What is a Power Inverter Circuit?
What is a power inverter circuit? A power inverter circuit is a crucial component in many electrical systems, especially for those that rely on renewable energy sources like solar panels. In simple terms, a power inverter converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
DC power flows in one direction, while AC power reverses direction periodically. Most household devices, including appliances, lights, and tools, operate on AC power. Since many energy sources, such as solar panels and batteries, provide DC power, an inverter is required to convert it to the appropriate AC form. Without inverters, off-grid power systems would not be practical, as most electrical devices cannot run on DC power.
Power inverters come in various sizes and configurations depending on the specific requirements. Small inverters are used for powering a few devices, while large inverters are used in industrial applications or large solar power systems to power entire buildings or grids.
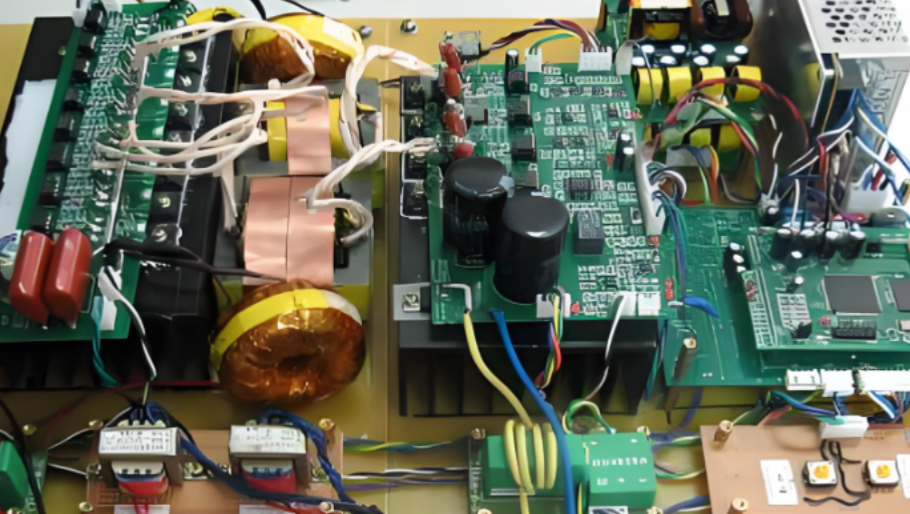
Power Inverter Diagram Circuit
To understand how a power inverter circuit works, it’s essential to know the basic components of an inverter include:
- DC Input (Battery or Solar Panel): The source of direct current, usually from batteries or renewable sources like solar panels.
- Oscillator Circuit: This generates a high-frequency AC signal from the DC input. The oscillator typically uses transistors to switch the current at a high frequency.
- Switching Circuit (Transistors or MOSFETs): These components act as the “switches” in the circuit that alternate the current, effectively turning DC into a pulsating AC signal.
- Transformer: The transformer steps up or steps down the voltage to the appropriate level. Inverters can be designed for low, medium, or high voltage applications.
- Rectifier/Filter Circuit: This smooths the pulsed AC signal into a more stable form of AC, reducing the ripple to make the output more consistent.
- AC Output: The final alternating current is available at the output terminals, ready to power devices.
A diagram for a power inverter would typically include these components arranged in a sequence that shows how energy flows through the system—from DC input to AC output. And here is a basic power inverter circuit diagram for your reference.
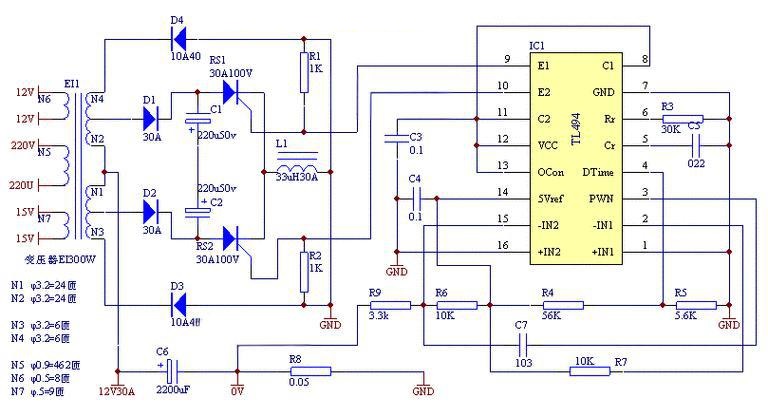
What is the Function of a Power Inverter?
