A 4 layer PCB assembly manufacturer is a specialized provider that manages the entire process, from fabricating the 4-layer printed circuit board to populating it with components, ensuring a functional, ready-to-use electronic assembly. This article comprehensively explores the 4-layer PCB ecosystem, covering the manufacturing process, cost drivers, the strategic advantage of Chinese suppliers, critical design and assembly considerations, and how to select a reliable partner for your project.
Choosing the right SMT partner for your 4-layer PCB project can be daunting. What are the most common pitfalls that derail projects, increase costs, and compromise quality?
- Signal Integrity Issues ‚Äď Poor stackup design can cause EMI, crosstalk, and signal instability in sensitive circuits.
- DFM Errors Causing Delays ‚Äď Designs that exceed manufacturing capability often require redesign and multiple revisions.
- Complex BOM and Component Sourcing ‚Äď Managing component supply can delay production, especially during shortages.
- Insufficient Testing ‚Äď Without proper testing, defective boards may reach the final product stage.
- High Costs for Prototypes or Small Batches ‚Äď Many manufacturers focus mainly on high-volume production.
Partnering with an expert 4 layer PCB assembly manufacturer directly addresses these pain points through integrated services and deep expertise.
- Optimized Stackup & SI Analysis ‚Äď Ensure signal integrity during the 4 layer pcb design for manufacturability stage.
- Free DFM Review ‚Äď Identify fabrication and assembly risks before production begins.
- Integrated Component Sourcing ‚Äď Manage the full BOM through stable global supply networks.
- Comprehensive Testing ‚Äď Electrical and functional testing verify board performance before shipment.
- Flexible Production ‚Äď Support both prototypes and volume manufacturing as a reliable 4 layer pcb assembly manufacturer.
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), a professional 4 layer pcb and assembly manufacturer. Our vertically integrated services, from advanced 4 layer pcb manufacturing‚Äč to precision assembly and rigorous testing, ensure quality, reliability, and on-time delivery. We empower your designs with expert engineering support, including a crucial Free DFM Review, to de-risk your project lifecycle. Pls feel free to contact our team anytime to start your 4 Layer PCB prototype and assembly project via sales@bestpcbs.com.
How Does The 4 Layer PCB Manufacturing Process Work From Fabrication To Assembly?
The journey from design files to a functional 4-layer PCB assembly is a meticulous, multi-stage process. It seamlessly integrates board fabrication (PCBA) with component assembly (PCBA) to produce a complete electronic module.
Fabrication (The Bare Board):
This process creates the physical 4-layer laminated board.
- Inner Layer Imaging:‚Äč The core layers (L2 & L3) are coated with photoresist, exposed to UV light through the circuit pattern film, and developed to etch away unwanted copper.
- Oxidation & Lamination:‚Äč The etched inner layers are oxidized to improve adhesion. They are then stacked with prepreg (insulating layers) and outer copper foils (L1 & L4) and laminated under high heat and pressure into a single board.
- Drilling & Plating:‚Äč Holes for vias and through-hole components are drilled. The entire panel undergoes electroless and then electrolytic copper plating to metallize the hole walls, creating electrical connections between layers.
- Outer Layer Patterning:‚Äč A process similar to Step 1 is applied to define the circuitry on the outer layers (L1 & L4).
- Solder Mask & Surface Finish:‚Äč A protective epoxy layer (solder mask) is applied, leaving only pads exposed. A surface finish (e.g., ENIG, HASL) is then applied to the exposed copper to prevent oxidation and aid solderability.
- Silkscreen & Electrical Test:‚Äč Component designators and logos are printed. Each board undergoes electrical testing (e.g., Flying Probe) to verify continuity and isolation.
Assembly (PCBA – Populating the Board):
- Solder Paste Application:‚Äč Solder paste is precisely deposited onto the component pads via a stencil.
- Component Placement:‚Äč Surface Mount Devices (SMDs) are accurately placed onto the pasted pads by a pick-and-place machine.
- Reflow Soldering:‚Äč The board passes through a reflow oven where the solder paste melts, creating permanent electrical and mechanical connections.
- Through-Hole & Mixed-Technology:‚Äč Any Through-Hole (THT) components are inserted, often by hand or automated, and soldered, typically via wave soldering or selective soldering.
- Cleaning & Conformal Coating (Optional):‚Äč Flux residues are cleaned. A protective conformal coating may be applied for harsh environments.
