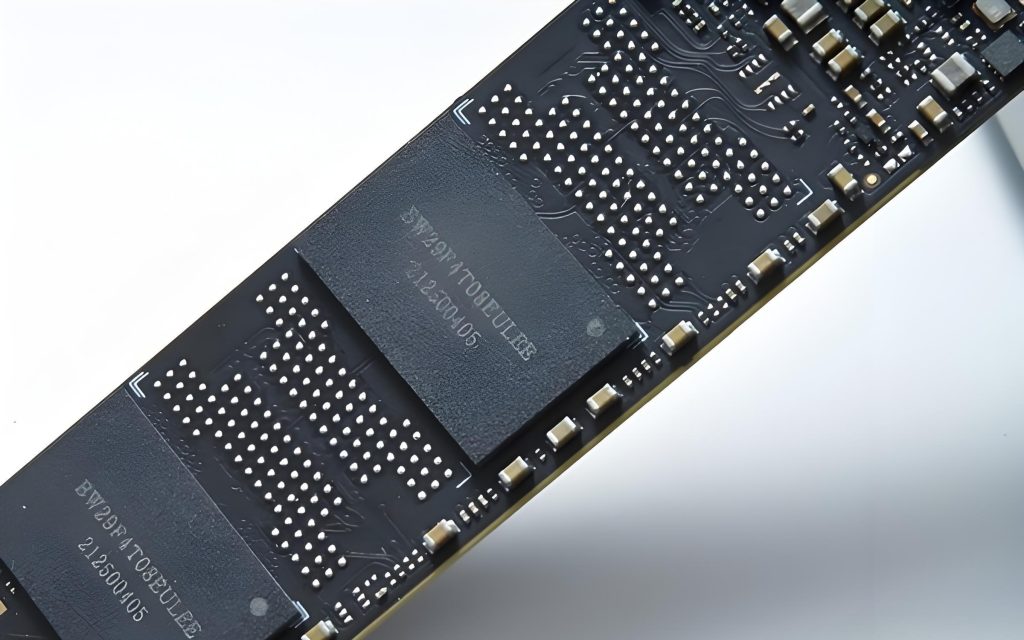
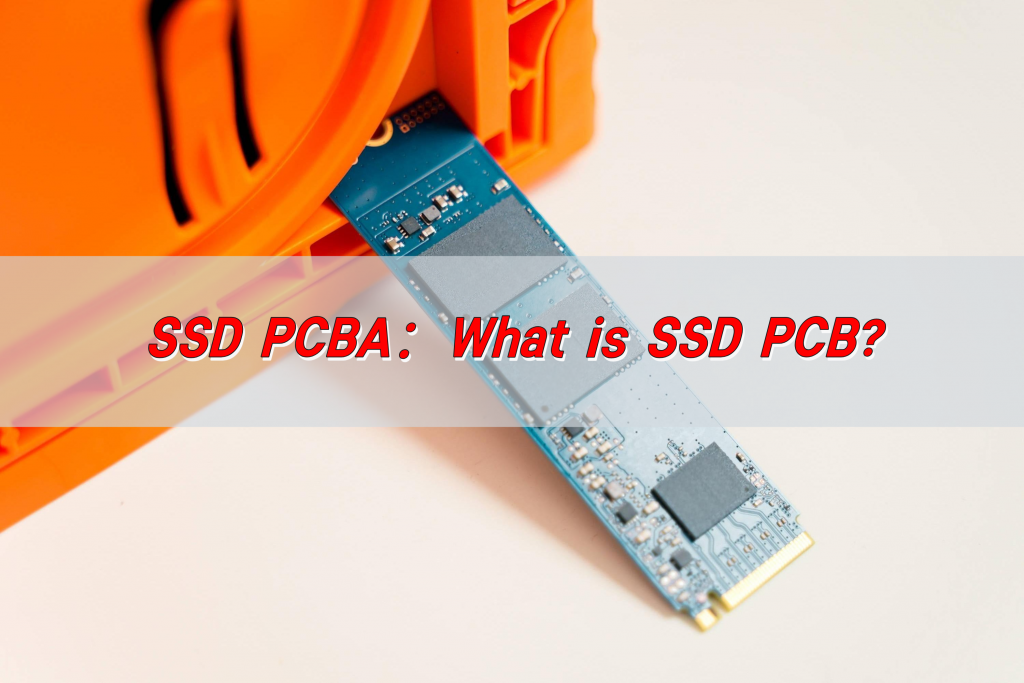
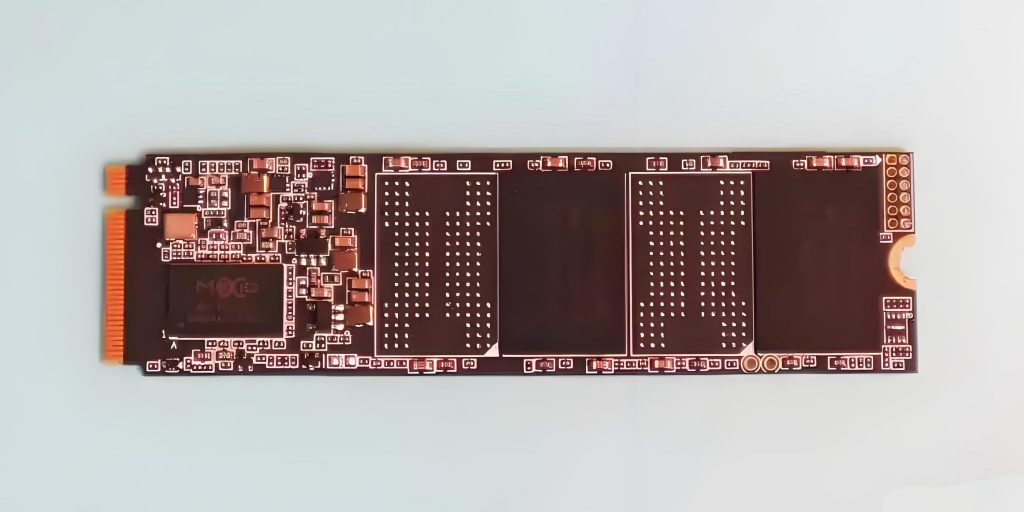
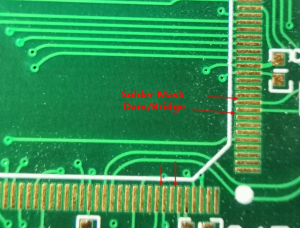
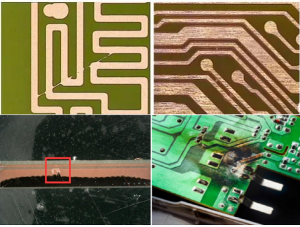
SSD PCBA refers to the process of soldering electronic components to the PCB of a solid-state drive through SMT or DIP processes to form a circuit board assembly with specific functions. It includes components such as controllers, flash memory chips, capacitors, resistors, etc., which are used to realize functions such as data storage, read and write operations, and transmission.
What is SSD PCB?
An SSD PCB is the circuit board where all the critical components of an SSD are mounted. It is designed to provide electrical connections between NAND flash memory chips, the SSD controller, voltage regulators, and capacitors.
The quality and design of the PCB impact the SSDÔÇÖs speed, power consumption, and lifespan. High-quality materials and precise manufacturing processes are crucial in ensuring the reliability and durability of an SSD.
Different types of SSDs have varying PCB designs, optimized for form factors such as M.2, SATA, and PCIe NVMe SSDs. Each form factor has a specific PCB layout to accommodate the required components while maintaining efficiency. For instance, M.2 SSDs use compact PCBs that allow them to fit into ultra-thin laptops and high-performance desktops.
What is SSD in semiconductor?
An SSD is fundamentally a semiconductor-based storage device that uses NAND flash memory instead of spinning disks. In semiconductor technology, SSDs consist of multiple layers of NAND memory cells fabricated on silicon wafers.
These memory cells store data electronically and retain it even when power is turned off. The semiconductor industry has continuously innovated SSD technology, introducing 3D NAND to increase storage density and reliability.
Unlike mechanical hard drives, SSDs have no moving parts, making them more resistant to shock and vibration. The advancement of semiconductor technology has enabled higher-capacity SSDs with faster read/write speeds, reduced power consumption, and longer lifespans.
What does SSD mean in manufacturing?
