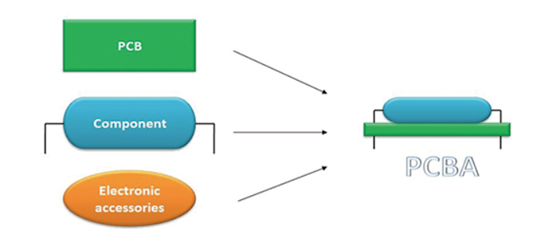
What Does the PCBA Stand For?
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly.
It’s a complete board where all parts are mounted and ready to work. The bare board itself is called a PCB. But once components like resistors, capacitors, and chips are soldered onto it, it becomes a PCBA. Sometimes, some electronic accessories will be soldered onto the PCB surface as well.
Key Components in PCBA
The value of a PCBA comes from the components it carries. Each part plays a role in how the circuit works. Let’s go over some of the most common parts:
- Resistors: Control the flow of current.
- Capacitors: Store and release energy when needed.
- Inductors: Manage signals, especially in filters.
- Diodes: Let current flow in one direction only.
- Transistors: Switch or amplify signals.
- ICs (Integrated Circuits): Small chips with many tiny parts inside. They perform complex functions.
- Connectors: Help connect the board with other systems.
- Transformers: Change voltage levels for safer or better operation.
All these parts must be carefully chosen and placed. A small mistake can stop the board from working right. That’s why design and assembly matter so much.
Types of PCBA Assembly Techniques
1. Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
This is the most common method today. Components are placed directly on the surface of the board. Pick and place machines handle most of the work, which keeps it fast and accurate. SMT supports miniaturized parts and high-speed production.
2. Through-Hole Technology (THT)
This technique uses components with leads that go through holes in the PCB. These leads are soldered on the other side. THT is strong and used for large or high-stress parts like connectors or transformers.
3. Mixed Technology Assembly
Some boards use both SMT and THT. Surface-mount parts go on first, then through-hole components are added by manually. This mix allows for flexible, compact, and reliable designs.
What is the difference in PCB and PCBA?
Though the terms PCB and PCBA are often used together, they describe very different stages in the electronics manufacturing process. And you must to know: PCB are one of important part of PCBA, but PCBA not. Below we listing the key differences between them:
| Factor | PCB | PCBA |
| Stage | Blank board | Assembled with components |
| Components | No | YES |
| Functionality | Non-functional | Fully operational |
| Manufacturing Cost | Low | Higher (because include the components cost) |
| Testing | Basic inspection | Complete electrical testing |
| Assembly Techniques | Not applicable | SMT, THT, or hybrid |
| Files Needed | Gerber, drill files | Gerber, BOM, pick & place, assembly files |
| Lead Time (under same design) | Short | Related longer than PCB |
What Is the Use of PCBA?
PCBAs are used in almost everything you see around:
- Phones: Control your screen, camera, and sound.
- Computers: Process data, run programs.
- Vehicles: Support GPS, safety features, engine control.
- Medical devices: Power equipment like MRI or ECG machines.
- Home appliances: From smart TVs to microwave ovens.
Without a PCBA, none of these would work. It’s like the brain of any electronic device. From simple tools to high-end gadgets, PCBA plays a big role.
How to Do PCBA Testing?
Testing makes sure the board works as expected. It helps catch issues before the board goes into the final product. There are several ways to test a PCBA:
1. Visual Inspection
This is the first step. Technicians or machines check if parts are in the right place. They also look for bad solder joints, cracks, or missing items.
2. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI mainly uses a camera system scans the board. It checks for incorrect or misaligned parts. It’s faster than manual inspection and works well for large batches.
3. In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
ICT checks each component directly. It makes sure resistors, capacitors, and connections work properly.
4. Functional Testing
This test powers the board and simulates how it will be used. It checks whether the PCBA can perform the expected tasks.
5. X-Ray Inspection
Used when components are hard to see, like BGAs (Ball Grid Arrays). The X-ray looks through the board to catch hidden problems.
6. Flying Probe Test
For small batches, probes test different points without a custom fixture. It’s flexible and cost-effective.
7. Testing with jig
This is used for mass production, jig tools are made according to the design files, so it is a customized. Jig testing can save much time compared with flying probe.
Best Technology deeply know the importance of the product quality, so we pay more attention to the PCB board quality checking process. We set a QC department according to ISO9001:2015 and ensure all processes are compliance with quality system.
How Do You Clean a PCBA?
