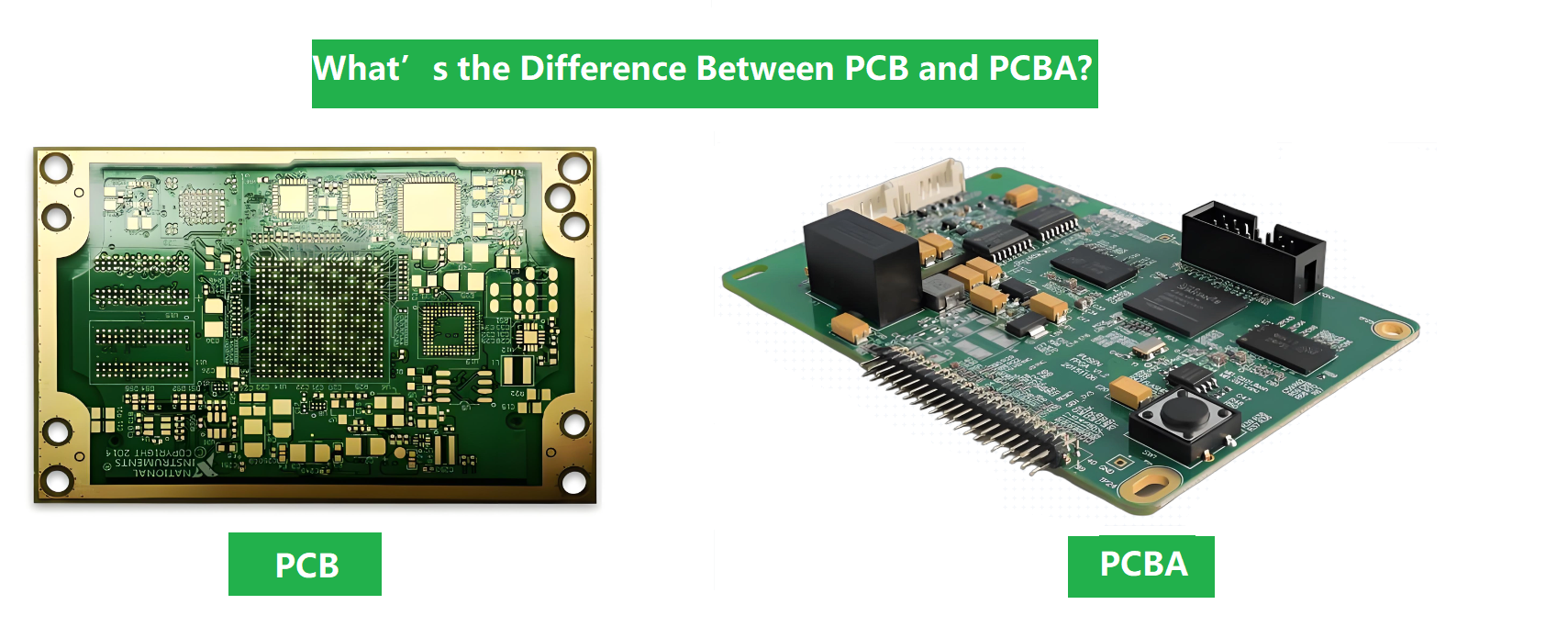
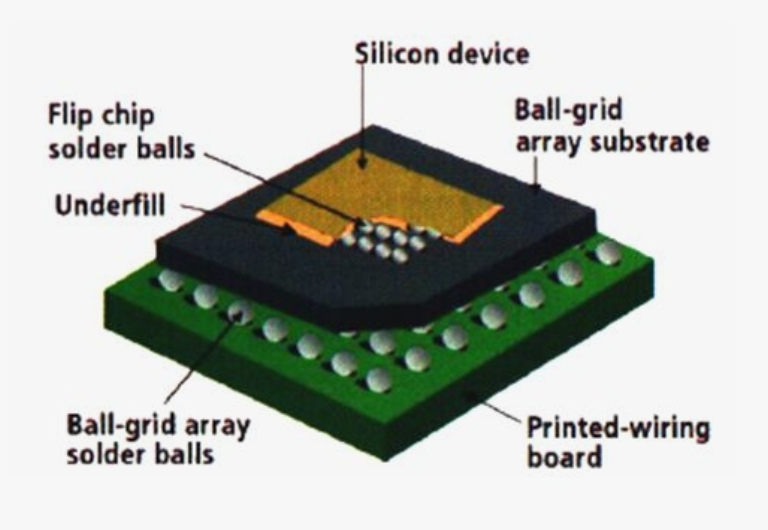
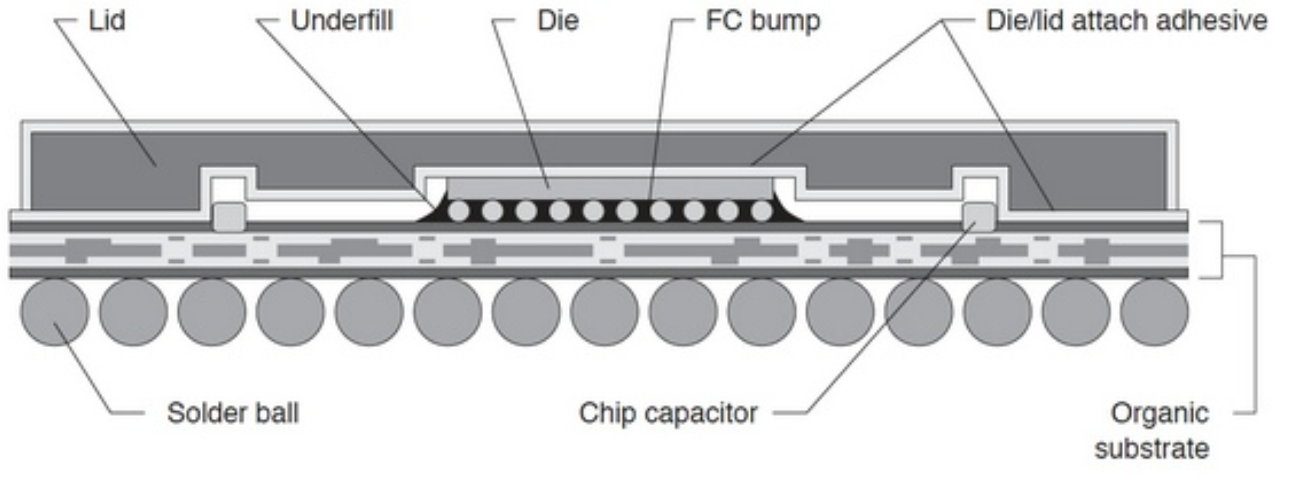
Low volume PCB assembly manufacturer means a production partner that can reliably build prototype-to-small-batch PCBAs‚ÄĒoften high-mix, fast-turn, and BOM-sensitive‚ÄĒwithout forcing ‚Äúmass-production‚ÄĚ constraints on early-stage hardware. This guide explains who low-volume assembly is for, what makes China and USA options different, how wholesale fits, and how to choose the best partner with fewer surprises.
Why does low volume assembly feel simple on paper, but messy in practice?
- Quotes swing wildly once component availability, alternates, and test requirements enter the picture.
- Lead times slip because ‚Äúin-stock‚ÄĚ parts were not actually reserved when the order was placed.
- First-build risk stays high when DFM/DFA feedback arrives late or is too generic.
- Quality is inconsistent if inspection standards and acceptance criteria are not clearly defined up front.
- Communication costs time when engineering questions bounce between sales, sourcing, and the SMT line.
A capable manufacturer reduces this friction by turning it into a controlled process with clear checkpoints.
- Transparent quoting that separates PCB fab, SMT labor, sourcing, and NRE so you can change one variable at a time.
- Sourcing discipline (AVL alignment, alternates strategy, reservation windows) to protect schedule.