In manufacturing, SSD production involves PCB assembly (PCBA), NAND memory integration, controller programming, and rigorous testing.
SSD manufacturing begins with designing and fabricating the PCB, ensuring it meets industry standards for high-speed data processing.
During PCB assembly (PCBA), components such as the SSD controller, DRAM cache, and NAND flash chips are mounted onto the board using Surface Mount Technology (SMT).
Advanced SMT processes ensure precise placement, strong solder joints, and minimal defects. After assembly, firmware is loaded onto the SSD controller, enabling it to manage data transfer and error correction.
The final stage includes extensive testing and quality control, where SSDs undergo thermal, electrical, and performance tests to ensure they meet durability and speed requirements.
How to assemble SSD PCB?
Assembling an SSD PCB requires multiple steps, integrating semiconductor chips, power management circuits, and high-speed interfaces onto a compact board.
- PCB Fabrication: The process begins with manufacturing a high-quality PCB, typically made from multilayer FR4 or high-frequency materials.
- Component Placement: Using automated SMT machines, components such as NAND flash memory, SSD controllers, and capacitors are precisely placed onto the board.
- Soldering and Reflow Process: After placement, the board undergoes a reflow soldering process, where it is heated to secure the components.
- Firmware Installation: Once assembled, the SSD controller is programmed with firmware to optimize data processing, wear leveling, and error correction.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Each SSD undergoes performance testing, including stress tests, endurance tests, and data integrity checks to ensure reliability.
What are the three types of SSDs?
SSDs are categorized based on form factors and interfaces, determining their speed, compatibility, and application.
- SATA SSDs: These SSDs use the Serial ATA (SATA) interface, offering speeds up to 600MB/s. They are commonly found in older laptops and desktops.
- NVMe SSDs: Utilizing the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface, NVMe SSDs provide significantly faster speeds, reaching up to 7,000MB/s in high-end models.
- M.2 SSDs: Designed for compact spaces, M.2 SSDs come in both SATA and NVMe variants, making them ideal for ultrabooks, gaming PCs, and high-performance systems.
Each type has distinct advantages, with NVMe SSDs being the fastest and most efficient, while SATA SSDs remain a cost-effective choice for general storage.
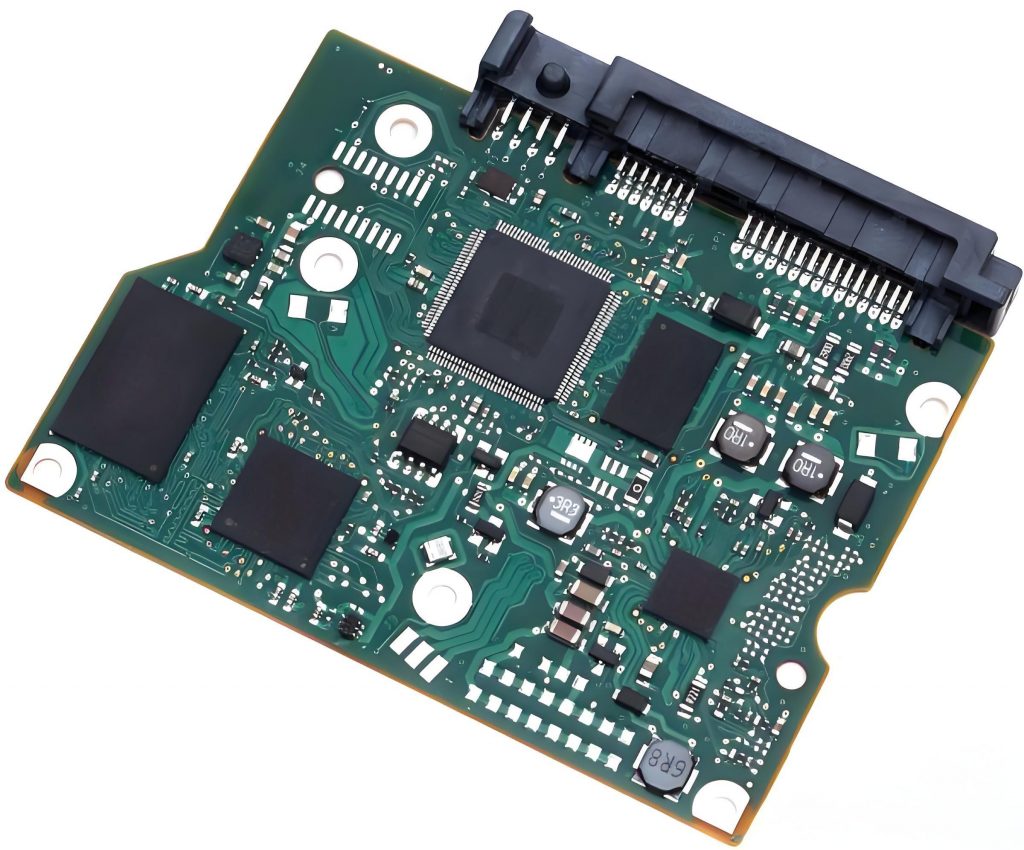
SSD PCB vs HDD PCB, what are their differences´╝č
There are many differences between SSD PCB (solid state drive printed circuit board) and HDD PCB (mechanical hard disk printed circuit board), as follows:
The main control chip on the SSD PCB is responsible for managing and transmitting data, the flash memory chip is used to store data, and some have cache chips for accelerated reading and writing. The main control chip on the HDD PCB is responsible for data transmission and instruction processing, the motor drive chip controls the rotation of the disk and the movement of the head, and the cache chip temporarily stores data.
