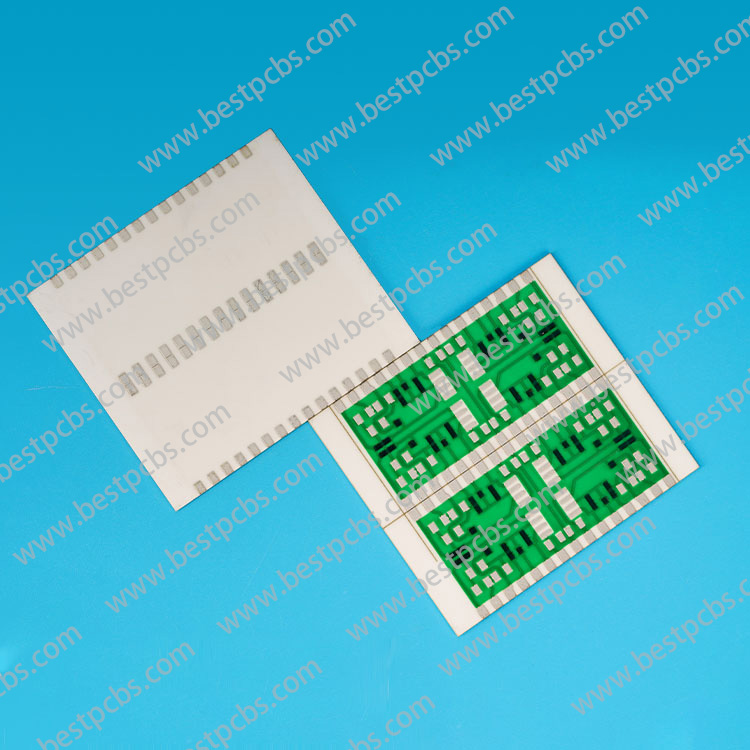
FR4 material is a highly popular and widely used substrate in the PCB industry due to its exceptional mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and flame retardant properties. It has become the standard for PCB fabrication.
What is FR4 Material and Why is it Used in PCBs?
FR4 is a type of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate. The term “FR4” comes from its flame-retardant properties, meeting the UL94V-0 standard. It is made from woven fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin, which together provide great strength and durability.
Electrical engineers and designers prefer FR4 because of its many benefits, such as:
- Low cost
- High dielectric strength
- Excellent strength-to-weight ratio
- Moisture resistance
- Temperature endurance
- Good electric loss characteristics
- Flame retardance and self-extinguishing capabilities
- Mechanical robustness
- Insulating properties
FR4 is also suitable for marine PCBs because it absorbs very little water. In a standard FR4 PCB, a layer of FR4 is placed between two thin layers of laminated copper.

What are the Key Performances of FR4 Material?
FR4 material, also recognized as flame retardant 4, is a composite of glass fabric and epoxy resin, predominantly utilized as a foundational material for printed circuit boards. Familiarity with the specifications of FR4 is crucial for selecting the appropriate substrate for PCB manufacturing. Key specifications include:
1. The thickness of FR4 sheet is usually 0.2 mm to 3.2 mm, and other special thickness also available.
2. The specific gravity of FR4 material is about 1.85g/cm3, which means that it is heavier than water.
3. Coefficient of thermal expansion of FR4 is about 1.0Ă10^-5cm/cm/â, which means that its length or width will expand slightly when the temperature changes.
4. The thermal decomposition temperature of FR4 materials is usually between 280C and 320C, which makes it able to withstand high temperature applications.
5. FR4 material has a dielectric constant around 4.0-4.8, which makes it an ideal material for circuit board manufacturing.
6. FR4 has good arc resistance, which means that in the case of high voltage, it can effectively prevent arc discharge.
7. FR4 material good hydrolysis resistance and can maintain good performance even in a humid environment.
What are the Types of PCB Materials in the Industry?
PCB materials can be broadly categorized based on their composition and intended application. Nowadays, the commonly used are including FR4, polyimide (PI), Metal material (copper or aluminum), ceramic substrate like Al2O3, AlN, Si3N4, and so on. Different materials have its unique functions and well-suited in specific environment. Here we introduce their properties and suited applications simply.
FR4 (Fiberglass Epoxy Laminate)
At present, almost of PCB you seen in the market or electronics used the FR4 material. It widely used because of its superb equilibrium of mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and cost-efficiency. Actually, according to the different reinforcement materials, the circuit board is mainly classified into the following types:
1) FR-4
2) FR-1, FR-2, etc.
3) CEM series: Composite substrate
FR-4 used frequently because of its high fire resistance rating.
High Tg FR4
Though normal FR4 material has good electrical insulation, it is not an ideal option for high frequency circuit board. And then, high Tg FR4 stands out by using an advanced technology. “Tg” refers to glass transition temperature, the juncture at which the material transitions from a rigid, glassy state to a pliable, rubbery state. High Tg FR4 boasts a Tg of 170°C or higher.
Polyimide (PI)
Polyimide materials are renowned for their excellent flexibility, superior thermal stability and chemical resistance. It is always used as raw material of flex circuits, rigid flex circuit boards or membrane switches. Due to the good chemistry properties, they can endure temperatures up to 260°C and are highly flexible, making them ideal for those small and limited PCB designs.

Metal base material
Metal materials always used in metal core PCBs (MCPCB), usually used aluminum core or copper core. The metal base has great thermal conductivity to enhance the thermal management of the device, buy using metal core, the device can dissipate heat away from the critical component such as LED chips, ICs, BGAs, to remain the reliability and performance of the PCB.
Ceramic substrate
Ceramic PCB substrate offers excellent thermal conductivity and stability than that metal core PCBs, making them suitable for high-power and high-frequency applications. But due to the high cost and complex manufacturing, the ceramic PCB is much expensive than metal core PCB, therefore, they are always be used in high-end applications, such as the military, defense, aerospace and some special fields where requires excellent thermal management.
Understanding these materials enable to help engineers and designers in selecting the most appropriate substrate for their projects, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency. Best Technology provides a comprehensive array of PCB materials, guaranteeing high-quality solutions for all your electronic needs.
What are the Applications of FR4 PCB Material in Various Industries?
FR4 material is versatile and finds applications in numerous industries, including:
- Consumer Electronics like smartphones, laptops, and other personal electronic devices.
- Applied in vehicle electronics for infotainment systems, engine control units, and more.
- Industrial Equipment such as control systems, power supplies, and industrial automation.
- Essential for telecommunications, network devices, routers, and communication infrastructure.
- Medical instrumentation and diagnostic equipment.
- Aerospace and defense in avionics, radar systems, and defense electronics.
This is all of this sharing, thanks for your reading. Welcome to contact us if you have other questions about FR4 or other raw materials of PCB. Best Technology engaging in the PCB manufacturing about 18 years, we are one of the leading PCB manufacturers in China. And we have such confidence to provide with you the best PCB and PCBA fast solution for your projects.