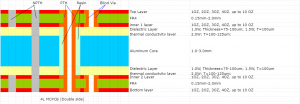
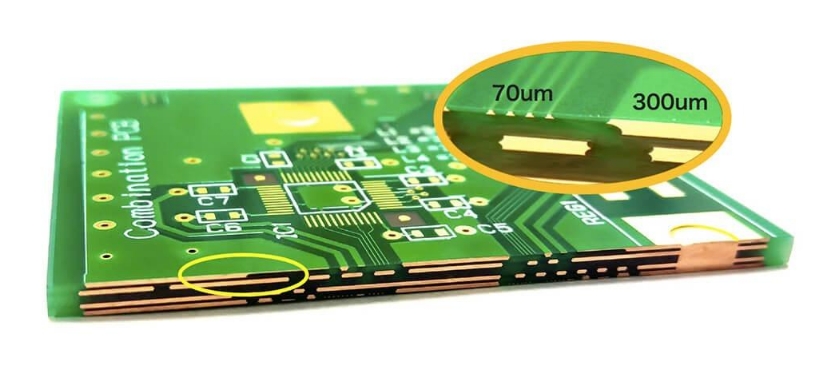
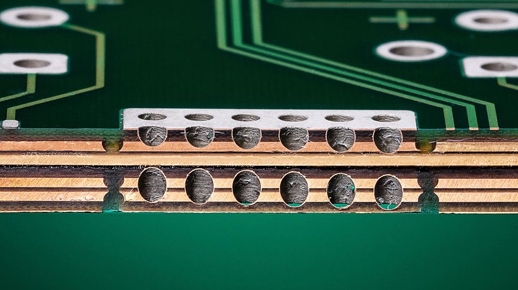
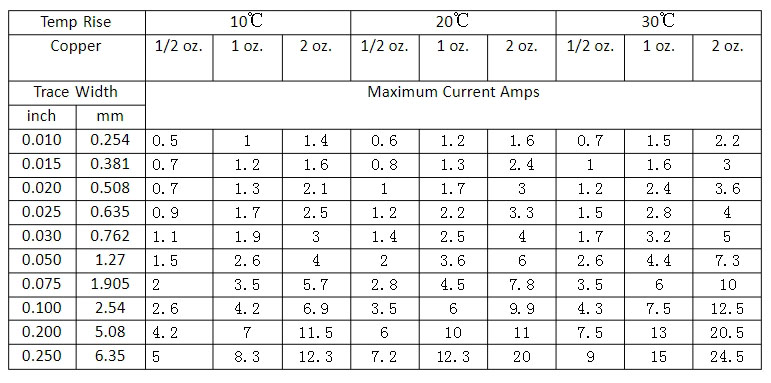
Relays in power systems are important components that play a vital role in controlling circuits. The core of a relay is an electric switch that can automatically or manually open or close a circuit according to the design. Relays are commonly used in a variety of applications, from small electronic devices to large power systems, and they provide a reliable way to control high-power circuits using low-power signals.
What is relay?
Relay refers to a transfer device in a circuit that controls the switch through the electromagnetic principle to achieve the purpose of automatic control. In power systems, relays can control the switch of circuits by detecting changes in parameters such as current and voltage to achieve protection and control of the system.
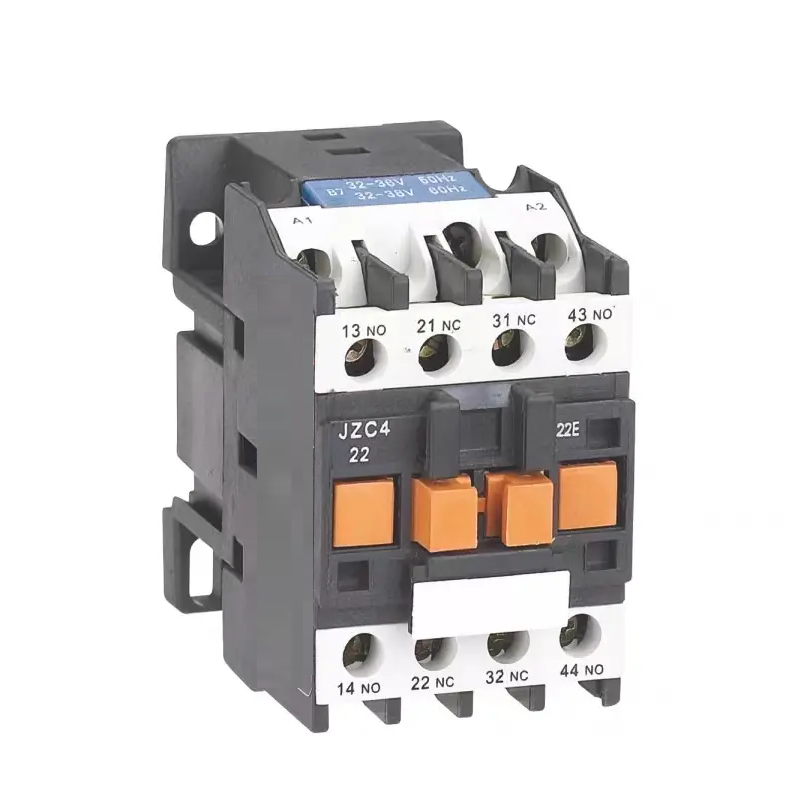