The main function of a power inverter is to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), making it usable for common household appliances or industrial equipment. For example, when you’re off the grid and using solar panels, they generate DC power. However, most of your home appliances, like refrigerators, air conditioners, and lighting, run on AC power. Without an inverter, you wouldn’t be able to use the power from your solar panel or battery system to run these devices.
Inverters are also used in backup power systems, where DC power is stored in batteries and then converted to AC power for temporary use during power outages. They ensure that electricity is supplied in the form that most appliances can safely use. Moreover, power inverters are critical for maintaining the stability of power in renewable energy systems, ensuring that the power generated can be fed into the grid or used to power homes and businesses.
How Does a Power Inverter Work?
The operation of a power inverter revolves around switching and transforming electrical energy. It works by these processes: the inverter receives direct current from the battery or storage battery as input. After the input DC is processed by the rectifier, it enters the inverter bridge. Inverter bridge is the core component of the inverter, by controlling the switching elements (such as IGBT) on and off, the direct current is converted to high frequency periodic alternating current.
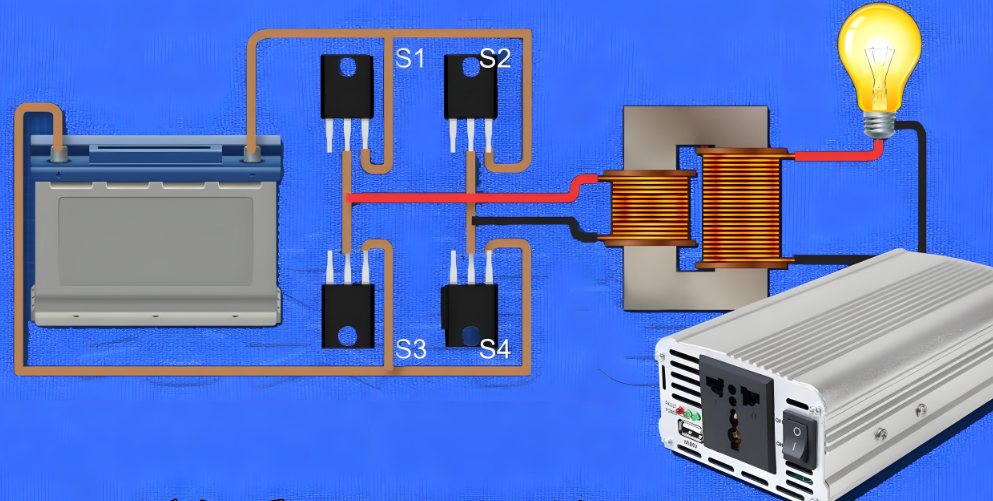
Using pulse width modulation (PWM) technology, the phase alternating current is modulated into sine wave or square wave of a certain frequency, so that its waveform is close to the alternating current of the mains. Then the modulated AC passes through the filter circuit to filter out the high-frequency harmonics and get a smooth AC output. The inverter is equipped with a protection system to ensure stable operation in the case of load changes or failures, to protect the inverter and connected electrical equipment.
How to Build a DC to AC Power Inverter Circuit?
Building a DC to AC power inverter circuit can be a rewarding and educational project, especially for those interested in renewable energy or electronics. While there are many different types of power inverters, from simple square wave designs to complex sine wave designs, here we will focus on creating a basic square wave DC to AC inverter. This type of inverter can be used for low-power applications and is easier to build compared to more advanced inverters.
Before starting, it’s important to gather the necessary components in the inverter:
- Oscillator Circuit Components (555 Timer IC or a simple transistor-based oscillator): The oscillator is responsible for converting DC into a high-frequency AC signal. You can use a 555 timer IC to generate a square wave, or you can use a transistor circuit if you prefer.