During the PCB assembly process, cleaning a PCBA is an important step, especially after soldering. Residual flux, dust, or moisture can affect the performance of the board. Nowadays, the common cleaning methods used in Best Technology are:
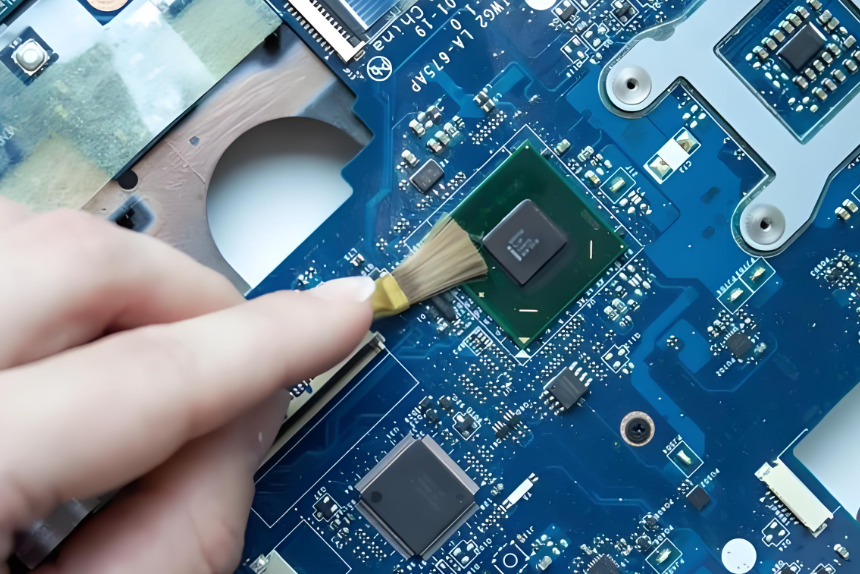
1. Manual Cleaning
This is the most basic method. A technician uses a soft anti-static brush and high-purity isopropyl alcohol to remove visible flux or dirt. It’s ideal for prototypes, small batches, or after rework or repair. Manual cleaning gives the operator control, especially in tight or delicate areas. However, it’s time-consuming and not suitable for large-scale production.
2. Ultrasonic Cleaning
Ultrasonic cleaning is widely used for complex boards and mass production. The PCBA is submerged in a tank filled with a cleaning solution. High-frequency sound waves pass through the liquid, creating microscopic bubbles. These bubbles collapse rapidly, producing a scrubbing action known as cavitation.
This technique reaches tiny gaps under components where brushes can’t go. It’s very effective for removing dried flux, fine dust, or ionic contamination. The process is gentle on components but powerful enough to clean even the most compact assemblies. After cleaning, the board is rinsed and dried with warm air or placed in a drying chamber.
3. Dry Ice Cleaning
Dry ice cleaning is a newer, eco-friendly technique. It uses solid CO₂ pellets, also called dry ice, blasted at high speed onto the PCBA surface. As the pellets hit, they turn into gas instantly. This process lifts off dirt, flux, and even adhesives without leaving moisture or residue behind.
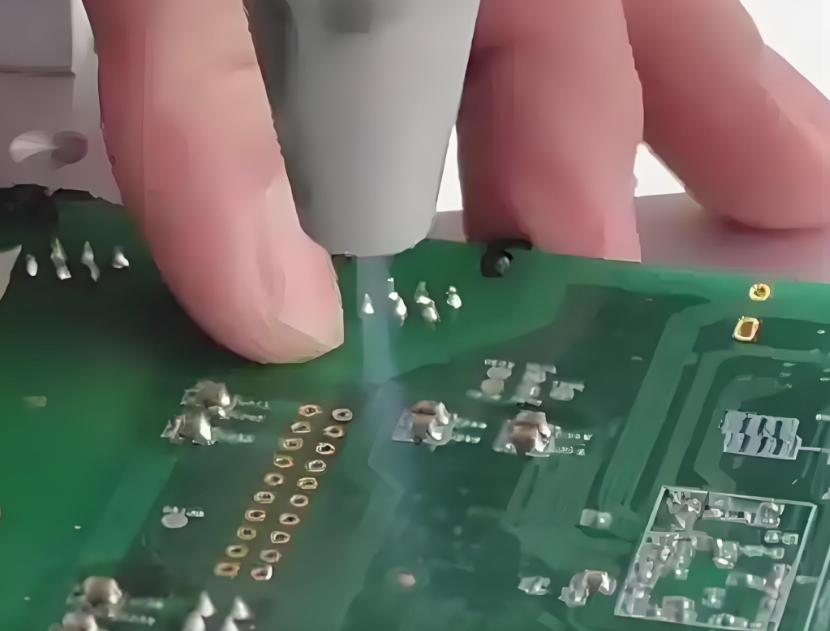
Dry ice cleaning works well for delicate electronics and is especially useful in industries where cleanliness must meet strict standards. To give customer a highest quality of the PCBA, our SMT factory equipped with the dry ice cleaning machine to ensure a clear surface while improve the efficiency.
