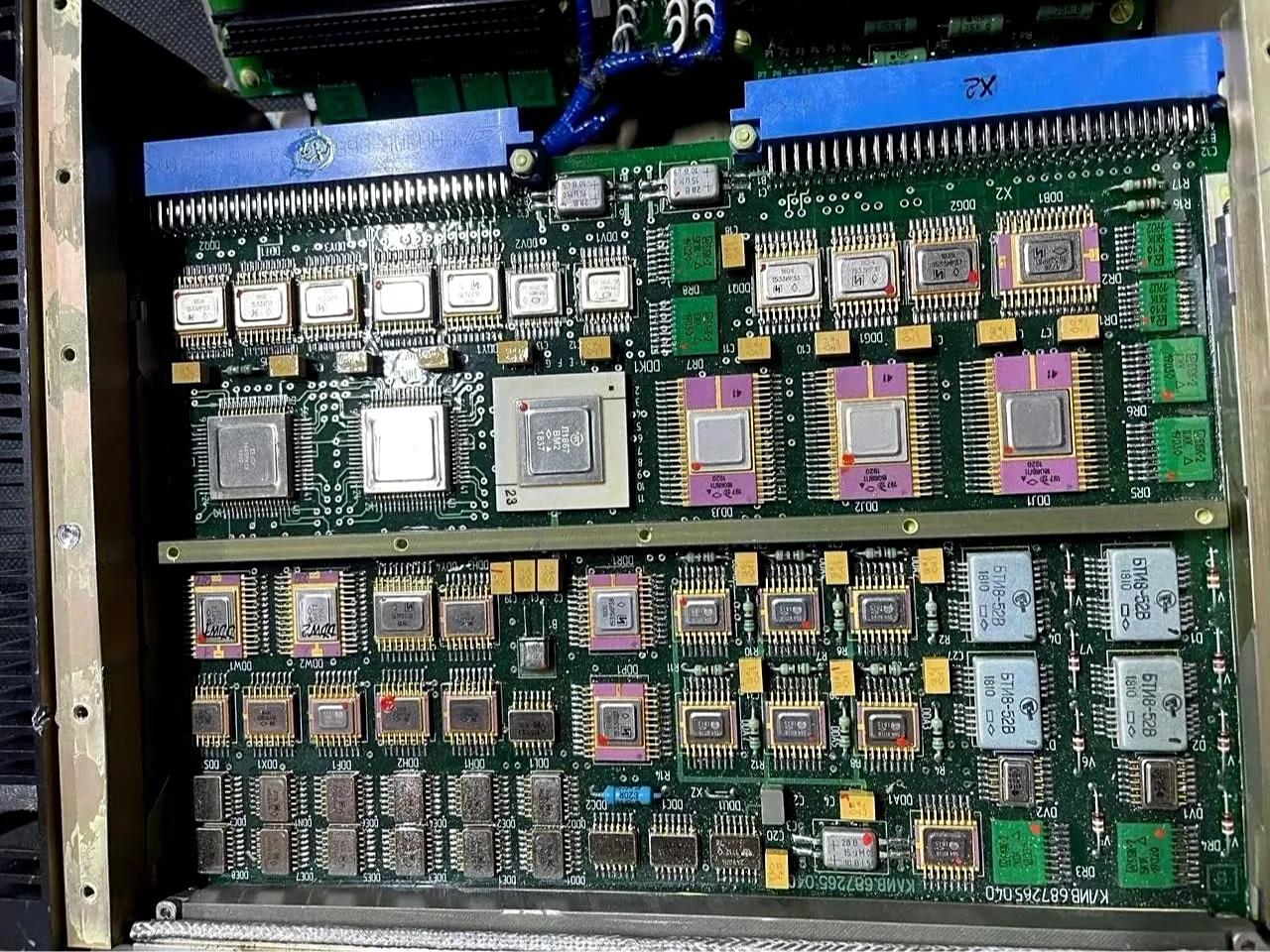
PCB assembly Germany stands out as a premier choice for anyone seeking reliable, precise electronic assembly services. Germany’s globally renowned engineering precision and attention to detail shine through in its PCB assembly sector, combining cutting-edge technology, rigorous quality standards, and streamlined workflows to deliver consistent, high-reliability results.
