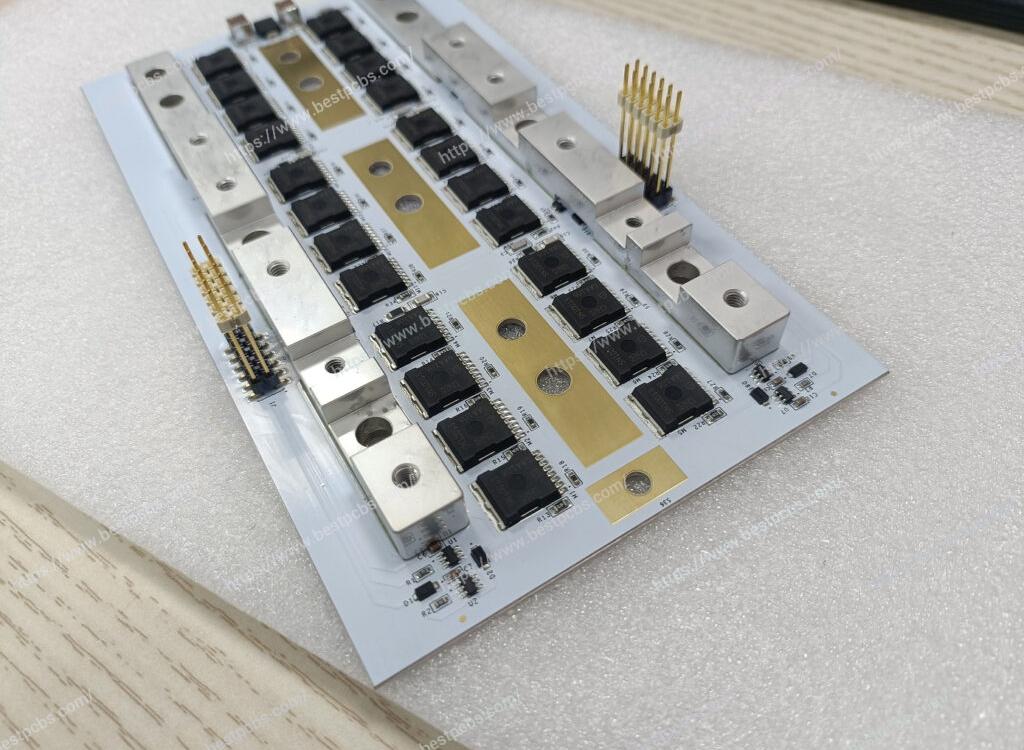
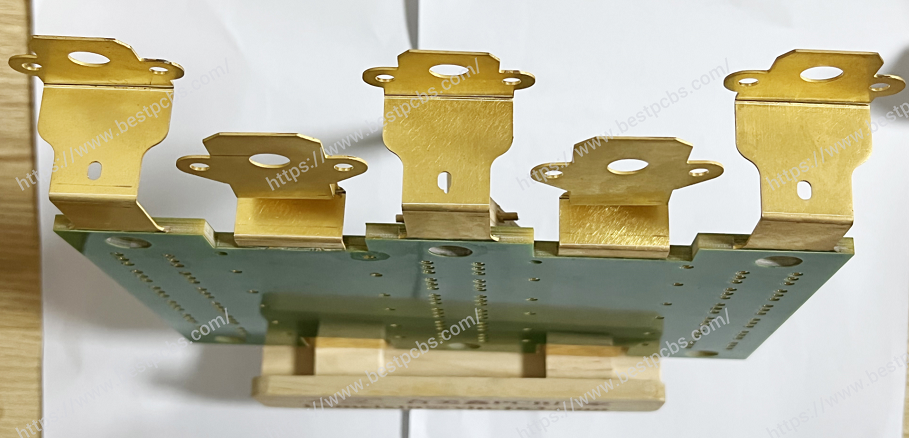
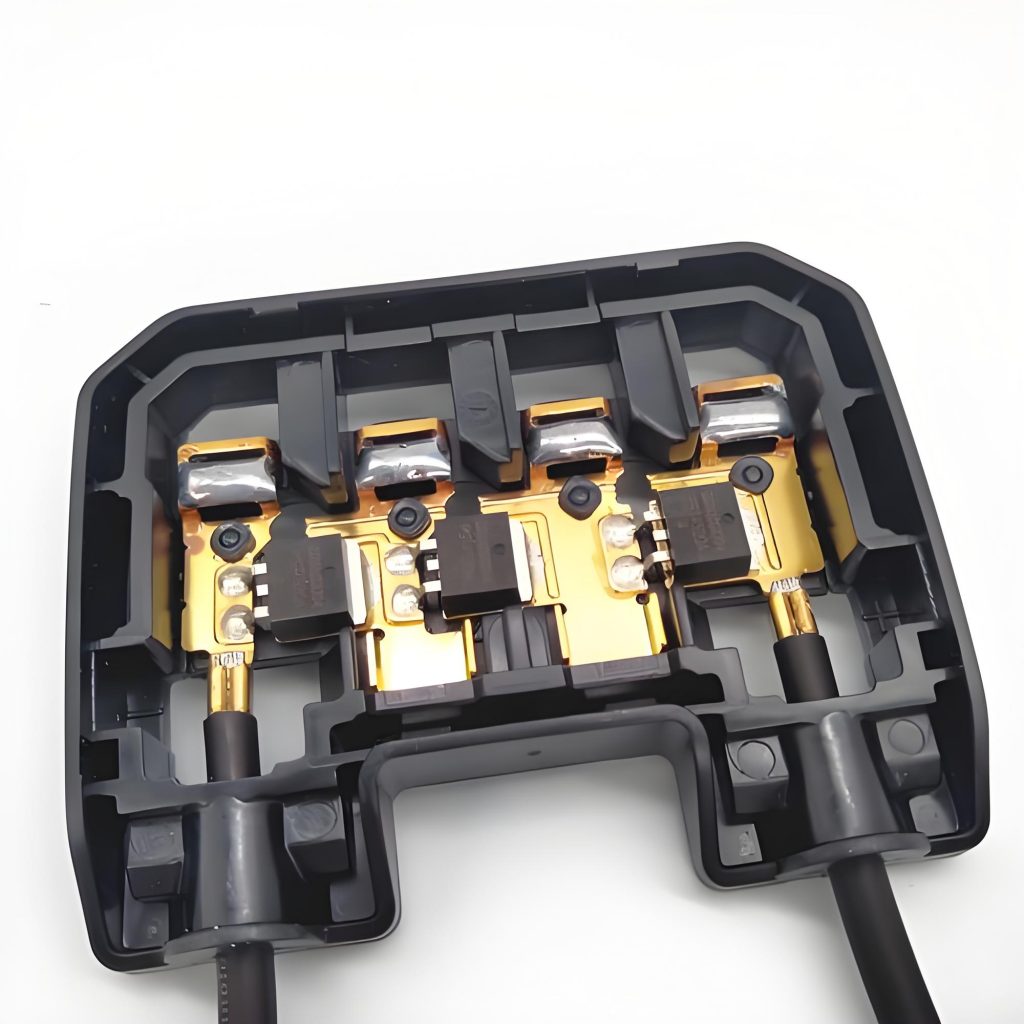
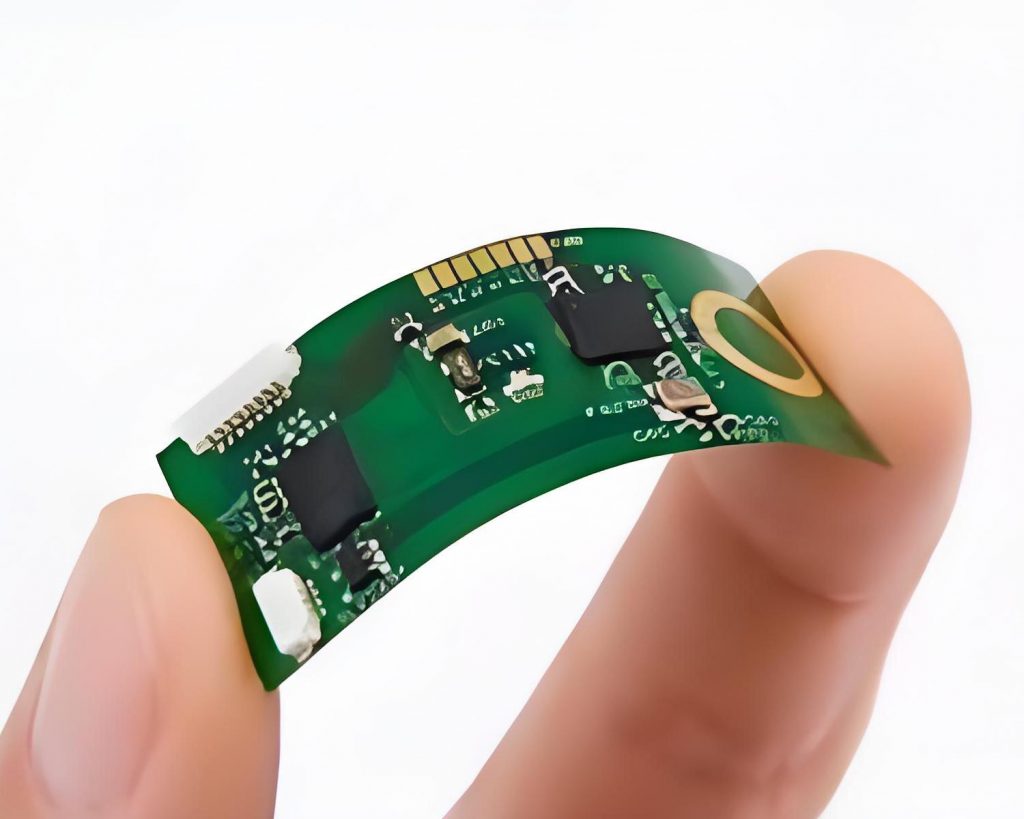
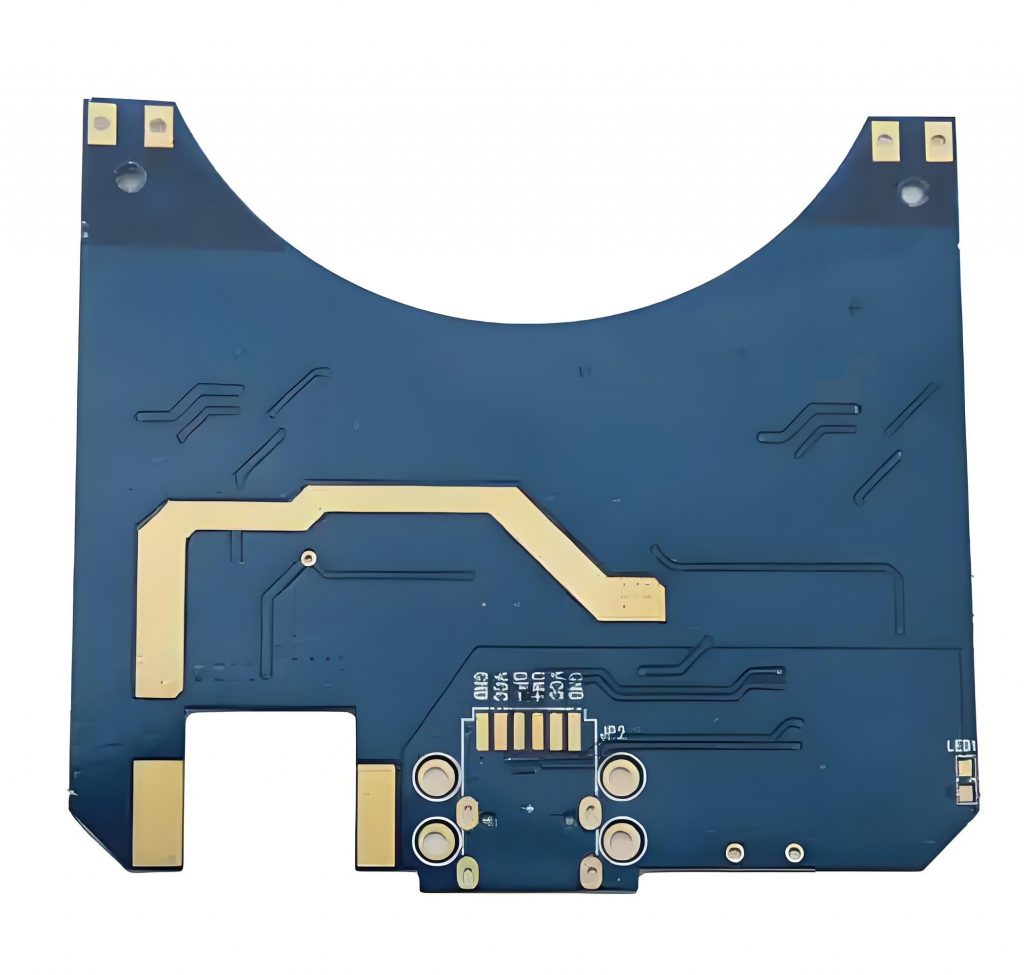