PCBA Assembly Process
The PCBA assembly process is relatively simple than PCB manufacturing, actually the most tedious step is to load all the components on the pick and place machine, and set the program parameters. Here we break down all the processes of the mass production PCB assembly, from the solder paste printing to function testing.
1. Solder Paste Printing
First, solder paste is applied to the bare PCB. This paste is mainly consists of silver and tin, a mix of tiny solder particles and flux. A stencil is placed over the board, and the paste is spread across it using a squeegee. The paste sticks only to the exposed pads where components will be mounted.
2. Load components feeder
Load all the components in the feeder of the pick and place machines, make sure all the parameter of components are correct, and double check the direction of chips. It is a simple but tedious step and need much time to check everything is okay.
2. Pick and Place
After applying solder paste, automated pick-and-place machines begin placing surface-mount components onto the board. These machines work fast and accurately. They follow a file created during PCB design that tells them the exact location for each part. The components sit on the solder paste, which holds them in place temporarily.
3. Reflow Soldering
Next, the assembled board goes through a reflow oven. The oven slowly heats the board in stages. When it reaches a high enough temperature, the solder paste melts and forms strong electrical and mechanical connections between the parts and the board. After this, the board cools down, and the solder solidifies.
This step is only for SMT components. If the board has only through-hole parts, this step may be skipped.
4. Inspection (AOI and Visual)
Once the soldering is done, the board goes through inspection. Automatic Optical Inspection (AOI) machines scan the board using high-resolution cameras. They check for misaligned parts, soldering problems, or missing components. For small production or sensitive areas, manual inspection is also performed to catch anything machines might miss.
5. Through-Hole Component Insertion (If Needed)
If the board uses through-hole technology (THT), this is when those parts are added. Workers or machines insert the components into the holes, and the leads go through to the other side of the board. These components are often bulkier, like connectors or transformers.
6. Wave Soldering (For THT)
For boards with many through-hole parts, wave soldering is used. The board passes over a wave of molten solder that touches the underside. This solders all the leads at once. It’s fast and effective, especially for high-volume production. For small-scale or sensitive boards, hand soldering might be used instead.
7. Final Inspection and Quality Control
After soldering, the entire board is checked again. Technicians or AOI machines inspect the final assembly. They look for cold joints, excess solder, or misplaced parts. Boards may also be tested with X-ray machines to inspect solder joints under BGAs or hidden areas.
8. Functional Testing (FCT)
The next step is functional testing. The board is powered up and tested to make sure it works correctly. This could include checking voltages, signals, response times, and communication with other devices. Engineers may use test jigs or test programs based on the end application.
9. Cleaning (If Needed)
After all soldering and testing, the board might be cleaned to remove flux residue. Depending on the flux used, this could be manual, ultrasonic, or dry ice cleaning. Clean boards are especially important in high-reliability fields like aerospace, automotive, or medical.
10. Conformal Coating or Protection (Optional)
For some applications, a conformal coating is applied. This is a protective layer that shields the board from moisture, dust, and chemicals. It’s often used in harsh environments. Coating can be applied by spraying, dipping, or brushing.
11. Packaging and Shipping
Finally, once the PCBA passes all checks, it’s packed carefully. Anti-static bags, foam, and trays protect it during transport. Labels are added for tracking and traceability. From here, it’s ready to be installed into the final product. Here is a whole process of pcb assembly in Best Technology.
PCBA HS Code
Every product for trade needs a code. The HS code for PCBA usually is 8517799000
But depending on the use or market, some customs may use a different classification. For example:
853400 for bare board parts, sometimes be used on certain assembled parts.
847330 for boards used in computers.
853710 for board which used as controller or controller unit.
Noted: Always check with your country’s customs for the right code. Using the wrong one may cause delays or extra costs.
Our PCBA Services
At Best Technology, we specialize in end-to-end PCBA services. From design to delivery, we support your project with speed, quality, and reliability. We can be your first choice because:
- We have 18+ years in PCB industry
- One-Stop Service: PCB fabrication, parts sourcing, SMT/THT assembly, testing
- Custom Solutions: From prototypes to mass production, no MOQ
- Skilled Engineers: For DFM & DFA checks and process optimization
- Strict Quality Control: 9-times QC check, including AOI, X-ray, ICT, and functional testing
- Global Delivery: Fast and on time, wherever you are
- Component Sourcing: Only original, trusted parts, we have cooperated with digikey, findchips, mouser for over 10 years, and we can get the most competitive price from them.
- PCB Fabrication: Rigid, flex, metal-core, ceramic, and more.
Whether you’re working on a simple control board or a multi-layer high-speed system, we’re here to support you.
Tags: meaning of pcba, PCBA, pcba process