- Front-loaded DFM/DFA with actionable comments before the first stencil is cut.
- Defined quality targets (IPC class, inspection coverage, rework rules) that match your product risk.
- Fast engineering communication with one owner who can close questions the same day.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is a one-stop PCB & PCBA manufacturer focused on engineering-led execution for prototypes, low volume PCB assembly, and scale-up builds. We combine PCB fabrication, component sourcing, SMT/THT assembly, inspection, and functional test planning so early-stage teams can iterate faster while keeping quality stable. For more information or if you would like to send us any inquiry, please send us an email through the contact form at the bottom of our Contact Page.

Top 5 Low Volume PCB Assembly Manufacturers
Identifying a reliable partner is the first step. This section highlights five leading global manufacturers renowned for their excellence in low to mid-volume production, considering factors like technical capability, service range, and geographic reach.
- PCBWay:‚Äč A giant in the online manufacturing space, known for its user-friendly platform, instant quoting, and extensive community support. Ideal for hobbyists, startups, and engineers seeking a straightforward, cost-effective entry into low volume PCB assembly.
- JLCPCB:‚Äč Revolutionized the market with incredibly low-cost prototyping and assembly. Their strength lies in a massive inventory of basic components for their SMT assembly service, offering unbeatable speed and price for simple to moderately complex designs.
- MacroFab:‚Äč An excellent Low volume PCB assembly manufacturer USA‚Äč option, operating a cloud-managed manufacturing platform. They provide a network of factories across North America, offering transparency, scalability, and strong supply chain management for clients wanting domestic production.
- Sierra Circuits:‚Äč Caters to the high-reliability and high-complexity end of the spectrum. While not the cheapest, they are a top choice for aerospace, medical, and military applications requiring stringent certifications (AS9100, ISO 13485) and advanced capabilities like RF and HDI PCB assembly.
- EBest Circuit (Best Technology):‚Äč Specializes in turnkey and technically challenging assemblies, with deep engineering support, proven expertise in medical PCBA and industrial control PCBA, and a long-term partnership approach for iterative product development.
In summary, the best choice depends on your project’s priority: ultra-low cost (JLCPCB), platform ease (PCBWay), US-based flexibility (MacroFab), high-reliability (Sierra Circuits), or specialized engineering partnership (EBest Circuit).
Why Engineers Choose A Low-Volume PCB Assembly Manufacturer For Early-Stage Projects?
Early-stage hardware changes fast. The right low-volume partner is essentially a risk-reduction system that keeps iteration moving.
Key reasons teams choose low-volume:
- Iteration speed beats unit cost in early builds (faster learning ‚Üí fewer redesign loops).
- High-mix readiness: small batches often include multiple variants, ECOs, or firmware spins.
- Controlled exposure: you validate mechanics, thermal, EMC, and usability before committing to volume.
- Sourcing flexibility: a good low volume PCB assembly manufacturer can manage alternates without ‚Äúsilently swapping‚ÄĚ parts.
- Test evolution: you can start with boundary checks and expand to functional testing as the design stabilizes.
- Better documentation habits: early builds force clean BOM/XY data, polarity, and revision control.
Practical checkpoint table (what to lock down per build):
| Build Stage | Must-Have Inputs | Output You Should Expect |
|---|---|---|
| EVT | BOM/XY + polarity + stack-up notes | First-pass DFM/DFA + clean assembly |
| DVT | Test plan + acceptance criteria | Repeatable yields + stable rework rules |
| PVT | Final AVL + packaging + labeling | Production-like flow with traceability |
Ultimately, low volume assembly is less about ‚Äúsmall quantity‚ÄĚ and more about ‚Äúfast learning with disciplined controls.‚ÄĚ
How A China Low Volume PCB Assembly Manufacturer Balances Cost And Lead Time?
A China low volume PCB assembly manufacturer typically wins on cost structure and supply-chain proximity, but lead time still depends on how well the project is prepared.