- Final Assembly & Testing:‚Äč The assembled board undergoes final inspection, programming, and functional testing.
In summary, the 4 layer pcb manufacturing process‚Äč is a symphony of precise chemical, mechanical, and thermal steps, culminating in assembly to transform a design into a reliable electronic heart.

What Factors Affect Cost, Lead Time, And Quality In 4 Layer PCB Manufacturing?
Understanding the drivers behind cost, lead time, and quality helps engineers plan projects and choose the right manufacturing partner. These factors are closely connected.
Key Factors Influencing 4 Layer PCB Manufacturing
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Impact on Lead Time | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Board Complexity | High | Medium | Critical |
| Material Selection | High | Low‚ÄďMedium | Fundamental |
| Board Quantity | Lower at volume | Low | Stable |
| Layer Count | Medium | Low | Improves SI |
| Surface Finish | Medium | Low | Important |
| Testing Rigor | Medium | Medium | Essential |
| Geographical Location | Lower in Asia | Variable | Process dependent |
Quick Explanation of These Factors
Board Complexity
Dense routing, fine traces, HDI structures, and tight tolerances increase fabrication difficulty and production cost.
Material Selection
Standard FR-4 is economical, while high-Tg, RF, or specialty laminates raise material cost but improve performance.
Board Quantity
Higher production volumes reduce unit price due to economies of scale and optimized manufacturing runs.
Layer Count
A 4 layer PCB is considered a standard configuration. Additional layers increase processing steps and cost.
Surface Finish
Options such as HASL, ENIG, Immersion Silver, or ENEPIG influence solderability, shelf life, and component compatibility.
Testing Rigor
Additional inspection methods such as AOI, X-ray, and functional testing increase reliability but also add processing time.
Geographical Location
Working with an experienced China 4 layer pcb manufacturer often reduces cost while maintaining reliable manufacturing standards.
In general:
- Cost is mainly driven by board complexity, materials, and production volume.
- Lead time depends on process steps, testing requirements, and logistics.
- Quality comes from controlled materials, precise fabrication, and rigorous verification.
Working with a reliable 4 layer pcb assembly manufacturer ensures these factors are balanced to achieve stable quality, competitive pricing, and predictable delivery.
Why Is A China 4 Layer PCB Manufacturer Often Preferred For Global PCB Supply Chains?
China 4 layer pcb manufacturers‚Äč have become a cornerstone of global electronics due to a powerful combination of scale, expertise, and integrated supply chains that deliver unparalleled value.
- Unmatched Economies of Scale & Cost Efficiency:‚Äč Massive, centralized production volumes drive down the unit cost of everything from raw materials (copper-clad laminates, chemicals) to consumables. This allows them to offer highly competitive pricing on standard and advanced 4 layer pcb manufacturing.
- Complete Vertical Integration & Supply Chain Dominance:‚Äč The entire PCB ecosystem‚ÄĒfrom laminate producers, chemical suppliers, and copper foil mills to component distributors‚ÄĒis concentrated regionally. This minimizes logistics delays, reduces material costs, and provides resilience against shortages, ensuring stable production schedules.
- Rapid Technological Adoption and Advanced Capabilities:‚Äč Fierce competition drives continuous investment in the latest equipment (laser direct imaging, high-precision drilling, automated optical inspection) and process expertise. Many leading China 4 layer pcb manufacturers‚Äč are at the forefront of HDI, high-frequency, and rigid-flex technology.
- Scalability and Manufacturing Flexibility:‚Äč Large factories are equipped to handle orders ranging from 10 prototypes to 100,000+ production units without significant cost or lead time penalties, seamlessly supporting a product from NPI to mass production.
- Established and Efficient International Logistics:‚Äč Decades of exporting have refined shipping, customs, and logistics channels, making reliable and predictable delivery to North America, Europe, and elsewhere a routine, managed service.
Therefore, the preference stems from a strategic value proposition: accessing high-quality, technologically advanced manufacturing at a significantly lower total cost, backed by a robust and scalable supply chain, making them indispensable for global 4 layer pcb assembly manufacturer‚Äč sourcing.
How Does A 4 Layer PCB Assembly Manufacturer Optimize Stackup Design For Signal Integrity?
A professional 4 layer pcb assembly manufacturer‚Äč doesn’t just assemble; it advises on optimal stackup design‚ÄĒthe arrangement of copper and insulating layers‚ÄĒwhich is foundational for signal integrity (SI), EMI control, and power integrity in a 4-layer board.
