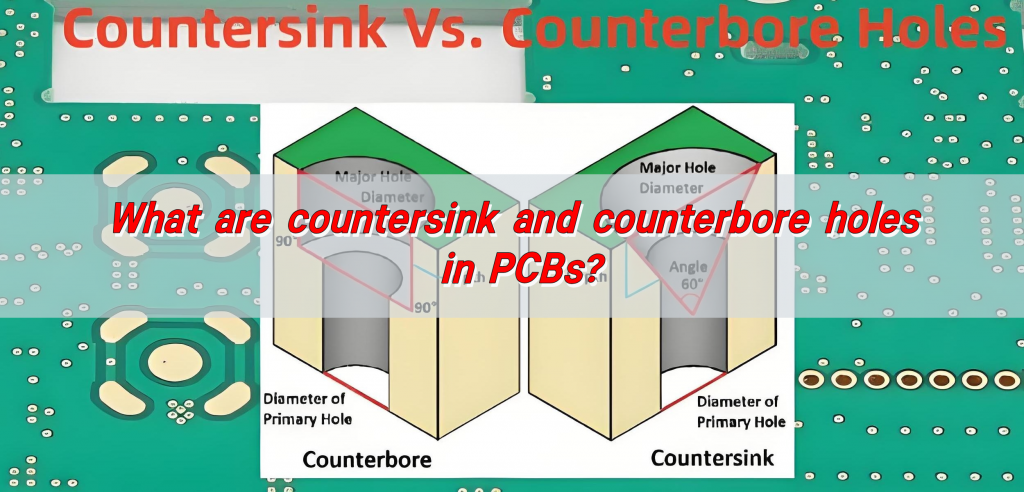
Countersink holes and counterbore holes are two special hole types used to install fasteners on PCBs. Countersink holes are tapered holes, usually used to make flat head screws flush with the PCB surface after installation, and their hole walls are at an angle of 82° to 90° to the PCB surface. Countersink holes are stepped holes with straight walls and flat bottoms, used to install hexagon socket screws or other fasteners that require more head space.
What is a counterbore in a PCB?
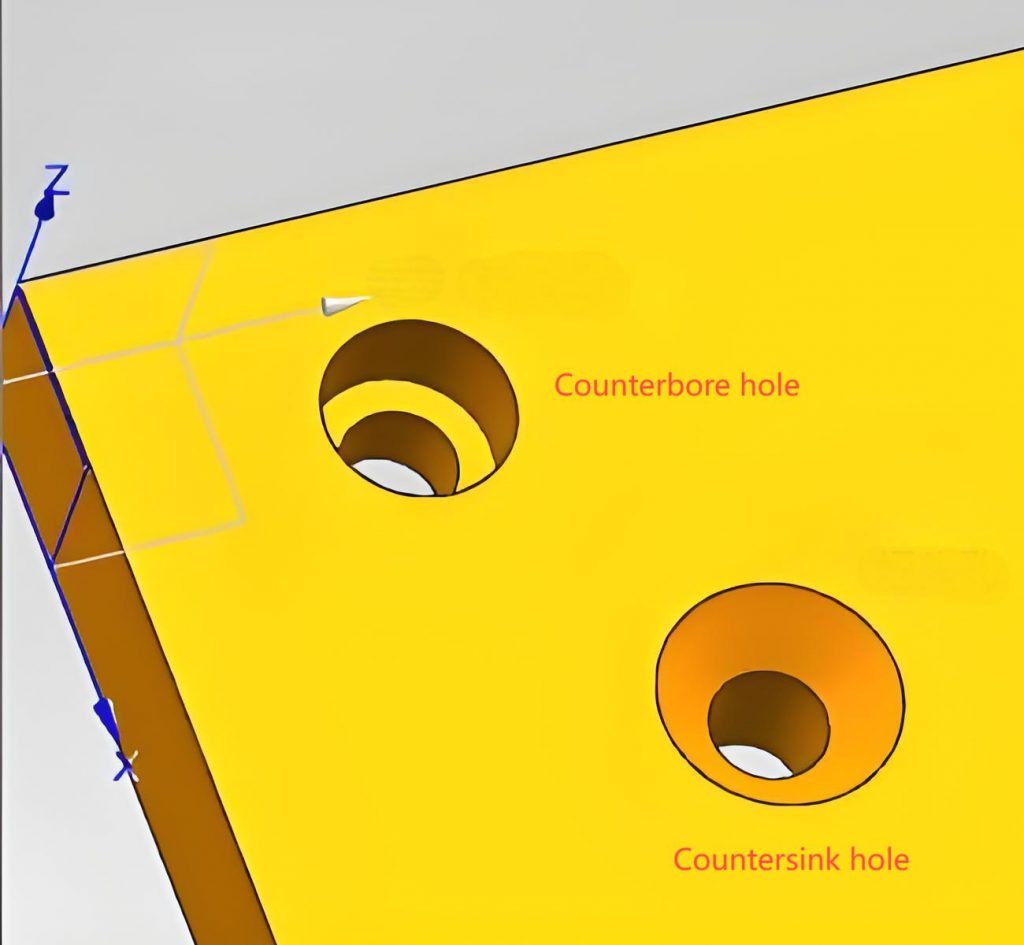
A counterbore is a cylindrical hole with a wider top section, allowing screw heads to sit flush or below the PCB surface. The hole consists of two distinct diameters: one for the screw head and a smaller one for the shaft. This design prevents protrusions that could interfere with other components or enclosures.
