What is an SMD Resistor?
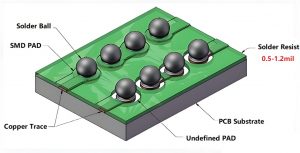
An SMD resistor is a surface-mounted component designed to limit current or divide voltage in electronic circuits, also known as Chip Fixed Resistor. It does the same job as a traditional resistor but without long leads. Instead, it sits directly on the PCB surface.
SMD stands for Surface-Mount Device. The SMD resistor is usually in a flat package form and can be welded directly to the surface of the circuit board without the need to be connected by a connector. It is suitable for high-density assembly applications.
Features of SMD Resistors
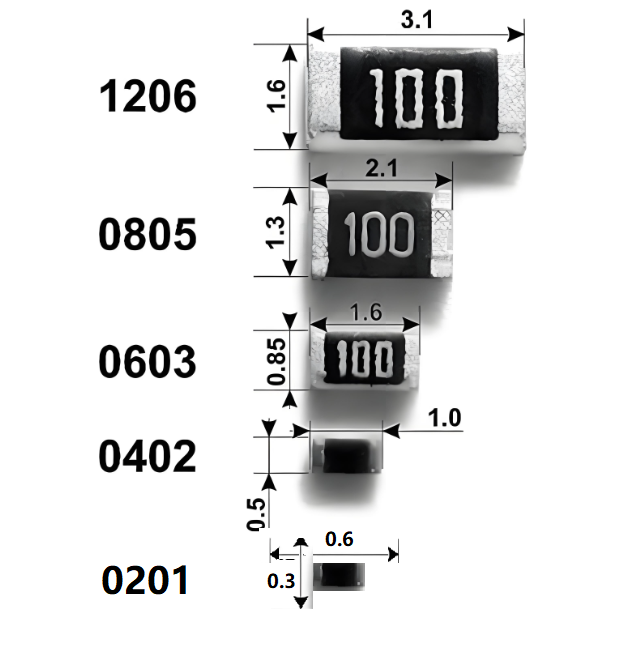
Dimensions: Usually expressed in 4 digits (imperial, unit: inches) or 2 digits + letters (metric, unit: millimeters). Common package sizes include 0201, 0402, 0603, 0805, 1206, etc.
Power rating: Based on 70°C ambient temperature, it needs to be derated in high temperature environments. For example, the power of a resistor in a 1206 package is 250mW at 100°C, and the actual available power needs to be reduced to 125mW.
Resistance range: The resistance range of conventional resistors is 1Ω to 10MΩ. Low-resistance resistors are often used for current detection, with typical values of 0.005Ω to 0.1Ω.
Accuracy: Common accuracy levels include ±5% (E24 series), ±1% (E96 series), ±0.5%, ±0.1% (high precision).
Temperature coefficient: The temperature coefficient of conventional thick film resistors is ±200ppm/°C to ±400ppm/°C, and the temperature coefficient of precision thin film resistors is ±25ppm/°C to ±50ppm/°C.
SMD Resistor Package Sizes Chart
The shapes and sizes of surface-mount resistors have been standardized, and most manufacturers follow JEDEC standards. SMD resistors are typically identified by numerical codes, such as 0603, which indicate the package’s length and width. For instance, the 0603 imperial code refers to a resistor that is 0.060 inches long and 0.030 inches wide.
SMD package codes can be given in either imperial or metric units. In general, imperial codes are more commonly used to describe package sizes. However, it can be confusing because even when imperial codes are used, the actual dimensions are often referred to in millimeters during the PCB design process. Below is a table of SMD resistor package sizes chart, listing the dimensions and specifications of commonly used SMD resistor packages.
| Imperial Code | Metric Code | Length (mm) | Width (mm) |
| 0201 | 0603 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| 0402 | 1005 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| 0603 | 1608 | 1.6 | 0.8 |
| 0805 | 2012 | 2.0 | 1.25 |
| 1206 | 3216 | 3.2 | 1.6 |
| 1210 | 3225 | 3.2 | 2.5 |
| 1812 | 4532 | 4.5 | 3.2 |
| 2010 | 5052 | 5.0 | 2.5 |
| 2512 | 6432 | 6.4 | 3.2 |
The smaller the code, the smaller the component. For example, 0201 resistors are tiny and used where space is limited, like in smartwatches or hearing aids.