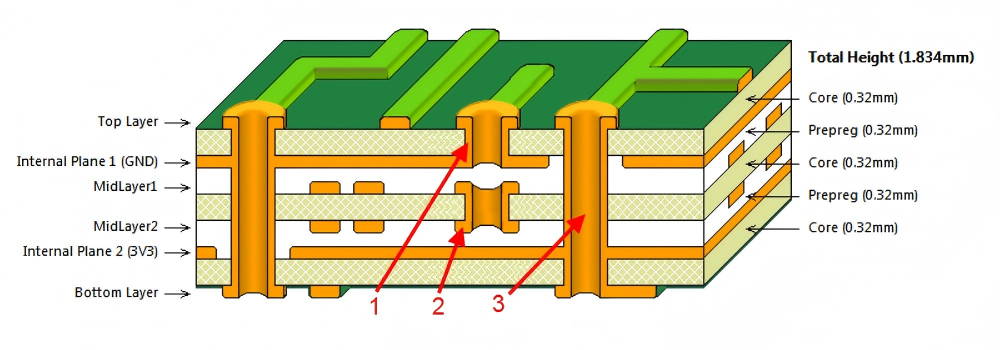
Optimal 4-Layer Stackup Configuration:
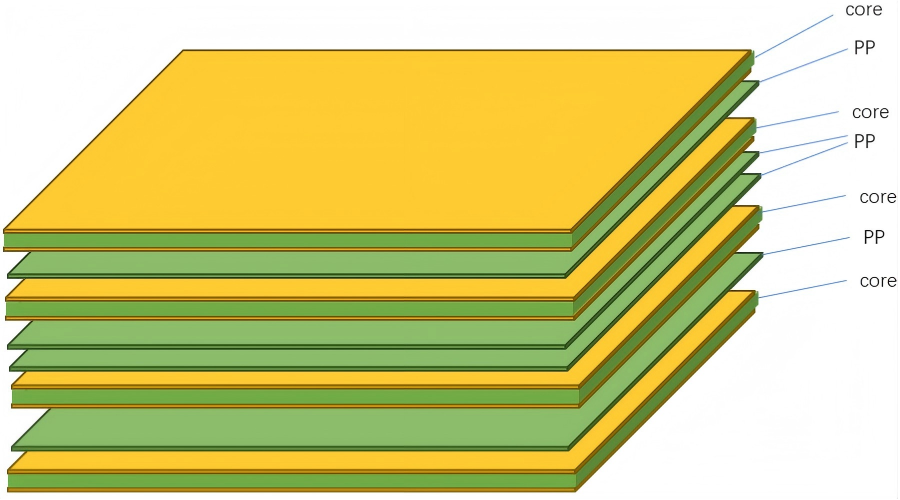
The industry-standard, SI-optimized stackup is: Top Layer (L1 – Signals) / Ground Plane (L2) / Power Plane (L3) / Bottom Layer (L4 – Signals).
- L2 & L3 as Solid Planes:‚Äč These continuous copper planes provide:
- Low-Inductance Return Paths:‚Äč High-speed signals on L1/L4 reference the adjacent plane (GND or PWR), minimizing loop area and radiated EMI.
- Decoupling:‚Äč The thin dielectric between L2 and L3 creates inherent interplane capacitance, helping to suppress high-frequency power rail noise.
- Shielding:‚Äč The planes act as shields, reducing crosstalk between signal layers on L1 and L4.
Key Optimization Strategies During DFM:
- Symmetry is Mandatory:‚Äč The stackup must be symmetrical around the central core (L2/L3) to prevent warping (bow and twist) during lamination and reflow soldering, which is a core 4 layer pcb design for manufacturability‚Äč guideline.
- Minimize Dielectric Thickness:‚Äč Use the thiest feasible dielectric (e.g., ~5-8 mil prepreg) between the outer signal layer (L1/L4) and its adjacent reference plane (L2/L3). This tight coupling reduces impedance discontinuities and improves signal quality. The formula for characteristic impedance (Z‚āÄ) highlights this relationship: it is inversely proportional to the square root of the effective dielectric constant and directly influenced by the trace’s geometry and distance to the plane.
- Define Controlled Impedance Early:‚Äč Specify required impedance values (e.g., 50ő© for single-ended, 100ő© for differential) to your manufacturer during the free DFM review. They will calculate the precise trace width and dielectric spacing needed based on their specific materials (e.g., FR-4 with Dk ~4.2-4.5).
