The debate of non-flex cut vs flex cut PCB has been a common topic for engineers and manufacturers. When designing printed circuit boards (PCBs), one key decision is whether to use a flex cut or non-flex cut PCB. These two types of PCBs serve different purposes, with unique advantages depending on the application. But how do they differ, and when should you use each? This guide will dive into the specifics, providing you with insights to make an informed decision.
What is a Flex Cut PCB?
A flex cut PCB is a type of printed circuit board that’s designed to be flexible. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, flex PCBs can bend and flex without compromising the performance of the electrical circuits. This flexibility is achieved by using materials such as polyimide, which allows the board to conform to various shapes and spaces.
Flex cut PCBs are commonly used in devices where space is limited or for designs that require a dynamic or compact setup, such as in wearable tech or mobile phones. Their flexible nature provides the freedom to design intricate layouts without being restricted by rigid geometries.
What is the Difference Between Flex Cut and Non-Flex Cut PCB?
The main difference between flex cut and non-flex cut PCBs lies in their physical structure and flexibility. As mentioned, flex cut PCBs are made from flexible materials, which means they can be bent, twisted, or folded. This flexibility makes them suitable for applications where space constraints are a concern, and the board needs to fit into non-traditional forms or be more compact.
In contrast, non-flex cut PCBs, often referred to as rigid PCBs, are built using rigid substrates like FR4 or aluminum, providing stability and durability. These boards do not bend and are generally used in devices that do not require flexibility.
Both types of PCBs have their unique advantages. Flex cut PCBs are best for space-saving and adaptability, while non-flex cut PCBs are ideal for products that need more stability and rigidity.
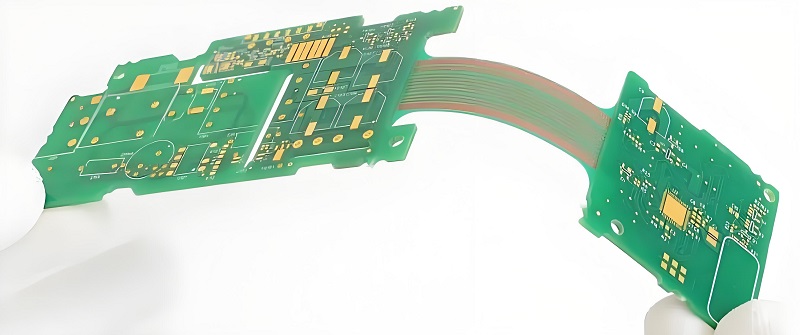
Why Use a Flex PCB?
There are several reasons to opt for a flex PCB in certain applications. One of the biggest advantages is its ability to save space. Flex PCBs can be folded or shaped to fit into areas where rigid PCBs cannot. This makes them an excellent choice for compact electronic devices such as smartphones, cameras, and medical equipment.
Additionally, the flexibility allows for more robust designs in environments with high mechanical stress, such as robotics or wearables. Flex PCBs can withstand vibration and movement better than rigid boards, offering better durability in these conditions.
Finally, the lightweight nature of flex PCBs contributes to the overall efficiency of the product, making them an essential component in modern, miniaturized electronics.
What is an FR4 Plate?
FR4 is a widely used material in the manufacturing of rigid PCBs. It stands for “Flame Retardant 4” and is a type of fiberglass epoxy laminate. The FR4 material provides excellent strength, low moisture absorption, and good electrical insulation properties.
While FR4 is typically used for non-flex cut PCBs, it can also be used in multi-layer flexible PCBs in certain designs. Its role is to provide stability and electrical insulation, making it a crucial material in traditional PCBs.
What is Tri-Mode Non-Flex Cut Hotswap PCB?
Tri-mode non-flex cut hotswap PCBs are a specialized type of PCB designed for mechanical keyboards, offering a flexible, user-friendly experience. The term “tri-mode” refers to the ability to support multiple connection types, such as wired, Bluetooth, and wireless.
The non-flex cut hotswap design enables users to easily replace or swap out switches on the keyboard without the need for soldering. This makes it ideal for enthusiasts who want to customize their keyboards with different types of switches. It combines the advantages of non-flex cut rigidity with the versatility of hotswapping.
