for both standard and custom builds. It’s not too thin to compromise the keyboard’s structure, and it’s not so thick that it adds unnecessary bulk.
What is the minimum thickness of a PCB?
The minimum thickness of a PCB depends on several factors, including the materials used, the intended application, and the manufacturing process. Typically, the thinnest PCB available is around 0.2 mm, though PCBs thinner than this can become fragile and less durable.
For practical applications like keyboards, it’s rare to see PCBs thinner than 1.2 mm, as they may struggle to support the components required for stable keypresses. A thinner PCB can result in a less solid typing experience, which is why manufacturers typically avoid using extremely thin PCBs for high-performance builds.
What is the thinnest PCB material?
The thinnest PCB materials are typically made from flexible substrates, such as polyimide or polyester films. These materials allow for extremely thin designs that can be as low as 0.2 mm. These ultra-thin PCBs are often used in applications where space is limited, such as in wearable electronics or medical devices.
However, it’s important to note that these thin materials often sacrifice some rigidity and may not be suitable for all types of keyboards. While they work well for compact or flexible designs, a more rigid PCB like the 1.2 mm or 1.6 mm versions is usually preferred in mechanical keyboards for their stability and performance.
Does PCB thickness matter?
Yes, PCB thickness does matter, especially when designing keyboards or other precision electronics. The thickness of the PCB affects the overall rigidity, weight, and feel of the final product. In a keyboard, for example, a thicker PCB (like the 1.6 mm version) will create a sturdier, more solid feel with less flex during typing.
Thicker PCBs are often preferred in mechanical keyboards because they provide a more premium typing experience and reduce the likelihood of issues such as warping or bending. On the other hand, thinner PCBs (such as the 1.2 mm version) offer a lighter and more flexible feel, making them suitable for custom builds or portable devices where weight and space are critical considerations.
Are PCB switches hot swappable?
Hot-swappable PCB switches allow users to change switches without soldering. Many mechanical keyboards now feature hot-swappable PCBs, providing the flexibility to try different switches or replace worn-out ones with ease.
However, not all PCBs are hot-swappable. A PCB must be designed specifically with hot-swapping functionality in mind, meaning that the PCB must have switch sockets and a proper electrical layout to support this feature. Many high-end 1.6 mm PCBs include this option, while thinner or cheaper PCBs might not.
In summary, the choice between 1.6t vs 1.2 PCB comes down to the specific needs of your project. While the 1.6 mm PCB offers greater rigidity and durability, the 1.2 mm PCB provides a lighter and more flexible option. For keyboards, both thicknesses have their merits, depending on whether you’re looking for a more solid typing experience or a sleeker, more portable design.
When selecting a PCB thickness, it’s essential to consider not only the thickness itself but also the application and overall design goals. Whether you’re building a custom keyboard or upgrading an existing one, understanding these PCB variations will ensure that you choose the right components for your needs.
By opting for the right PCB thickness and features like hot-swappable switches, you can enhance your keyboard’s functionality and enjoy a superior typing experience. We offer a full range of PCB products in small quantities, ensuring fast delivery and the highest quality standards at Best Technology. Reach out to us at sales@bestpcbs.com for more information or questions.
Tags: 1.6 mm PCB, 1.6t vs 1.2 pcb, PCB, pcb design, printed circuit board