- Plan Power Distribution Network (PDN):‚Äč While L3 is a main power plane, split it carefully for multiple voltages. Use wide traces or additional copper pours on signal layers for minor power rails, ensuring adequate current capacity and minimizing voltage drop.
In summary, optimization involves enforcing a symmetrical stackup with closely coupled signal/plane pairs, precisely calculating impedance, and strategically managing power distribution‚ÄĒall areas where an experienced manufacturer’s input during design review is invaluable.
What Assembly Challenges Do Engineers Face When Working With 4 Layer PCB Designs?
While 4-layer PCBs solve many design challenges, they introduce specific complexities during the assembly phase that engineers and 4 layer pcb assembly manufacturers must collaboratively manage.
- Thermal Management and Warpage:‚Äč The multilayer lamination can trap heat and, if the stackup is not symmetrical, lead to warping during the high-temperature reflow process. This can cause poor solder paste deposition, component misalignment (tombstoning), and open solder joints.
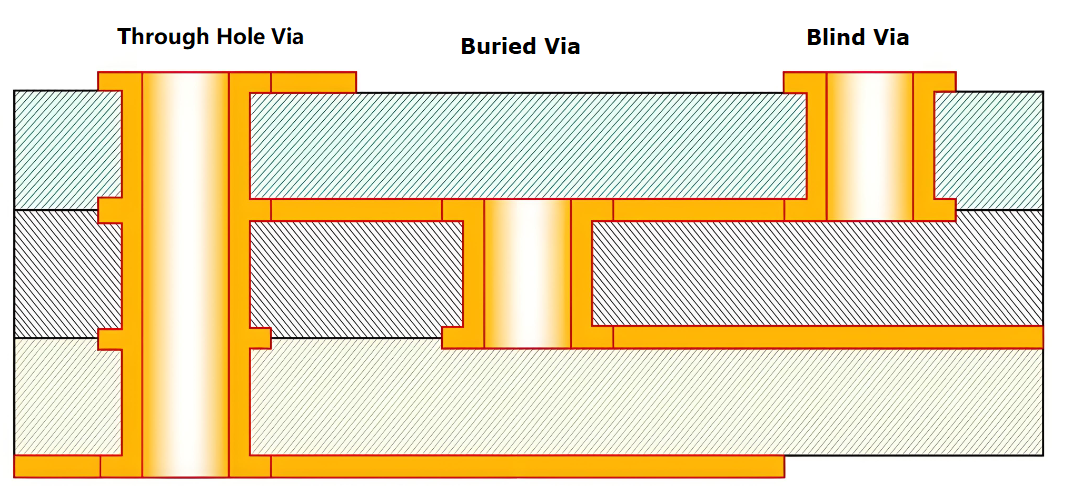
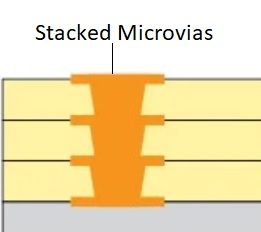
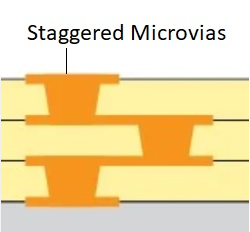
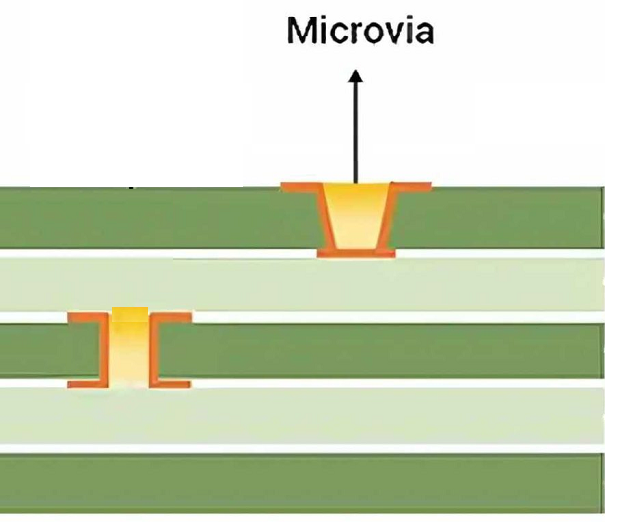
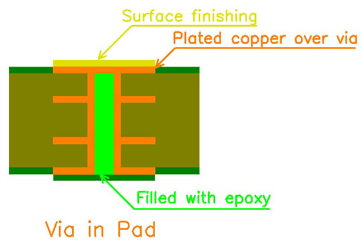
- Via Treatment and Reliability:‚Äč Vias connecting layers must be properly plated and protected. Tentative vias under solder mask can trap chemicals causing later corrosion. Improperly filled or capped vias for via-in-pad designs can lead to solder wicking away from the component pad, creating voids and weak joints.