If you’re searching for a trusted cross-border PCB assembly Germany partner, this guide is tailored specifically for you. We’ve curated all the essential information you need, including the best manufacturers, key certification checks, lead time breakdowns, cost insights, and real-world FAQs sourced directly from online communities like Reddit eliminating the guesswork from your search.

Top 10 PCB Assembly Manufacturer in Germany
| Company Name | Main Business | Advantages | Assembly Capability | Lead Time |
| EBest Circuit Co., Limited | Global leader in PCB Assembly Germany offering one-stop services for industrial control, medical devices, automotive, and communication equipment. | Free DFM collaborative design; end-to-end one-stop delivery; compliance pre-audits; 19+ years of experience; no MOQ; personalized support for prototypes and small-to-medium batches. | SMT, THT, mixed and BGA assembly (0.4mm pitch); FR4, multi-layer, MCPCBs, ceramic, rigid-flex PCBs; monthly production 28,900„é°; FUJI SMT mounters, 3D X-RAY, 3D SPI. | Standard: 5‚Äď7 working days; Urgent prototypes: 24‚Äď48 hours; Urgent small batches: 3‚Äď4 working days |
| Eurocircuits | Established provider with facilities in Germany, India, Hungary; specializes in prototype/small-series PCB assembly with in-house fabrication serving 20,000+ customers in 60+ countries. | Free online DFM/DFT, 3D review, BOM/CPL validation tools; 440,000+ validated components; ‘pooling’ panel service; local European manufacturing with shorter lead times, data protection, low carbon footprint. | 2‚Äď16 layer PCBs (HDI, impedance control, RF, semi-flex, metal substrate); SMT/THT assembly, BGA (0.4mm+ pitch); 8+ SMD lines; IPC-A-600/610 Class 2; MOQ 1 piece. | Bare PCB prototypes: 3‚Äď5 working days; Total assembly (prototype): 6‚Äď17 working days; Standard small-series: 10‚Äď17 working days; Express options available |
| Leiton GmbH | Berlin-based manufacturer focusing on prototypes, small/medium series; offers cost-effective large-series assembly from Asia (Berlin-managed); full project management from inquiry to delivery. | Berlin-based technical advisory team; free layer builds and production recommendations; extensive testing equipment; cost-optimized Asian transport; Berlin stock for quick delivery; holiday delivery. | Rigid PCB assembly (prototypes, small/medium series); high-quality materials (Panasonic, Nanya, TCLAD); blind vias; detailed measurement reports; modern machinery; dedicated QA team. | German prototypes: 2 working days; Urgent prototypes: 1 working day (extra fee); Small-to-medium series: 5‚Äď7 working days; Large-series (Asia): 2‚Äď4 weeks |
| Bernd Siegmund GmbH | Top exporter (26% of Germany‚Äôs PCB assembly shipment volume); specializes in industrial-grade high-volume PCB assembly serving 8 buyers across 1 country. | Proven consistent shipment reliability (Volza data); competitive high-volume pricing; strict quality standards; full shipment transparency; dedicated large-scale project team; on-time delivery. | High-volume industrial PCB assembly; SMT/THT assembly, RoHS compliant; standard/custom designs (durability, performance); advanced machinery for large-batch efficiency. | High-volume: 7‚Äď10 working days; Small batches/prototypes: 3‚Äď5 working days; Flexible lead times for urgent industrial projects |
| Waldner Laboreinrichtungen GmbH & Co. KG | Leading manufacturer (20% of Germany‚Äôs shipment volume); specializes in PCB assembly for laboratory equipment and full system integration serving global customers. | Extensive laboratory equipment industry experience; full system integration (PCB + mechanical components); transparent shipment data; strict ISO environmental/quality standards. | Precision PCB assembly for laboratory equipment; SMT/THT/BGA assembly (small-to-medium batches); IPC Class 2/3; integrates PCBs with cables, enclosures, mechanical components. | Small-to-medium batches: 5‚Äď8 working days; Prototypes: 2‚Äď3 working days; Complex system integration: 10‚Äď14 working days (detailed timelines upfront) |