Counterbore holes are commonly used in applications that require strong and stable fastenings, such as industrial control systems, automotive electronics, and aerospace circuits.
What are countersink holes on PCBs?
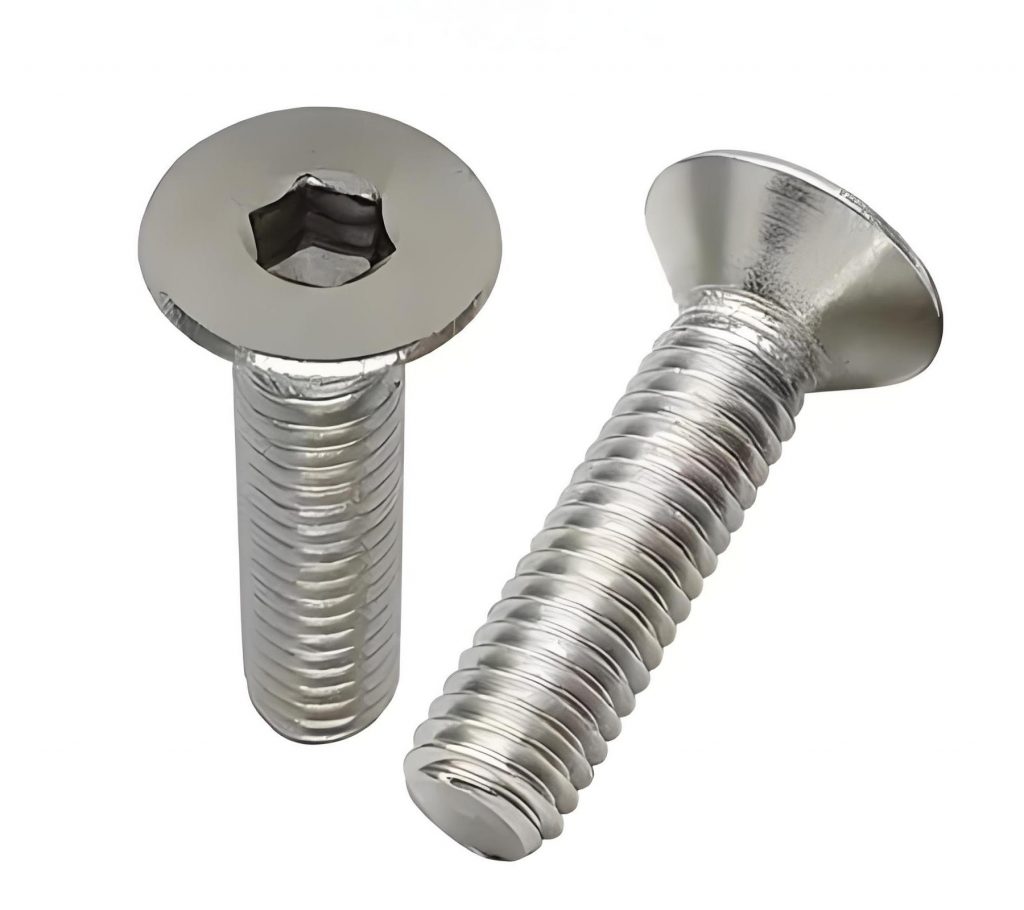
A countersink hole is a conical recess that accommodates flat-head screws, ensuring they sit flush with the PCB surface. The angled design allows screws to fit seamlessly, eliminating protrusions that could affect assembly.