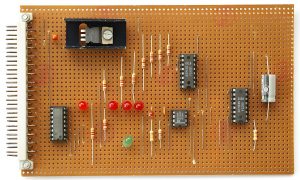
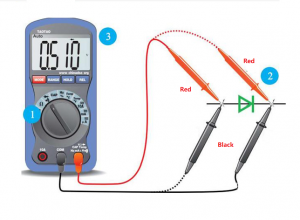
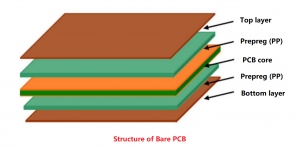
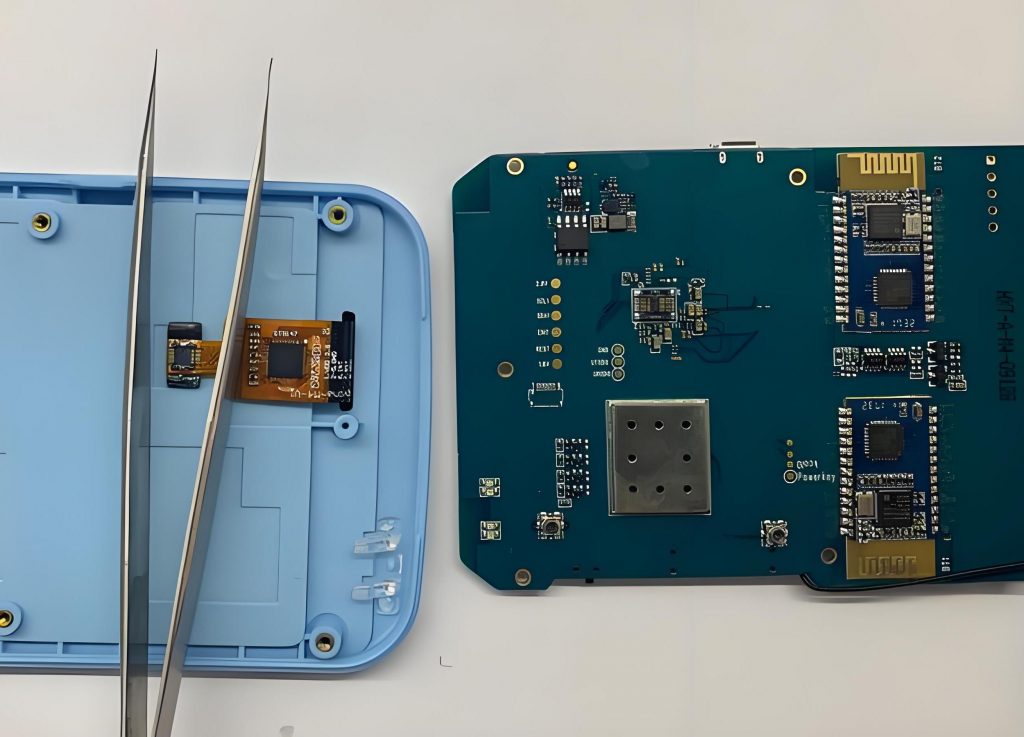