What Do the Numbers on SMD Resistors Mean?
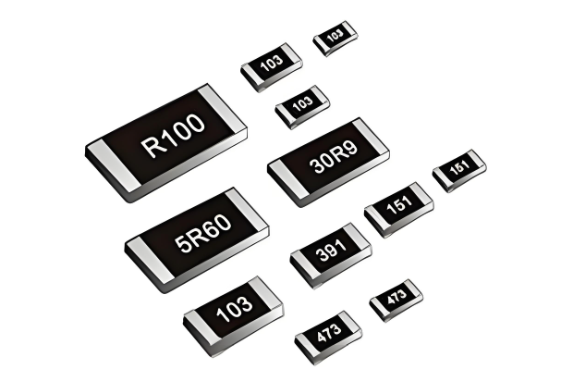
The numbers printed on an SMD resistor represent its resistance value. These markings follow a system called EIA-96 or 3-digit/4-digit code.
For the 3-digit system:
The first two digits are significant figures.
The third digit is the multiplier (number of zeros to add).
Example:
Code “472” means 47 * 100 = 4,700 ohms.

For the 4-digit system (used in precise resistors):
The first three digits are the base value.
The fourth is the multiplier.
Example:
Code “4702” means 470 * 100 = 47,000 ohms or 47kΩ.

How to Read SMD Resistor Code?
Reading the code on an SMD resistor might seem tricky at first. But once you understand the logic behind the numbers and letters, it becomes simple. SMD resistors don’t have color bands like traditional through-hole types. Instead, they use numbers—or sometimes numbers and letters—printed directly on the component. There are 4 ways to read the smd resistor values:
1. 3-Digit Code Format (Most Common)
This is the most widely used format for general-purpose SMD resistors. The first two digits represent significant figures, and the third digit is the multiplier (in powers of ten).
Example:
“472”
- First two digits: 47
- Third digit (multiplier): 2 → means 10² = 100
- So the resistance = 47 × 100 = 4700 ohms or 4.7kΩ
Another example:
“101” → 10 × 10¹ = 100 ohms
If you see a code like “220”, it’s 22 × 10⁰ = 22 ohms
2. 4-Digit Code Format (For Higher Accuracy Resistors)
This is used for resistors with tighter tolerance. The first three digits are significant figures, and the fourth digit is the multiplier.
Example:
“1001”
- First three digits: 100
- Fourth digit: 1 → 10¹ = 10
- Resistance = 100 × 10 = 1,000 ohms or 1kΩ
Another example:
“4702” → 470 × 100 = 47,000 ohms or 47kΩ
3. Codes with “R” (Used for Decimal Values)
When the resistance is below 10 ohms, the code often includes the letter “R” to indicate a decimal point.
Examples:
“4R7” → 4.7 ohms
“0R22” → 0.22 ohms
“R100” → 0.1 ohm

This format helps avoid confusion, as a simple “047” might be misunderstood. “R” clearly marks the decimal location.
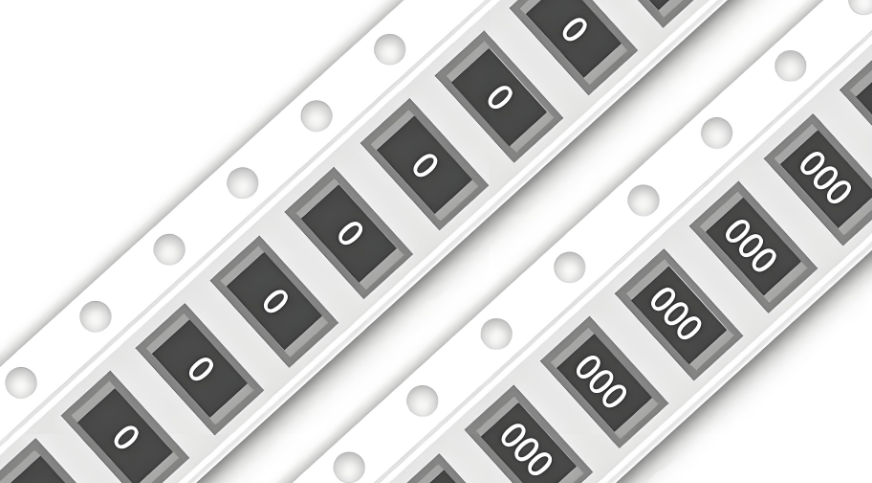
4. Zero Ohm Resistors
If you ever see a resistor labeled “000” or “0”, this is a zero-ohm jumper. It acts like a wire and is often used for PCB routing flexibility. There’s no resistance value to read—it’s simply a bridge.