- Mixed-Technology Component Placement:‚Äč Designs often combine fine-pitch BGAs or QFNs (on the outer layers) with through-hole connectors. This requires a mixed assembly process (reflow + wave/selective soldering), increasing complexity. The shadowing effect of taller components during wave soldering must be planned for.
- Test Point Access and Fixturing:‚Äč Denser routing on 4 layers can make it difficult to place adequate test points for in-circuit testing (ICT). Designing for testability is crucial, as creating a reliable bed-of-nails test fixture for a dense, multilayer board is more challenging and expensive.
- Rework and Repair Difficulty:‚Äč Replacing a component on an inner layer is impossible, and reworking a BGA on a board with internal power/ground planes requires careful control of heat to avoid delaminating the board or damaging nearby components.
Proactively addressing these challenges through design choices (symmetrical stackup, adequate test points) and clear communication with your assembly partner is key to a smooth and successful production run.
Why Is DFM Review Critical When Working With A 4 Layer PCB Assembly Manufacturer?
A Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review is a non-negotiable gatekeeper between a theoretically functional design and a reliably, cost-effectively producible product. It is the process where the 4 layer pcb assembly manufacturer’s practical expertise is applied to the designer’s intent.
- Prevents Costly Late-Stage Redesigns:‚Äč Catching errors in the design files beforefabrication starts avoids the extreme cost and weeks-long delays of scrapping production panels or revising tooling (e.g., solder stencils, test fixtures).
- Optimizes for the Specific Manufacturing Process:‚Äč A DFM review aligns the design with the manufacturer’s exact capabilities‚ÄĒminimum annular ring size, solder mask sliver tolerances, drill aspect ratios, and panelization preferences‚ÄĒensuring the design can be built successfully on their line.
- Enhances Yield and Reliability:‚Äč It identifies potential failure points like acid traps in copper, thermal imbalances that cause warping, or insufficient spacing for solder mask, which directly translates to higher production yield and more reliable end products.
- Validates Assembly Feasibility:‚Äč The review checks component footprints, pad sizes, and spacing against the assembly equipment’s capabilities, ensuring parts can be placed and soldered correctly, preventing tombstoning, bridging, or misalignment.
- Facilitates Efficient Testing:‚Äč It verifies that adequate, accessible test points are included for Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and In-Circuit Test (ICT), which is essential for guaranteeing the quality of the final assembled board.
Therefore, a thorough DFM review, especially one offered as a free DFM review, is a critical risk-mitigation and value-engineering step. It transforms a design from a set of instructions into a recipe for manufacturable success, saving time, money, and ensuring quality from the first article onwards.
What Testing Methods Ensure Quality From A Professional 4 Layer PCBA Manufacturer?
Quality assurance in PCB assembly relies on multiple inspection layers. A professional 4 layer PCBA manufacturer combines several complementary testing methods to detect defects early and ensure reliable board performance.
Common Testing Methods Used In 4 Layer PCB Assembly
| Test Method | Stage Applied | What It Checks | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) | Post-Reflow | Component placement, solder joints | Fast defect detection |
| X-Ray Inspection (AXI) | Post-Reflow / BGA | Hidden solder joints, voids | Inspect hidden connections |
| In-Circuit Test (ICT) | Post-Assembly | Shorts, opens, component values | Accurate electrical test |
| Flying Probe Test | Post-Assembly | Continuity, isolation | No fixture required |
| Functional Test (FCT) | Final Stage | Board functionality | Real-world validation |
Quick Explanation Of Each Test
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI systems use high-resolution cameras to inspect component placement and solder joints after reflow soldering. It quickly detects common defects such as solder bridges, missing components, or incorrect polarity.
X-Ray Inspection (AXI)
AXI is essential for inspecting hidden solder joints under packages such as BGA or QFN. It reveals internal alignment issues and solder voids that optical inspection cannot detect.