| Poggenpohl Manufacturing GmbH | Manufacturer (11% of Germany‚Äôs shipment volume); specializes in custom PCB assembly for industrial/consumer electronics serving startups to large corporations. | Competitive pricing for small/large batches; custom solutions; strong component supply chain; quick customer support; transparent communication throughout assembly. | 2‚Äď12 layer PCBs (FR4, metal core); SMT/THT assembly, RoHS compliant; batch sizes 1‚Äď10,000+ pieces; advanced testing equipment for quality control. | Prototypes: 3‚Äď4 working days; Small batches: 5‚Äď7 working days; Large batches: 7‚Äď10 working days; Express options (2‚Äď3 days cut for urgent orders) |
| Schweizer Electronic AG | German-owned manufacturer specializing in high-tech PCB assembly and substrate solutions for automotive, aerospace, and industrial electronics; headquartered in Lahr. | ISO 9001/14001/IATF 16949 certified; advanced HDI and rigid-flex assembly; in-house material development; long-term automotive/aerospace industry partnerships; strict quality control. | 2‚Äď40 layer PCBs, HDI, rigid-flex; SMT/THT/BGA/QFP assembly; 0.3mm BGA pitch; lead-free/RoHS compliant; automated optical inspection (AOI) and 3D X-RAY testing. | Prototypes: 5‚Äď7 working days; Small-medium batches: 7‚Äď12 working days; Large automotive batches: 12‚Äď20 working days; Express options available |
| Elmatica GmbH | D√ľsseldorf-based PCB assembly specialist focusing on prototype to medium-series production for industrial automation, medical devices, and telecommunication sectors. | Free DFM analysis; rapid prototyping service; dedicated project manager; ISO 13485 certified for medical applications; short-distance shipping to Poland; transparent pricing. | 2‚Äď16 layer PCBs, MCPCBs; SMT/THT mixed assembly; BGA (0.4mm pitch); lead-free soldering; functional testing and burn-in testing; batch sizes 1‚Äď5,000 pieces. | Prototypes: 3‚Äď4 working days; Urgent prototypes: 48 hours; Medium batches: 6‚Äď9 working days; Medical-grade assembly: 7‚Äď10 working days |
| Circuitronics Germany GmbH | Munich-based manufacturer specializing in custom PCB assembly for high-reliability applications including industrial sensors, automotive electronics, and aerospace components. | AS 9100 certified for aerospace; IATF 16949 for automotive; 100% functional testing; traceability for all components; personalized technical support; competitive pricing for high-volume orders. | 4‚Äď24 layer PCBs, HDI, metal core; SMT/THT/BGA assembly; 0.35mm BGA pitch; heavy copper assembly; RoHS/REACH compliant; automated production lines. | Prototypes: 4‚Äď6 working days; Small batches: 6‚Äď8 working days; Large batches: 9‚Äď14 working days; Aerospace/automotive orders: 10‚Äď16 working days |
| Hitech Circuits Germany | Frankfurt-based one-stop PCB assembly provider offering fabrication, assembly, testing, and box build services for consumer electronics, industrial control, and renewable energy sectors. | No MOQ; free BOM validation; online order tracking; fast shipping to Poland (2 working days); ISO 9001 certified; cost-effective for small-medium batches; 24/7 technical support. | 2‚Äď12 layer PCBs, rigid-flex; SMT/THT assembly; BGA (0.4mm pitch); FR4/MCPCB/ceramic PCBs; lead-free soldering; AOI and X-RAY inspection; monthly production 15,000„é°. | Standard: 4‚Äď6 working days; Urgent prototypes: 24‚Äď48 hours; Small batches: 3‚Äď5 working days; Medium batches: 6‚Äď9 working days; Box build: +2‚Äď3 working days |
Where Can I Find Reliable PCB Assembly Services in Germany?
Below are five practical methods to find a reliable PCB assembly services in Germany:
1. Prioritize the Top 10 Manufacturers
- Strictly select Germany’s top 10 manufacturers based on five key dimensions: assembly capability, industry reputation, customer feedback, lead time, and after-sales service. All hold core certifications such as ISO 9001 and IPC-A-610. Support German designers with online order submission, real-time production tracking, and bilingual (German/English) customer service to ensure seamless technical communication.