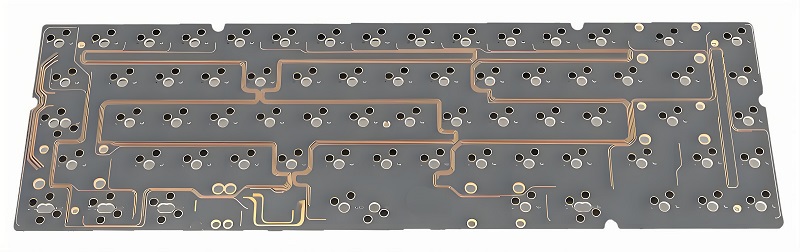
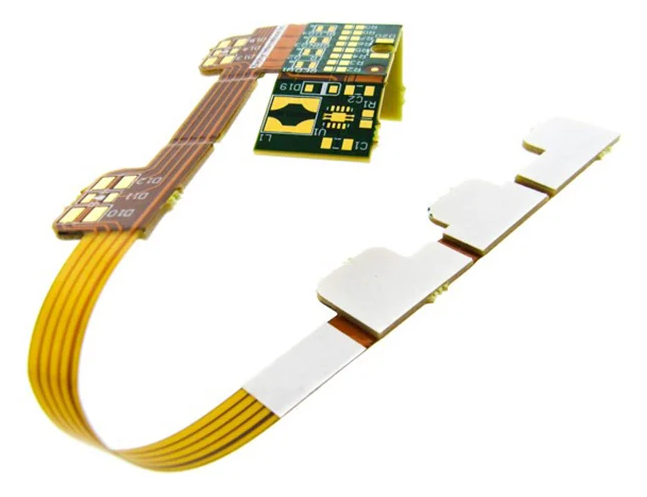
What is a Rigid-Flex PCB?
A rigid-flex PCB is a hybrid of both rigid and flexible PCB technologies. It consists of both rigid and flexible sections integrated into a single board. These PCBs offer the best of both worlds, combining the stability and reliability of rigid PCBs with the flexibility of flex PCBs.
Rigid-flex PCBs are often used in high-performance applications such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive systems. They provide a compact solution where multiple PCB types need to coexist, and their flexible sections can be bent or folded to fit complex spaces.
What Are the Disadvantages of Rigid-Flex PCBs?
Despite their advantages, rigid-flex PCBs come with some drawbacks. One major disadvantage is their cost. Due to the complexity of manufacturing, rigid-flex PCBs tend to be more expensive than traditional rigid or flex PCBs.
Additionally, the design and production process for rigid-flex PCBs is more intricate, requiring higher precision and more time. This can also lead to longer lead times for production, which may not always be ideal for projects with tight deadlines.
When Should I Use a Flex PCB?
Flex PCBs are perfect for applications where flexibility, compact design, and space-saving are important. You should use a flex PCB when your product needs to fit into tight or unique spaces, like wearable devices, medical equipment, or consumer electronics.
They are also a good choice for products that need to endure repetitive movement or vibrations. In situations where the PCB needs to be bent or folded without breaking, such as in robotics or automotive designs, flex PCBs offer exceptional reliability.
Are Flexible PCBs More Expensive?
Flexible PCBs generally come at a higher cost compared to non-flex cut PCBs. This is due to the specialized materials and the intricate manufacturing process required for flexible designs.
However, despite the initial cost increase, flex PCBs can provide long-term cost savings by reducing the overall size of the device and minimizing the need for additional components or connectors. For applications where space is crucial or where traditional PCB designs would be too bulky, the investment in a flex PCB can pay off in the long run.
In the debate of non-flex cut vs flex cut PCB, the right choice ultimately depends on the needs of your project. Flex PCBs excel in compactness and flexibility, making them a great choice for dynamic, space-constrained designs. On the other hand, non-flex cut PCBs offer superior stability and durability for applications where rigidity is key.
For some projects, you might even find that combining the benefits of both technologies, like in rigid-flex PCBs, offers the perfect balance of performance and flexibility. When making your decision, consider the design requirements, budget, and long-term needs of your application.
By understanding the differences between flex and non-flex cut PCBs, you can make the best choice for your next project, ensuring efficiency, durability, and performance. Best Technology sets itself apart by providing top-notch, customized Non-Flex Cut and Flex Cut PCB products, quick delivery, and superior customer care. Contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com for inquiries or further details.
Tags: Flex Cut PCB, Non-Flex Cut vs Flex Cut PCB, PCB, pcb design, printed circuit board