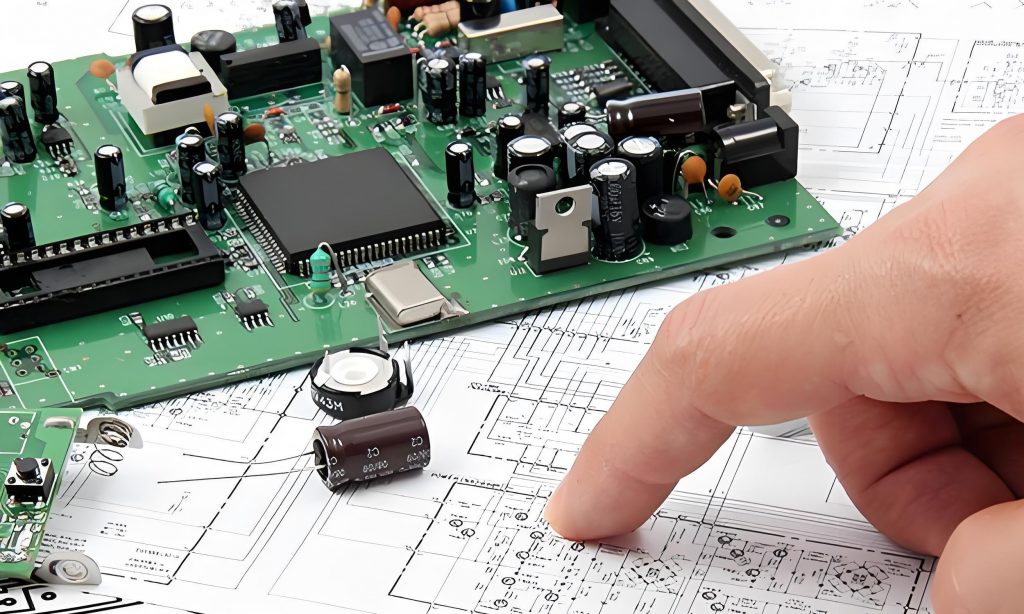
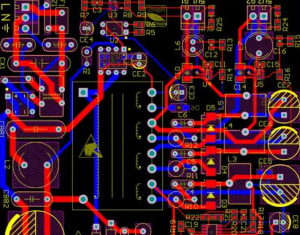
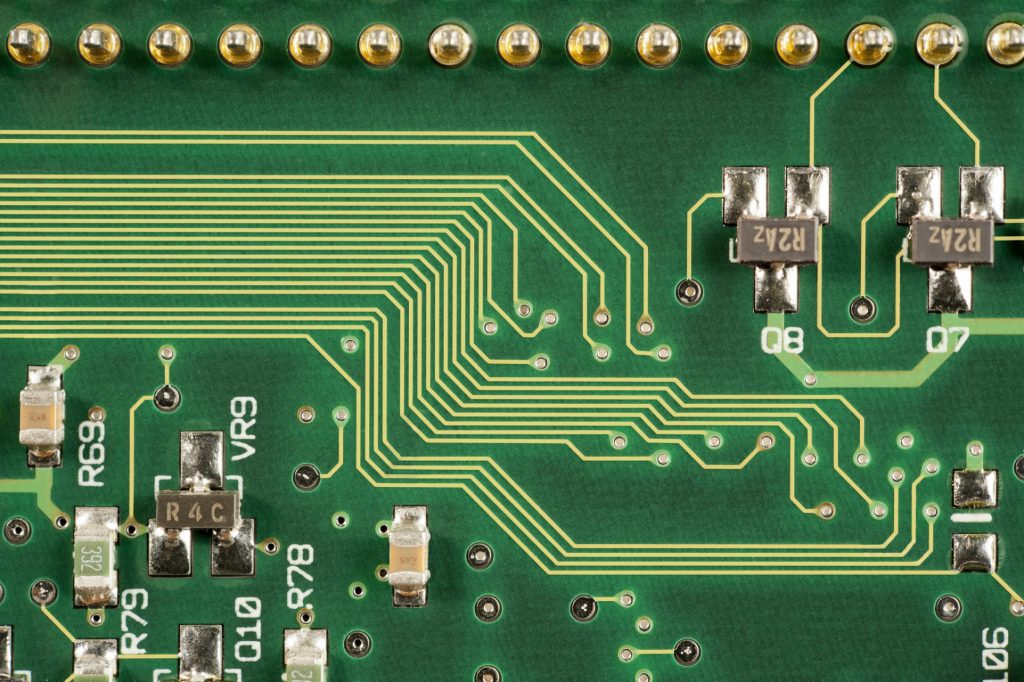
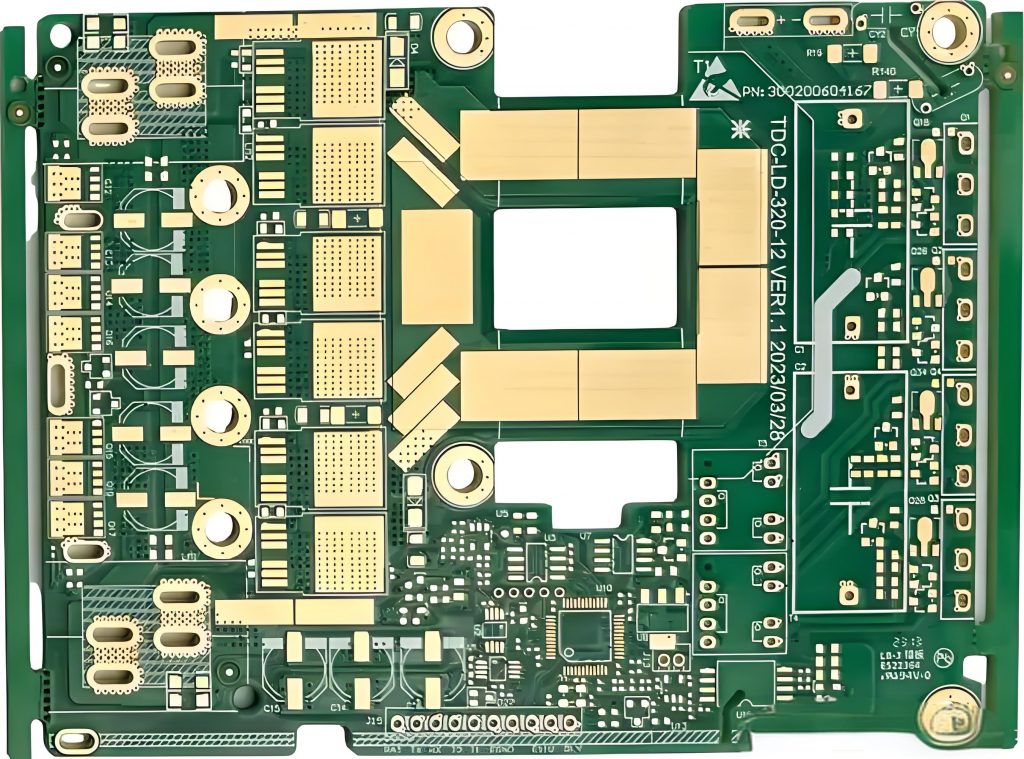
What is PCB prototyping? PCB prototype is a preliminary printed circuit board sample made according to the circuit design. It is used to realize the basic functions of the circuit and perform functional testing and verification. It usually adopts a rapid production method and has a relatively simple appearance and structure.
What is PCB Prototyping?
PCB prototyping is the process of creating a preliminary model of a PCB to test its functionality and design before mass production. This step is essential in electronics development, helping engineers and manufacturers identify and address design flaws early on.