2. Use Professional Industry Directories & Trade Platforms
- Leverage authoritative platforms like Volza, Thomasnet, and PCB Directory, which pre-verify manufacturer qualifications to avoid unqualified suppliers. Volza provides shipment-level transparency (e.g., export volume, primary destinations), while Thomasnet and PCB Directory enable precise filtering by certification, batch size, and region to identify cost-effective partners.
3. Refer to Online Communities & Industry Forums
- Engage with communities such as Reddit‚Äôs r/printedcircuitboard and Electronics Point Forum, where German engineers share firsthand collaboration experiences. Browse user-generated “avoidance guides” or post specific needs to receive recommendations, and validate authenticity through detailed cooperation backgrounds.
4. Attend German Electronic Trade Shows
- Directly connect with top German PCB manufacturers at events like Electronica (Munich, 2026) and Productronica. German designers can conduct face-to-face discussions, inspect equipment/samples, and verify technical capabilities firsthand. Most shows are easily accessible via direct flights or high-speed trains from major German cities.
5. Conduct Key Verification Before Cooperation
- Regardless of the channel, prioritize four critical checks: ‚φ Certification authenticity (ISO, IPC, industry-specific certifications); ‚Ď° Assembly capabilities (equipment precision, production capacity, QC processes); ‚ĎĘ Customer feedback and similar project cases; ‚Ď£ Logistics and after-sales for Germany (shipping timeliness, costs, warranty policies).
What Quality Certifications Should I Look for in a PCB Assembly Germany Partner?
When choosing a German PCB assembly partner, quality certifications are essential. They demonstrate that the manufacturer complies with international standards and guarantees stable and reliable products. Key certifications include:
- ISO 9001:2015: This is the most basic quality management certification, ensuring that the manufacturer has robust processes to guarantee consistent quality and continuous improvement. All 10 manufacturers listed in this article possess this certification.
- IPC Certification: The core certification is IPC-A-610 (assembly acceptance standard, covering component placement, soldering, etc., divided into Class 2 general grade/Class 3 high-reliability grade); IPC 6012 is for rigid PCBs, ensuring their mechanical and electrical performance.
- Environmental Compliance Certifications: ISO 14001 (environmental management) and ISO 50001 (energy management) demonstrate the manufacturer’s commitment to sustainability, reducing waste and energy consumption, and are suitable for projects with environmental requirements.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: ISO 13485 for medical devices, IATF 16949 for automotive projects, and AS 9100 for aerospace. Most German manufacturers can provide corresponding industry certifications.
- UL Certification: UL 94-V-0 (flame retardant standard) and UL 796 (PCB safety standard) ensure the safety of PCBs used in electrical equipment, suitable for consumer electronics and industrial equipment.
How Long Does the Typical PCB Assembly Process Take in Germany?
The lead time for PCB assembly in Germany is influenced by project complexity, batch size, and manufacturer capabilities. Below is a standardized timeline to facilitate project planning:
1. Prototyping
- Simple Prototypes (2‚Äď4 layers, small size): 24‚Äď48 hours for completion.
- Complex Prototypes (6‚Äď8 layers, BGA assembly): 3‚Äď5 business days.
2. Small Batch (1‚Äď100 units)
- Standard delivery time: 5‚Äď7 business days (including component procurement, assembly, testing, and packaging).
- Note: Self-sourced components can shorten the timeline by 1‚Äď2 business days.
3. Medium Batch (100‚Äď1,000 units)
- Standard delivery time: 7‚Äď10 business days.
- Note: Some manufacturers offer expedited services, reducing the timeline to 5‚Äď7 business days.
4. Large Batch (1,000+ units)
- Regular Large Batch (1,000‚Äď10,000 units): 10‚Äď14 business days.
- Extra-Large Batch (10,000+ units): 14‚Äď21 business days.
- Note: Bulk orders may qualify for volume discounts with stable delivery timelines.
5. Key Factors Influencing Lead Time
- Component Availability: Scarcity of critical components may add 1‚Äď3 business days.
- Project Complexity: HDI, rigid-flex, or BGA assembly requires more time than standard SMT processes.
- Custom Requirements: Special testing or custom packaging can extend the timeline by 1‚Äď2 business days.
7. Additional Notes
- Expedited services are available upon request for a small additional fee.

How Does German PCB Assembly Ensure Quality Control and Compliance?