In-Circuit Test (ICT)
ICT verifies electrical connectivity and basic component values on the assembled board. It is highly effective at detecting manufacturing defects such as opens, shorts, and wrong components.
Flying Probe Test
Flying probe testing uses movable probes to check electrical continuity without a dedicated fixture. This method is widely used for prototypes and low-volume production.
Functional Test (FCT)
Functional testing simulates the real operating environment of the board. It verifies that the entire system performs correctly, including firmware, signal processing, and power behavior.
In summary, an effective quality strategy combines multiple inspection layers:
- AOI and AXI detect soldering and placement defects.
- ICT and Flying Probe verify electrical connectivity.
- FCT confirms full system functionality.
This layered testing approach is especially important for complex 4 layer PCB assembly, ensuring that only boards meeting all specifications proceed to shipment.
How To Choose A Professional 4 Layer PCB Assembly Manufacturer For Reliable Production?
Selecting the right manufacturer is a strategic decision that impacts your product’s quality, cost, and time-to-market. Look beyond just quoted price and evaluate their holistic capability.
- Technical Competency and Explicit Capabilities:
- Verify their experience with 4 layer pcb manufacturing‚Äč and assembly, including your specific technologies (e.g., impedance control, BGA, QFN).
- Review their official capabilities document, noting minimum trace/space, hole size, and layer count.
- Assess their 4 layer pcb design for manufacturability‚Äč support‚ÄĒdo they offer a formal, free DFM review?
- Quality Certifications and Process Control:
- Require fundamental certifications like ISO 9001 (Quality Management) and ISO 14001 (Environmental). For automotive or medical, IATF 16949 or ISO 13485 are strong indicators.
- Inquire about their internal quality control processes, testing equipment (AOI, X-Ray, ICT), and their standard quality metrics (e.g., DPPM rates).
- Transparent Communication and Responsiveness:
- Gauge their communication during the quoting process. Are they asking insightful DFM questions?
- Identify your primary point of contact (a Project Manager or Engineer) and their availability.
- Ensure they provide clear documentation (test reports, assembly drawings) and proactive order updates.
- Supply Chain Strength and Sourcing Ability:
- For a 4 layer pcb assembly manufacturer, component sourcing is half the battle. Evaluate their component procurement network, especially for long-lead or obsolete parts.
- Understand how they manage supply chain disruptions and communicate component issues.
- Scalability, Logistics, and Total Value:
- Ensure they can support your needs from NPI/prototype through to high-volume production without changing partners.
- Evaluate their packaging standards and logistics partnerships for reliable, damage-free shipping to your location.
- Make a decision based on total value‚Äč (quality + service + support + cost) rather than unit price alone. A slightly higher cost from a more capable partner often results in lower total cost by avoiding delays, rework, and field failures.
In a nutshell, a 4 layer PCB assembly manufacturer‚Äč is a pivotal partner that transforms complex circuit designs into reliable, high-performance electronic assemblies. This guide has detailed the integrated process from fabrication to testing, the critical factors affecting your project, and the strategic value of leveraging global expertise.
For your next 4-layer PCB project, partner with a manufacturer that provides not just manufacturing, but engineering partnership. EBest Circuit (Best Technology)‚Äč combines advanced multi-layer pcb manufacturing‚Äč capabilities with expert assembly services, underscored by a commitment to quality and a proactive Free DFM Review‚Äč to ensure your design’s success from the start. Pls feel free to contact us anytime for a consultation and quote via sales@bestpcbs.com.
FAQs About 4 Layer PCB Assembly Manufacturer
1. What is the dielectric constant (Dk) of standard thin-core FR-4 material in the 0.1mm-0.25mm thickness range?
For standard FR-4 laminates, the dielectric constant is frequency-dependent. Typical values are:
- At 1MHz frequency: Dk approximately 4.0 – 4.6
- At 1GHz frequency: Dk approximately 3.5 – 4.3
2. What is the maximum size for thin-core boards?
For standard production, the board dimensions (length and width) cannot both exceed 500mm (e.g., 500 * 500mm). For designs with simpler structures, the maximum size can be up to 480 * 1200mm. For any special or panel sizes, please consult us for a feasibility assessment.
3. What is the smallest component you can assemble?
We can assemble components as small as the 1005 package (Imperial code, equivalent to 0402 metric: 1.0mm x 0.5mm).
4. What is the board size range your AOI equipment can scan?
Our Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) system has an effective scanning area with the following range:
- Length: from 25mm to 480mm
- Width: from 25mm to 330mm