What is a Flexible PCB for LED Strip?
A flexible PCB for LED strip is a thin, bendable circuit board that holds LED components. Unlike rigid boards, it allows easy installation on curved surfaces. These PCBs are made with flexible base materials, such as polyimide or PET (polyethylene terephthalate), to support LED lighting applications that require flexibility, lightweight construction, and compact form factors. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, flexible LED strips can be bent, twisted, or curved to fit various surfaces without breaking, so they are always used in wearable devices.

Structure of a Flexible PCB for LED Strip
A flexible LED PCB strip consists of multiple layers that work together to provide electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and heat dissipation:
- Base Material (Substrate): The most common base material is polyimide (PI) due to its excellent flexibility, high-temperature resistance (up to 400°C), and durability. PET is used in cost-sensitive applications but has lower heat resistance.
- Copper Layer: The conductive traces are made from rolled annealed (RA) copper or electrodeposited (ED) copper, typically 18µm (0.5oz) to 70µm (2oz) thick, depending on current requirements.
- Adhesive Layer: Some flexible PCBs use adhesive-based or adhesiveless constructions to bond layers. Adhesiveless designs provide better thermal and electrical performance.
- Solder Mask & Protective Coating: A flexible solder mask, such as PSR-9000FX from Taiyo, prevents oxidation and ensures insulation. Some LED strips use silicone or epoxy coatings for additional protection against moisture and dust.
Types of LED PCB Strip
LED PCB strips are classified based on the base material used for the PCB, which affects flexibility, heat dissipation, and durability. The most common types include FR4, aluminum, flexible polyimide, and ceramic PCBs (though copper base material has very good thermal conductivity, its heavy weight limited its usage in led PCB strip design).
- FR4 LED PCB Strip: FR4 is a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate that offers mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness. It has a low thermal conductivity (~0.3W/m·K), so it always used into low-power LED strips that do not generate excessive heat. However, it lacks flexibility, limiting its use in curved or flexible applications.
- Aluminum LED PCB Strip: Aluminum-backed PCBs are designed for high-power LED applications, where efficient heat dissipation is critical. With a thermal conductivity of 1.0–3.0W/m·K, they outperform FR4 in heat management, ensuring longer LED lifespan and stable performance. These strips are commonly used in outdoor lighting, automotive headlights, and industrial applications.
- Flexible Polyimide LED PCB Strip: Polyimide-based PCBs provide superior flexibility, allowing LED strips to bend without breaking. These PCBs typically have a thickness of 25–50µm, they are ideal for wearable lighting, signage, and decorative applications. While they do not dissipate heat as efficiently as aluminum PCBs, adding thermal vias can improve heat transfer.
- Ceramic LED PCB Strip: Ceramic PCBs, such as aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) and aluminum nitride (AlN), are used for high-temperature LED applications. They have an exceptional thermal conductivity of up to 180W/m·K (AlN). Due to it is expensive and classified into a kind of high-end product, it is mostly used in aerospace applications, where extreme durability is required.
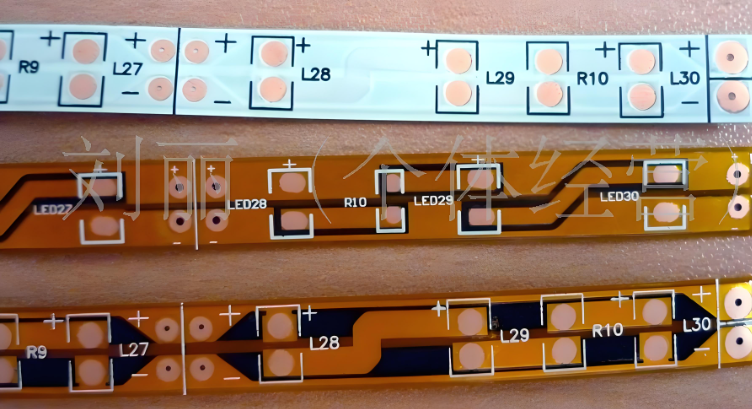
Advantages of LED PCB Strip
- Space-saving design – Thin and flexible, can be used in tight spaces that rigid PCB can’t achieve.