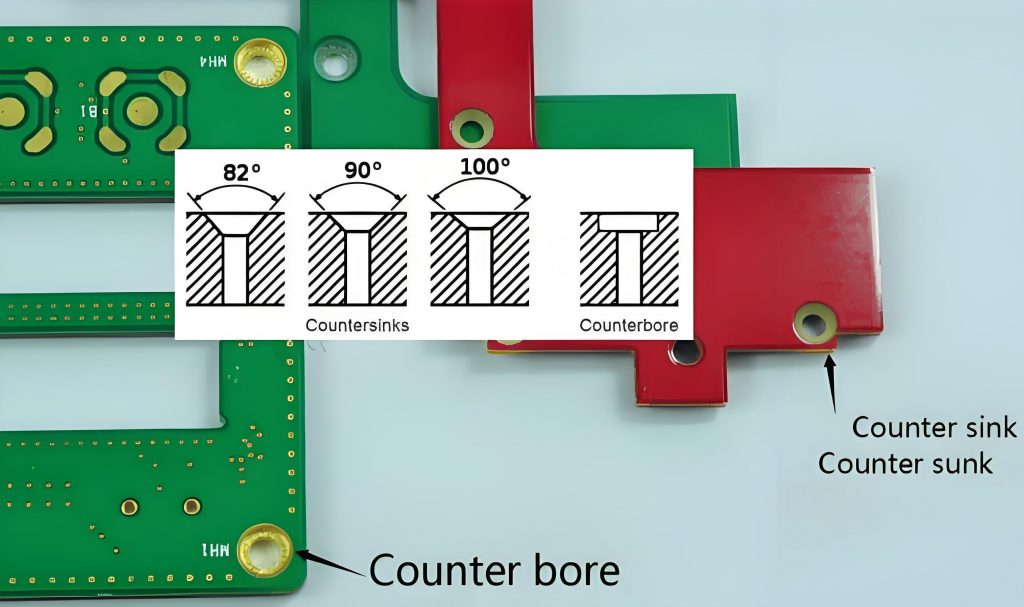
Common countersink angles include 82, 90, and 100 degrees, depending on the type of screw used.
Countersink holes are ideal for applications where a smooth, unobtrusive surface is needed, such as consumer electronics and compact PCB enclosures.
When should counterbore be used?
Counterbore holes are recommended when:
- A strong and stable connection is necessary.
- The screw head needs to sit flush or below the PCB surface.
- There is limited space in an enclosure, preventing protruding fasteners.
- A secure fastening method is required for high-vibration environments.
This hole type is often found in high-reliability electronic applications, where mechanical stability is crucial.
What is the symbol for a counterbore?
In PCB design and engineering drawings, a counterbore hole is represented by a square symbol. This notation indicates the diameter and depth of the counterbore, ensuring accurate drilling during manufacturing.
For example, if a drawing includes “â10 â´ 5,” it means the counterbore hole has a 10mm diameter with a 5mm depth.
What are the advantages of a counterbore?
Counterbore holes offer several benefits, making them an essential feature in many PCB designs:
- They provide a flat surface for fastening, preventing interference.
- They enhance mechanical stability by ensuring a secure connection.
- They support strong fasteners, reducing the risk of loosening due to vibration.
- They improve assembly efficiency, making installation easier.
Many industrial and high-power electronic systems rely on counterbore holes for stable and long-lasting performance.
What is the purpose of a counterbore?
The primary purpose of a counterbore is to allow screws or bolts to sit flush with or below the PCB surface. This prevents fastener heads from interfering with other components and ensures a smooth, stable assembly.
Counterbore holes are commonly used in applications requiring precise alignment, structural support, and secure mounting in high-vibration environments.
What is the difference between a counterbore and a countersink?
Although both counterbore and countersink holes serve the purpose of accommodating fasteners, they have distinct differences.
- A counterbore has a flat-bottomed, cylindrical recess, designed for socket head screws and cap screws. It provides a strong and stable hold.
- A countersink has a conical shape, designed for flat-head screws. It ensures the screw sits flush with the PCB surface for a smooth finish.
The choice between these two depends on the type of screw used and the design requirements of the PCB.
When should a countersink be used?
Countersink holes are ideal when:
- A smooth, flush surface is required.
- Flat-head screws are used in the assembly.
- The PCB is mounted in a housing where protruding screws could cause issues.
- Aesthetic considerations are important, such as in consumer electronics.
Smartphones, tablets, and other compact devices often utilize countersink holes for a clean, streamlined appearance.
What is the disadvantage of a countersink?
While countersink holes offer a sleek design, they also come with certain drawbacks:
- They reduce PCB thickness, potentially weakening the board.
- They limit screw selection since only flat-head screws fit correctly.
- They require precise drilling to ensure proper screw alignment.
If a countersink hole is not manufactured correctly, the screw may not sit flush, affecting the overall assembly quality.
Conclusion:
Countersink and counterbore holes play a crucial role in PCB design, ensuring secure fastenings and smooth assemblies. Counterbore holes provide a strong, stable hold for socket head screws, while countersink holes allow flat-head screws to sit flush for a sleek finish.
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we deliver high-precision PCB fabrication with expert hole-drilling techniques for optimal performance. Need customized PCB solutions? Contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com
Tags: counterbore, counterbore holes, countersunk