The basic working principle of a relay is to use the electromagnetic effect to control the on and off of mechanical contacts. When the coil with an iron core is energized, the coil current generates a magnetic field, which attracts the armature to move, thereby opening and closing the contacts.
Why would you need a relay?
The reasons for needing a relay mainly include safety isolation, remote control, timing or delay control, protection equipment, signal conversion, etc.
1. Safety isolation: When a low-voltage device (such as a microcontroller or sensor) is used to control a high-voltage device, the relay can act as an isolation layer to ensure safe operation.
2. Remote control: When a device needs to be controlled at a longer distance or in a longer environment, the relay can transmit and amplify the signal to achieve remote control.
3. Timing or delay control: When a device needs to be started or shut down at a specific time or after a delay, the relay can achieve timing or delay control.
4. Protective device: As a protective device, the relay can prevent the device from being affected by faults such as overload and short circuit.
5. Signal conversion: When one signal needs to be converted to another, the relay can perform signal conversion, such as converting an analog signal to a digital signal, or converting a wireless signal to a wired signal.
In addition, relays have the advantages of high reliability, long life, and low power consumption, which can improve the safety and stability of the equipment. Therefore, relays are indispensable and important components in automated control circuits, remote control, telemetry, communication, automatic control, mechatronics and power electronic equipment.
What is the main function of a relay?
The main functions of relays include amplifying signals, realizing remote control, protecting circuits, realizing logical control and improving system reliability and stability.
Amplifying signals: Relays can convert weak control signals into stronger control signals. Because the contact capacity of relays is large, they can control loads with large currents and high voltages.
Remote control: Through input signals, relays can control the switch state of load equipment at a distance and realize the function of remote control.

Protect circuit: Relays have overload protection and short-circuit protection functions. When abnormal conditions occur in the circuit, such as overload, short circuit, etc., the relay can automatically cut off the power supply to prevent the fault from expanding and protect the safety of circuits and equipment.
Realize logical control: Relays can realize complex logical control through multiple sets of normally open and normally closed contacts, and are widely used in automation control systems, industrial control and other fields.
Improve the reliability and stability of the system : Relays have high stability and reliability, which can reduce the failure rate in the system and improve the stability and reliability of the entire system.
In addition, relays also have isolation functions, which can protect the control circuit from the influence of the external environment and prevent electric shock accidents, which is very useful in some occasions with high safety requirements.
What is the difference between a switch and a relay?
Switches and relays have significant differences in function, application, structure and usage scenarios.
1. Function and application
Switches are mainly used to connect and disconnect circuits, while relays are mainly used to control the on and off of circuits to achieve protection and control of circuits.
Switches can be regarded as a basic electrical component used to simply connect or disconnect circuits, while relays control the on and off of large currents by controlling small currents in the circuit to achieve remote control or automatic control.
2. Structure and design
The contacts of switches may be small and are generally used to control small currents. In contrast, the contact switches of relays are larger and can be used to drive larger loads.
Contactors generally have arc extinguishing devices, while relays do not. This shows that relays and switches are different in design and application. Relays are more suitable for use in control circuits, while switches are used in main circuits.
3. Use scenarios
Switches are usually used to directly control the on and off of the main circuit, such as motor start-up, shutdown control, etc. Relays are more used in auxiliary circuits, such as the on and off of the control circuit, or after power is on or off, the on and off of the circuit is controlled by the change of position state, or the output node is given to other circuits.
Although switches and relays both play important roles in electrical systems, they have obvious differences in design, function and purpose. Switches are mainly used for simple circuit on and off operations, while relays are more used for the protection and control of control circuits, controlling the on and off of large currents by small currents, and realizing remote control or automatic control.
What is a relay vs fuse?
Fuses and relays play different roles in automotive circuits and have obvious differences.
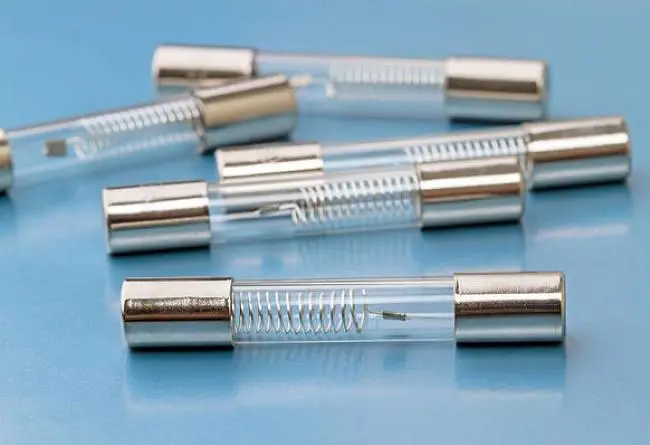

Fuse is a non-resettable one-time thermal protection device, mainly used for overload protection. When a circuit fails or is abnormal, the current continues to increase. The increased current may damage some important components in the circuit, burn the circuit, or even cause a fire.
The function of the fuse is to disconnect the power supply of the electrical equipment on the vehicle when a short circuit or overload occurs, so as to protect other electrical appliances and lines.
The relay is an automatic control device. When the input (electricity, magnetism, sound, light, heat) reaches a certain value, the output will change in a jump-like manner. Relays are mainly used for overload protection. They control larger currents with smaller currents, and play the role of automatic adjustment, safety protection, and circuit conversion.
The working principle of the relay is to generate a magnetic field through the electromagnet coil, magnetize the iron core, attract it to the magnetic pole of the electromagnet, and then drive the contacts to close or open, so as to realize the switch control of the circuit.
In short, the function of the fuse is to cut off the current automatically when the current abnormally rises to a certain height and heats up, so as to protect the safe operation of the circuit; while the relay protects the circuit and electrical equipment from the influence of overload, short circuit and other faults by controlling the circuit, and at the same time improves the reliability of the circuit operation.
Conclusion:
As technology continues to evolve, relays become more sophisticated and in a world where the demand for power is increasing and the need for reliable power systems is more important than ever, relays will continue to play a vital role in ensuring our power systems remain safe, efficient, and more.