Prototyping allows for the evaluation of components, circuits, and connections in a controlled setting. It ensures that the final PCB design performs as intended, saving time and reducing costs associated with errors.
What is the Point of Prototyping?
Prototyping serves as a safety net in the PCB manufacturing process. By creating a prototype:
- Flaws are identified early: It prevents costly errors in large-scale production.
- Design validation: Ensures that the circuit works as expected.
- Component testing: Verifies compatibility and performance of components.
- Cost efficiency: Saves resources by addressing issues before production.
This process bridges the gap between theoretical design and practical application, reducing risks.
Why Prototype Circuits Before Making a PCB?
Testing circuits before creating a PCB is vital. It allows:
- Performance Evaluation: Determines how circuits function under real-world conditions.
- Optimization: Refines layouts to improve performance and reliability.
- Debugging: Identifies and fixes potential electrical issues.
- Risk Mitigation: Ensures the design meets safety and compliance standards.
By prototyping, you ensure a smooth transition from design to final product.
How to Make PCB Prototyping?
The process of PCB prototyping includes several steps:
- Design Creation: Use a PCB design tool like Altium Designer or KiCAD.
- Material Selection: Choose materials suitable for your application.
- Schematic Development: Draw circuit diagrams and plan connections.
- Layout Design: Arrange components on the PCB for optimal performance.
- Fabrication: Manufacture the prototype using a reliable service.
- Testing: Test the prototype to identify and resolve any issues.
Each step is crucial to ensure the prototype meets your requirements.
How to Use a PCB Prototype Board?
A PCB prototype board is a platform for testing and validating designs. To use it effectively:
- Prepare the schematic: Transfer the design to the board.
- Assemble components: Place components in the designated positions.
- Connect traces: Solder the components and complete the circuit.
- Test functionality: Verify the board’s performance.
Prototype boards simplify the testing process, allowing for quick adjustments.
How Do Prototype PCBs Work?
Prototype PCBs work as functional testbeds for new designs. They replicate the final product but are made with less expensive materials and simpler processes. Engineers use them to:
- Test circuit connectivity.
- Assess signal integrity.
- Verify design specifications.
Successful prototypes pave the way for full-scale production.
What is the Best PCB Design Tool?
Choosing the right PCB design tool is key to successful prototyping. Popular options include:
- Altium Designer: Comprehensive and professional.
- KiCAD: Open-source and user-friendly.
- Eagle: Widely used with extensive libraries.
- OrCAD: Robust for complex designs.
Select a tool that matches your project’s complexity and budget.
How Much Does a PCB Prototype Cost?
The cost of a PCB prototype depends on several factors:
- Size and complexity: Larger and more complex designs cost more.
- Material choice: High-quality materials increase costs.
- Turnaround time: Faster delivery options come at a premium.
- Quantity: Small batches are often more expensive per unit.
On average, costs range from $50 to several hundred dollars per board.
What is the difference between PCB prototype and breadboard?
| Feature | PCB Prototype | Breadboard |
| Durability | Long-lasting | Temporary |
| Performance | High performance, precise connections | Limited to basic circuits |
| Customization | Fully customizable | Restricted by design |
| Applications | Suitable for production testing | Ideal for initial testing |
While breadboards are ideal for early experiments, PCB prototypes are essential for final design validation.
Why Choose Us as Your PCB Manufacturer?
At Best Technology, we excel in providing comprehensive PCB prototyping and manufacturing solutions. With over 18 years of experience, we ensure:
- High-quality fabrication: Advanced techniques for superior results.
- Customization options: Tailored designs to meet your needs.
- Quick turnaround: Rapid prototyping to keep your project on track.
- Global presence: Facilities in China, Vietnam, and the US.
Our team is dedicated to turning your ideas into reality. For expert PCB prototype services, contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com
Conclusion:
PCB prototyping is a crucial step in electronics design. It ensures accuracy, performance, and reliability, saving time and costs. For top-tier PCB prototype fabrication services, reach out to sales@bestpcbs.com today. Let us help you bring your ideas to life.