- Durability – Resistant to bending, vibrations, and mechanical stress.
- Heat dissipation – Transfers heat efficiently, improving LED lifespan.
- Energy efficiency – Supports low power consumption, reducing costs.
- Lightweight – Reduces overall weight in applications like automotive and wearable tech.
- Customizable – Allows different layouts, colors, and LED densities, various material base available.
LED PCB Strip Design Considerations
Designing an LED PCB strip requires careful consideration of electrical, thermal, mechanical, and environmental factors to ensure efficiency, durability, and reliability. Here Best Technology listing some must-have to smooth your design phase:
1. Power Distribution: Voltage drops can cause inconsistent brightness, especially in long LED strips. For every 1-meter length, a 12V LED strip can lose 0.5V to 1V due to resistance. To prevent this, using parallel power feeds and power injection every 2–5 meters helps maintain stable voltage and brightness.
2. Current Handling: The copper thickness directly affects the strip’s ability to handle current. A 1oz (35µm) copper layer can safely carry up to 1.5A per mm of trace width, while a 2oz (70µm) copper layer can handle about 2.4A per mm. Selecting the right copper weight reduces resistance and prevents overheating, especially for high-power LED strips drawing more than 3A per meter.
3. Voltage Selection: Choosing the correct voltage improves efficiency. A 5V LED strip is best for short lengths but has higher current draw, while 12V and 24V LED strips offer better efficiency and lower current demand. A 24V strip allows longer runs (up to 10m) without noticeable voltage drop, making it ideal for commercial installations.
4. Heat Dissipation: LEDs convert 20-40% of electrical energy into light, with the rest generating heat. Aluminum-backed PCBs can dissipate heat 3-5 times more efficiently than standard FR4, reducing the risk of LED failure. Thermal vias with 0.3-0.5mm hole diameter can also improve heat dissipation by transferring heat from LED pads to the copper layers below.
5. Material Selection: FR4 PCBs are commonly used but have low thermal conductivity (~0.3W/m·K), making them less effective for heat dissipation. Polyimide flexible PCBs are better for bendable applications but require additional thermal management. Aluminum PCBs provide superior thermal conductivity of 1.0-3.0W/m·K, making them ideal for high-power LED applications.
6. Bendability and Flexibility: Flexible LED strips should maintain a minimum bend radius of 10mm to avoid stress fractures. For extreme flexibility, a polyimide PCB with 50µm thickness can be used. Components should be placed at least 1.5mm away from bending zones to prevent mechanical stress and circuit damage.

LED PCB Strip Applications
- Automotive lighting – Interior and exterior vehicle lighting.
- Home and commercial lighting – Decorative and functional lighting solutions.
- Wearable technology – Integrated into smart clothing and accessories.
- Medical devices – Used in diagnostic tools and surgical lights.
- Signage and displays – Ideal for advertising boards and digital screens.
- Consumer electronics – Found in keyboards, gadgets, and ambient lighting.
Best Flexible PCB for LED Strip Manufacturer – Best Technology
When selecting a flexible LED PCB strip manufacturer, quality and reliability matter. Best Technology has been producing LED PCB strips for over 18 years. They offer:
- High-quality materials – Ensuring durability and performance.
- Customization options – Tailored designs to meet specific needs.
- Advanced manufacturing – Cutting-edge technology for precise production.
- Fast delivery – Efficient processes to meet deadlines.
- Excellent customer service – Professional support from design to delivery.
FAQs of LED PCB Strip
1. What is the lifespan of a flexible LED PCB strip?
With proper materials and design, an LED PCB strip can last over 50,000 hours.
2. Can flexible PCB strips handle high temperatures?
Yes, polyimide-based PCBs offer good heat resistance, but additional cooling may be needed.
3. Are flexible LED PCBs waterproof?
Some designs include waterproof coatings or encapsulation for outdoor use.
4. What is the best material for a flexible PCB?
Polyimide is the most durable and heat-resistant option.
5. Can I cut an LED PCB strip?
Yes, but it should be cut at designated points to avoid damage.
For the best flexible PCB for LED strip, Best Technology offers customized, high-quality solutions. Contact us today to discuss your project!
Tags: flexible pcb for led strip, led pcb strip manufacturer