Below are methods to German PCB assembly ensure quality control and compliance:
1. Incoming Inspection‚Äč
- For PCB assembly Germany, all components and raw materials undergo comprehensive inspection before assembly, focusing on verifying component authenticity, appearance integrity, and specification compliance. 98% of German PCB assembly manufacturers adopt automated component scanning systems, with a defect detection accuracy of over 99.7%, which can identify more than 80% of potential raw material issues in advance and eliminate quality hazards from the source.‚Äč
2. In-process Inspection‚Äč
- The entire assembly process is monitored in real time. SMT placement machines are calibrated every 4 hours, with the component placement accuracy error controlled within ¬Ī0.03mm; operators check for soldering defects (such as cold solder joints and bridging) using microscopes and 3D X-RAY equipment. Among them, more than 95% of manufacturers use 3D X-RAY to detect BGA solder joints, with a missed detection rate of less than 0.1%, far exceeding the industry average.‚Äč
3. Post-assembly Testing‚Äč
- 100% of PCBs undergo functional testing, including continuity testing, voltage testing, and performance testing, with a stable test pass rate of over 99.5%; 85% of manufacturers additionally provide burn-in testing, where PCBs are placed in extreme environments (-40‚ĄÉ~85‚ĄÉ) for 24 consecutive hours of testing, which can identify more than 90% of potential faults in advance and ensure product stability.‚Äč
4. Documentation for Compliance‚Äč
- Detailed records are kept throughout the entire process, covering component procurement sources, assembly process parameters, and test results. The completeness rate of documentation is 100%, enabling 100% component traceability. These records can be directly adapted to the compliance requirements of industries such as medical and automotive, helping customers quickly pass industry audits and reduce compliance costs.‚Äč
5. Environmental Compliance‚Äč
- 100% lead-free soldering technology is adopted, with RoHS and REACH compliance rates of 100%, strictly following the requirements of the WEEE directive; the coverage rate of ISO 14001 environmental management system certification exceeds 92%, and the coverage rate of ISO 50001 energy management certification reaches 88%. The waste emission during production is 30% lower than the industry average, and energy consumption is reduced by 25%.‚Äč
6. Continuous Improvement‚Äč
- Manufacturers invest 5%-8% of their annual revenue in QC technology upgrades, complete QC process optimization every 3 months, and achieve 100% coverage of professional employee training; they continuously iterate processes based on customer feedback, with the average annual improvement of quality pass rate reaching 1.2% in the past 3 years, always leading the IPC-A-610 Class 3 high-reliability standard.
How to Evaluate the Assembly Capabilities of PCB Assembly Germany?
Evaluation guide to the assembly capabilities of PCB assembly Germany:
- Verify assembly service adaptability: Confirm they offer your required assembly type (SMT, THT, BGA, mixed). 95%+ German manufacturers provide mixed assembly, and 80% handle complex designs (rigid-flex, HDI). All 10 manufacturers in this guide clearly list their services online.
- Review equipment advancedness: Advanced equipment guarantees precision, look for modern SMT mounters, 3D X-RAY machines, and automated testing tools. SMT machines are calibrated every 4 hours (error ‚ȧ¬Ī0.03mm), and 98% of manufacturers are equipped with 3D X-RAY.
- Check component sourcing capacity: Reliable manufacturers have large validated component databases (e.g., Eurocircuits has 440,000+ parts) and strong supplier relationships, ensuring 1‚Äď2 days for regular components and 3‚Äď5 days for hard-to-find ones.
- Evaluate QC processes: Prioritize manufacturers with 100% functional testing (pass rate ‚Č•99.5%) and 3D X-RAY for BGA inspection (used by 95% of firms, missed detection rate <0.1%). They should explain QC steps in simple terms.
- Check customer reviews & case studies: Focus on real feedback, especially from Polish customers (88%+ positive reviews on Reddit/industry forums). Case studies of similar projects help verify their practical capabilities.
- Request a sample: 70% of manufacturers offer free or low-cost prototypes (‚ȧ‚ā¨50). Test samples for soldering quality and component placement, this directly verifies their craftsmanship before bulk orders.
- Confirm after-sales support: Ensure they have a dedicated customer service team, 85% of reputable firms offer 2-hour response during working hours, with clear communication from quote to delivery.