- Transistors or MOSFETs: These are used to switch the current flow in the inverter circuit. They act as the key components to generate the alternating current (AC) waveform from the direct current (DC).
- Transformer: A transformer is used to step up or step down the voltage. In the case of a 12V DC input and a desired 120V AC output, you’ll need a step-up transformer. The transformer also helps in isolating the AC output from the DC input.
- Capacitors: Capacitors help filter and smooth the output waveform, reducing the ripple in the AC signal.
- Resistors: Resistors are used for biasing transistors and controlling current flow in the oscillator.
- Diodes: Diodes can be used for rectifying or preventing reverse current flow (e.g., flyback diodes across the transistors).
- Heat Sinks: Since the transistors will be switching at high frequencies and can generate heat, using heat sinks can help prevent damage to the components.
- 12V Battery (or DC Power Source): This is the source of direct current for your inverter circuit. You can use a 12V lead-acid battery or a suitable DC power supply.
- Output Socket: You’ll need a socket for connecting the AC-powered devices that will be used with the inverter.
Here is a basic process to build a small power inverter:
- Create an Oscillator Circuit: You can use an integrated circuit (IC) like the 555 timer or a square wave oscillator to produce the necessary alternating signal.
- Set Up Transistor Switching: Use transistors like MOSFETs to switch the DC power on and off rapidly, creating a pulsing current.
- Add a Transformer: The transformer changes the voltage to the desired level. For example, if you’re using a 12V DC battery and want 120V AC output, a step-up transformer will do the job.
- Rectify and Smooth the Output: After the transformer, use a diode-based rectifier and capacitor to smooth the waveform to reduce ripple.
- Test and Fine-Tune: Finally, test your inverter, and ensure that the output voltage and frequency are stable enough for the devices you plan to power.
What is the Difference Between a Power Inverter and a Power Converter?
Power Inverter is used to convert DC to AC. This is important for powering devices that require alternating current, such as household appliances and equipment connected to the electrical grid. However, power converter converts AC to DC. Converters are used when you need to charge batteries or power devices that require DC input, such as most electronics like laptops, cell phones, and LED lighting.
In short, the primary difference between an inverter and a converter lies in the type of current they handle. Inverters make DC usable for AC devices, while converters provide the DC required by many modern electronic devices.
What Do You Need a Power Inverter For?
Power inverters are important in the modern society. They are used in various applications, both in homes and businesses. They can be seen everywhere in our daily life, like:
- Off-Grid Power Systems: For people who live off the electrical grid, inverters are essential. Solar panels or wind turbines generate DC power, and an inverter converts it into AC for use in the home.
- Emergency Backup Power: In the event of a power outage, an inverter can provide backup power. The inverter converts power from batteries into AC electricity to keep critical systems running.
- Powering Electronics: Portable inverters are often used to power laptops, lights, and other small appliances from a car battery or portable power bank.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Inverters are also used in renewable energy installations to convert DC power generated from solar panels into the AC needed for homes or commercial use.

FAQs of Power Inverter Circuit
1. What Should You Not Plug Into an Inverter?
When using an inverter, avoid plugging in devices that draw too much power, especially when the inverter’s rating is not high enough. For example, large appliances like air conditioners, refrigerators, and microwaves require a lot of power and might overload the inverter, causing it to shut down or even damage the device.
2. What Does a Power Inverter Fuse Do?
A fuse in a power inverter acts as a safety device. If the inverter is overloaded or the current exceeds the maximum safe limit, the fuse blows, preventing damage to the internal components. It essentially protects the inverter from short circuits, excessive current, or other electrical faults.
3. Do Power Inverters Drain Your Battery?
Yes, power inverters do drain the battery because they require energy to operate. The rate at which the battery drains depends on the inverter’s load and the capacity of the battery. Inverters with higher power ratings will drain the battery faster than smaller inverters.
4. What Size Battery Do I Need to Run a 2000W Inverter?
To run a 2000W inverter, you need a battery with enough capacity to supply the necessary power. A 12V battery with at least 200Ah (amp-hours) would be required to run a 2000W inverter.
Tags: dc ac power inverter circuit, power inverter circuit, power inverter diagram circuit