Common interfaces of SSD include SATA, M.2, PCI-E, U.2, etc. HDD generally uses SATA or SAS interface.
In order to achieve high-speed data transmission, the wiring requirements of SSD PCB are strict, and precise impedance control and signal integrity design are required. Multilayer boards are often used. HDD PCB wiring is relatively simple, and the focus is on connecting components such as heads, motors and main control chips to ensure data transmission and the operation of mechanical components.
SSD does not have high-power components such as motors, and the overall power consumption is low. The power management circuit only needs to provide a stable voltage for the chip. HDD needs to provide a large drive current for the motor to ensure disk rotation and head seek, and the power management circuit is more complex.
SSDs come in a variety of sizes, including 2.5-inch and M.2. HDDs are usually 3.5-inch or 2.5-inch.
SSDs have no mechanical parts and are highly shock-resistant, but flash memory chips have wear and power-off data loss problems, and wear leveling and other technologies are needed to improve reliability. HDD mechanical parts are susceptible to vibration and collision, causing the head to scratch the disk or motor failure, and protection circuits such as vibration sensors are often designed on the PCB.
What is a PCB in a computer?
A PCB in a computer is the fundamental electronic platform that connects components like the processor, memory, storage, and expansion cards. The most critical PCB in a computer is the motherboard, which serves as the communication hub between all internal hardware.
SSDs have their dedicated PCBs for managing data storage, but other PCBs in a computer include graphics card PCBs, power supply PCBs, and network adapter PCBs. Each PCB is designed to ensure seamless operation and efficient power management.
What are the advantages of SSD PCB?
The use of high-quality SSD PCBs offers numerous benefits:
- Faster Data Processing: SSD PCBs are optimized for high-speed memory access, allowing for quick boot times and fast application loading.
- Lower Power Consumption: Compared to HDDs, SSDs consume less energy, making them ideal for laptops and battery-powered devices.
- Durability and Shock Resistance: With no moving parts, SSDs are resistant to physical shocks, reducing failure rates and improving reliability.
- Compact Design: SSD PCBs are designed for smaller form factors, enabling them to fit into ultra-thin devices without compromising performance.
What are the disadvantages of SSD?
Despite their advantages, SSDs have some limitations to consider:
- Higher Cost per GB: SSDs are generally more expensive than HDDs, especially for higher storage capacities.
- Limited Write Cycles: NAND flash memory has a finite number of write cycles, leading to wear over time.
- Data Recovery Challenges: Unlike HDDs, data recovery from a failed SSD is more complex, requiring specialized tools and expertise.
Conclusion´╝Ü
SSD PCBs play a vital role in modern data storage, offering high-speed performance, reliability, and efficiency.
For high-quality SSD PCB manufacturing and assembly, Best Technology offers cutting-edge solutions tailored to your needs. Contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com for expert guidance and customized SSD PCB solutions.