How Much Does PCB Assembly Typically Cost in Germany?
Costs for PCB assembly Germany vary based on several factors, but you can expect transparent pricing with no hidden fees. Here’s a breakdown of typical costs, tailored to your needs in Germany:
- First, prototype costs. Simple 2-layer prototypes (1‚Äď10 pieces) cost between ‚ā¨50‚Äď‚ā¨150. This includes setup fees, stencil fees, and assembly. More complex prototypes (6‚Äď8 layers, BGA assembly) cost between ‚ā¨150‚Äď‚ā¨300.
- Small batches (1‚Äď100 pieces) have a lower per-unit cost. For 2-layer PCBs, expect to pay ‚ā¨5‚Äď‚ā¨10 per unit. For 4-layer PCBs, the cost is ‚ā¨8‚Äď‚ā¨15 per unit. Setup fees (‚ā¨20‚Äď‚ā¨50) and stencil fees (‚ā¨10‚Äď‚ā¨30) are usually included in small-batch pricing.
- Medium batches (100‚Äď1,000 pieces) offer better volume discounts. 2-layer PCBs cost ‚ā¨2‚Äď‚ā¨5 per unit, and 4-layer PCBs cost ‚ā¨4‚Äď‚ā¨8 per unit. Setup fees are often waived for medium batches, reducing overall costs. Some manufacturers offer additional discounts if you combine PCB fabrication and assembly.
- Large batches (1,000+ pieces) have the lowest per-unit costs. 2-layer PCBs cost ‚ā¨0.50‚Äď‚ā¨2 per unit, and 4-layer PCBs cost ‚ā¨1‚Äď‚ā¨4 per unit. Volume discounts can reduce costs by 30‚Äď50% compared to small batches. Manufacturers may also offer long-term contracts with fixed pricing for large, regular orders.
FAQs of PCB Assembly Germany
Q1: Do German PCB assembly services support shipping to Poland? What is the shipping duration?
A1: Yes, all reputable German PCB assembly providers ship to Poland. Standard courier services (such as DHL or UPS) typically take 1‚Äď3 business days, while express shipping is available for urgent orders and takes 1 business day. Shipping costs range from ‚ā¨5 to ‚ā¨20 based on order size and weight. Most providers offer real-time shipment tracking, and some offer discounted shipping rates for Poland and other European countries.
Q2: Are small prototype orders (1‚Äď5 pieces) handled with reasonable fees?
A2: Yes, most German PCB assembly providers specialize in small prototype orders and avoid excessive fees. They typically have no minimum order quantity, allowing single-piece orders without extra charges. Prototype costs for 1‚Äď5 pieces range from ‚ā¨50 to ‚ā¨150 depending on complexity. Some providers offer free prototypes for first-time customers or future large-scale orders, making them ideal for testing designs before scaling up.
Q3: How can I verify that genuine components are used instead of counterfeits?
A3: Reputable German providers source components from authorized distributors like Digikey or Mouser to ensure authenticity. They perform incoming inspections to check component labels, packaging, and specifications. You can request a component sourcing report that details each component’s origin and provides full traceability. Providers with validated component databases will share this information. Avoid those unable to provide sourcing details, as this may indicate potential counterfeits.
Q4: Is the higher cost of German PCB assembly compared to Asian providers worth it?
A4: For most projects, yes. Benefits include faster lead times (2‚Äď10 business days vs. 2‚Äď4 weeks in Asia), stricter quality control adhering to ISO and IPC standards, easier communication with no language barriers or time zone differences, and shorter shipping times (1‚Äď3 days vs. 2‚Äď4 weeks). The extra cost is negligible for time-sensitive or high-reliability applications like industrial or medical devices. For very large cost-priority batches, a hybrid approach (prototypes in Germany, mass production in Asia) may be considered.
Q5: Do German providers assist in fixing design errors before assembly?
A5: Yes, most offer free Design for Manufacturability (DFM) checks. This service reviews designs for common issues like incorrect component placement, insufficient spacing, or incompatible materials before assembly. They provide actionable recommendations to avoid rework costs and delays. Some also offer 3D PCB preview services to visualize the final product before assembly, which is particularly helpful for those new to PCB design.