What drives cost down (and when it doesn’t):
- Component ecosystem proximity often reduces procurement overhead and substitutions.
- Panel utilization and line changeover efficiency can make small runs economical.
- Standardized processes (stencils, AOI programs, common packages) reduce NRE per build.
- Shipping mode selection (express vs economy) can flip the ‚Äútotal lead time‚ÄĚ outcome.
What usually drives lead time up:
- Long-tail parts (MCUs, connectors, power inductors)
- Incomplete centroid/rotation or inconsistent refdes mapping
- Unclear acceptance criteria for rework, cosmetics, and solder joints
Decision table (fast, realistic planning):
| Lever | Improves Cost | Improves Lead Time | Best Practice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consigned parts | Often | Sometimes | Consign only the risk items you truly control |
| Turnkey sourcing | Sometimes | Often | Use an approved alternates list |
| Standard finishes | Yes | Yes | Avoid exotic options unless needed |
| Clear DFM notes | Indirectly | Yes | Call out polarity, thermal pads, press-fit rules |
In practice, China can be an excellent choice for low cost PCB assembly, but the schedule is won or lost on sourcing clarity and clean production data‚ÄĒnot geography alone.
What Makes China Low Volume PCB Assembly Manufacturers Competitive Globally?
China low volume PCB assembly manufacturers compete well because they combine supply chain density with scalable manufacturing workflows.
Competitive advantages you can actually feel in a project:
- Broad component access and faster alternate sourcing cycles.
- Mature turnkey models that integrate PCB fab + assembly + procurement (often ‚Äúupload-to-order‚ÄĚ flows).
- High-mix operational experience from serving prototypes, maker programs, and startup pilots.
- Scalability: many suppliers can move from 5 boards to 5,000 with fewer process changes than expected.
- Process options: SMT + THT, AOI, X-ray for BGA/QFN, selective solder, and functional test integration (varies by vendor).
A quick ‚Äúfit check‚ÄĚ list (use before you request a quote):
- Can they support your package risk (BGA, 01005, fine-pitch QFN)?
- Do they offer clear consigned vs turnkey terms?
- Do they state inspection scope (AOI/X-ray/ICT/functional)?
- Can they manage engineering questions quickly and in writing?
In reality, the global edge comes from integrated sourcing + repeatable high-mix execution‚ÄĒespecially when you are iterating fast.
When A Wholesale Low Volume PCB Assembly Manufacturer Is The Right Choice?
A wholesale low volume PCB assembly manufacturer makes sense when you have repeatable demand patterns and want pricing leverage without jumping to full mass production.
Pick wholesale-style low volume assembly when:
- You have multiple SKUs/variants sharing common processes.
- You can forecast in rolling windows (even if it’s imperfect).
- Your BOM is mostly stable, with alternates already approved.
- You want batch pricing and simplified reorder cycles.
- You’re trying to reduce per-build overhead (NRE, setup time, procurement cycles).
Where wholesale helps most:
| Scenario | Why Wholesale Fits |
|---|---|
| Reorders every month/quarter | Less re-setup and fewer ‚Äúfirst build‚ÄĚ questions |
| Multi-SKU product family | Shared stencil strategy and line programs |
| Component risk management | Bulk procurement reduces schedule shocks |
As a result, wholesale low-volume is the bridge between ‚Äúprototype chaos‚ÄĚ and ‚Äúproduction discipline,‚ÄĚ as long as your design and BOM have started to settle.
Top 10 Low Volume PCB Assembly Manufacturer USA
For projects requiring IP protection, strict regulatory oversight, or rapid physical collaboration, domestic US manufacturers are indispensable. This list highlights key players known for quality and service in low-volume production.
- Sierra Circuits:‚Äč The premier name for high-reliability, complex prototypes and production, especially in defense and aerospace.
- MacroFab:‚Äč A cloud platform that connects customers to a network of US-based factories, ideal for managing multiple projects and scaling from prototype to production.