0201 SMD Resistor Dimensions
The 0201 SMD resistor is one of the smallest types used today. It measures:
- Length: 0.6 mm
- Width: 0.3 mm
- Height: around 0.23 mm
Because of its tiny size, handling 0201 resistors requires advanced assembly machines and tight process control. These resistors are found in:
- Smart wearables
- High-end smartphones
- Advanced medical devices
Despite their size, they offer solid performance and accuracy when mounted correctly.
What is the Difference Between SMD and SMT Resistor?
Many confuse SMD with SMT. They are related but not the same:
- SMD (Surface Mount Device) refers to the actual component. A resistor, capacitor, diode—any small chip-shaped part.
- SMT (Surface Mount Technology) is the method used to attach these components to a PCB.
So, a SMD resistor is a type of part, while SMT is the process used to mount it. Think of it like this: SMD is the “what,” and SMT is the “how.”
In a factory, SMT lines are the equipment and process flow. SMD is what they’re working with. Both are key in modern electronics manufacturing.
SMD Resistor Applications and Benefits
SMD resistors are everywhere. Here are some common uses:
- Consumer electronics (phones, tablets, TVs)
- Automotive systems (ECUs, sensors)
- Industrial controls (inverters, PLCs)
- Medical devices (monitors, implants)
- Telecommunication Infrastructure (routers, switches, and base stations)
- Wearables and IoT Devices (Fitness trackers, smartwatches, and IoT sensors)
- Aerospace and Defense
The benefits are plenty:
- Compact size
- High reliability
- Excellent thermal stability
- Automated assembly
- Good frequency response
They help companies build faster, lighter, and smarter products. That’s why SMD resistors are chosen for both low-cost gadgets and mission-critical equipment.
SMD Components List
If you’re building or sourcing a full PCB, knowing common SMD components in electronics is better, here we listing the common smd components in the market:
| Component Type | Common Package Sizes | Description |
| Resistors | 0201, 0402, 0603, 0805, 1206 | Limits current, divides voltage, used in every circuit |
| Capacitors | 0402, 0603, 0805, 1210 | Stores and releases electrical energy, filters noise |
| Inductors | 0603, 0805, 1008 | Stores energy in magnetic fields, used in power circuits |
| Diodes | SOD-323, SOD-523, SMA, SMB | Controls current flow, used in protection and rectification |
| Zener Diodes | SOD-123, SOT-23 | Provides voltage regulation |
| Transistors | SOT-23, SOT-323, SOT-89 | Acts as switch or amplifier |
| MOSFETs | SOT-23, SOT-223 | High-efficiency switching in power circuits |
| LEDs | 0603, 0805, 1206 | Indicator or display lights |
| ICs (Chips) | SOIC, QFN, BGA, LGA | Logic processing, control units, memory, etc. |
| Oscillators / Crystals | 2.0×1.6mm, 3.2×2.5mm | Clock and timing devices |
| Connectors | DFN, LGA, micro USB, FPC | Electrical interface to other boards or cables |
| Sensors | LGA, QFN, DFN | Detect motion, temperature, light, humidity, etc. |
These parts work together to form the core of any electronics assembly. Choosing the right size and type is key for success.
Can Best Technology Mount 0201 SMD Resistors on PCB?
Absolutely! Best Technology is fully equipped to handle 0201 SMD resistor mounting. Our lines include:
- 6+ High-speed pick-and-place machines
- 3D SPI and AOI systems for inspection
- Nitrogen reflow ovens with precise profiling
- Cleanroom handling for micro-sized parts
- X-ray inspect machine to ensure the soldering quality
- Our minimum mounted package size is 01005
Whether you need a few PCBA samples or full production, we can meet your request. Our support includes layout reviews, DFM checks, and test plans. We’re proud to help customers push the limits of miniaturization.