- Sunstone Circuits:‚Äč Offers a full suite of low cost PCB manufacturing‚Äč and assembly services with a strong focus on user experience and fast prototype turns.
- PCB Universe:‚Äč Specializes in quick-turn, low-to-mid volume assembly with strong engineering support and a wide range of capabilities.
- Imagineering Inc.:‚Äč A well-established provider known for reliable prototype and low volume assembly‚Äč with a focus on military and commercial applications.
- Royal Circuits:‚Äč Excels in complex, high-layer-count PCBs and their assembly, serving advanced technology sectors.
- Accu-Tronics:‚Äč Provides full-turnkey assembly services with an emphasis on medical, aerospace, and industrial electronics.
- Epec Engineered Technologies:‚Äč Offers end-to-end services from design to box-build, with expertise in harsh-environment and demanding applications.
- Axiom Electronics:‚Äč Focuses on complex, high-mix assembly and is known for technical proficiency in BGA, micro BGA, and COB.
- Screaming Circuits (Milwaukee Electronics): Specializes in ultra-fast prototype and low volume PCB assembly, offering builds from as few as one board with strong DFM support and consistent quality for time-critical programs.
The US market offers deep expertise and security, with manufacturers catering to everything from simple prototypes to mission-critical systems, ensuring there is a partner for every need.
What Separates The Best Low Volume PCB Assembly Manufacturer From The Rest?
The Best low volume PCB assembly manufacturer is not defined by one feature. It’s defined by how consistently the supplier prevents hidden failure modes.
Seven differentiators that matter in real builds:
- DFM/DFA that is specific (not generic checklists).
- BOM governance: alternates policy, traceability, and part reservation discipline.
- Clear process windows for stencil, paste, reflow profiles, and moisture-sensitive parts.
- Inspection strategy you can audit (AOI/X-ray/functional scope is explicit).
- Rework standards that protect reliability (not just ‚Äúmake it pass‚ÄĚ).
- Revision control across Gerbers, BOM, XY, and assembly drawings.
- A real escalation path when something is ambiguous or risky.
Simple scoring table you can use:
| Category | Green Flag | Red Flag |
|---|---|---|
| Engineering Q&A | Questions closed within 24‚Äď48 hours | Vague answers, no written trail |
| Sourcing | Alternates pre-approved | Silent substitutions |
| Quality | Acceptance criteria agreed upfront | ‚ÄúWe‚Äôll handle it‚ÄĚ without standards |
In effect, the best partner behaves like an extension of your engineering team, not just a line that places parts.
How Low Volume PCB Assembly Supports Faster Design Iteration?
Low volume PCB assembly supports iteration by shortening the ‚Äúdesign ‚Üí build ‚Üí learn‚ÄĚ loop while keeping builds comparable across revisions.
How iteration speed is actually achieved:
- Build plans per revision (EVT/DVT/PVT mindset even if you don’t name it).
- Standardized deliverables: BOM, centroid, fab notes, assembly notes, test notes.
- Tighter feedback loops: early DFM comments prevent costly respins.
- Faster ECO handling with controlled change logs and clear delta scope.
- Yield tracking even for small runs so you know whether issues are random or systemic.
A compact ‚Äúiteration checklist‚ÄĚ (use every time):
- Freeze refdes and polarity marks
- Lock package footprints and courtyard rules
- Declare critical nets and impedance constraints
- Define functional test minimums (even basic power-up checks)
In this way, with a disciplined low-volume process, you iterate faster without degrading quality or losing track of what changed.

All in all, low volume PCB assembly manufacturer is the practical path for turning early-stage designs into reliable, testable hardware‚ÄĒfast‚ÄĒwithout forcing you into mass-production assumptions too early.
This article covered how to evaluate global and USA options, where China and wholesale models fit, and what separates the best suppliers from the average ones.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) supports prototype and low-volume PCBA with engineering-led DFM, sourcing control, and stable quality execution across builds. Pls feel free to reach out to start a conversation at sales@bestpcbs.com.