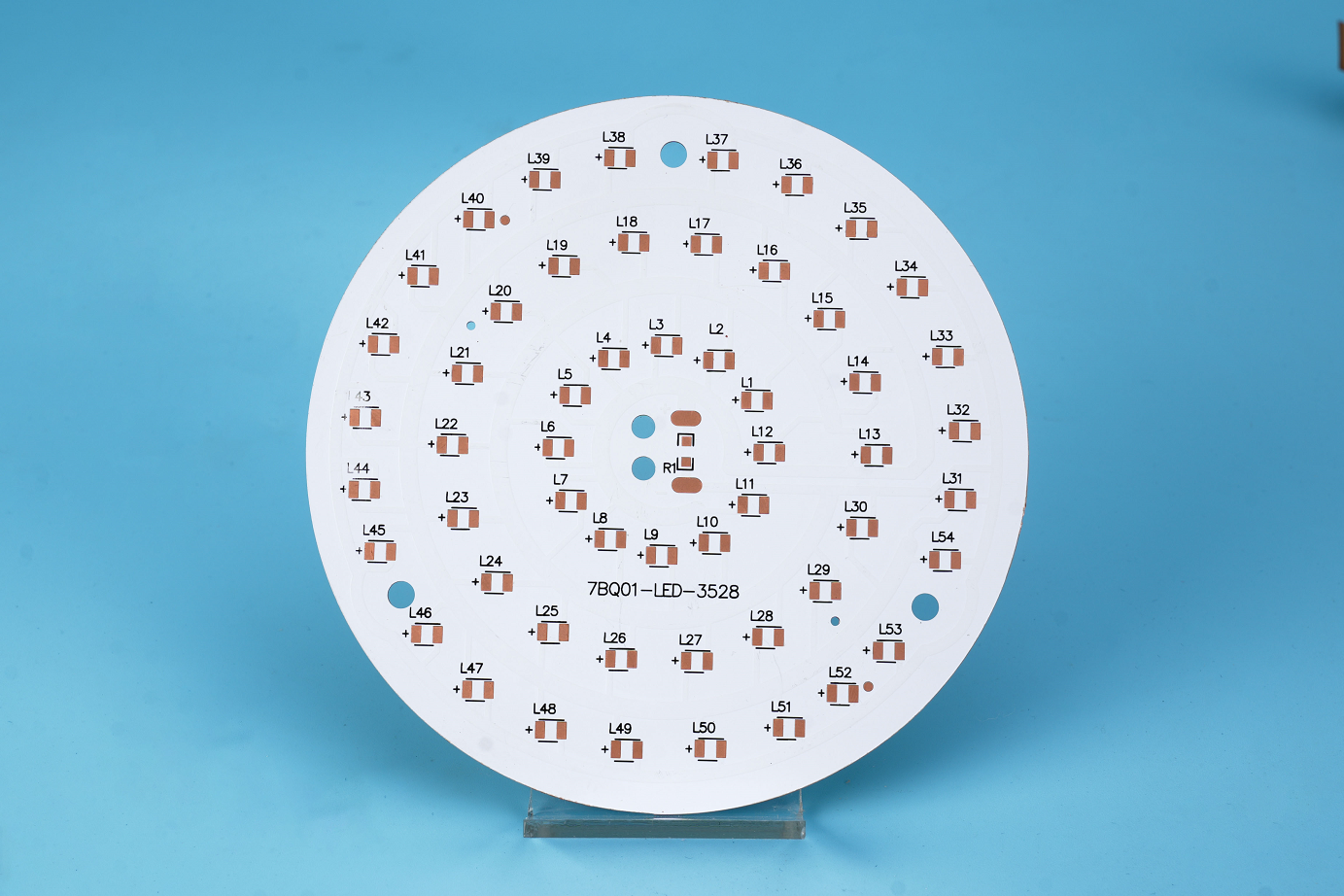
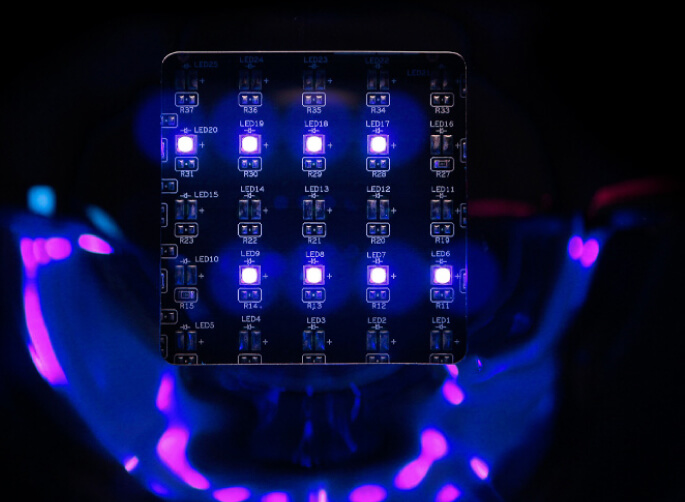
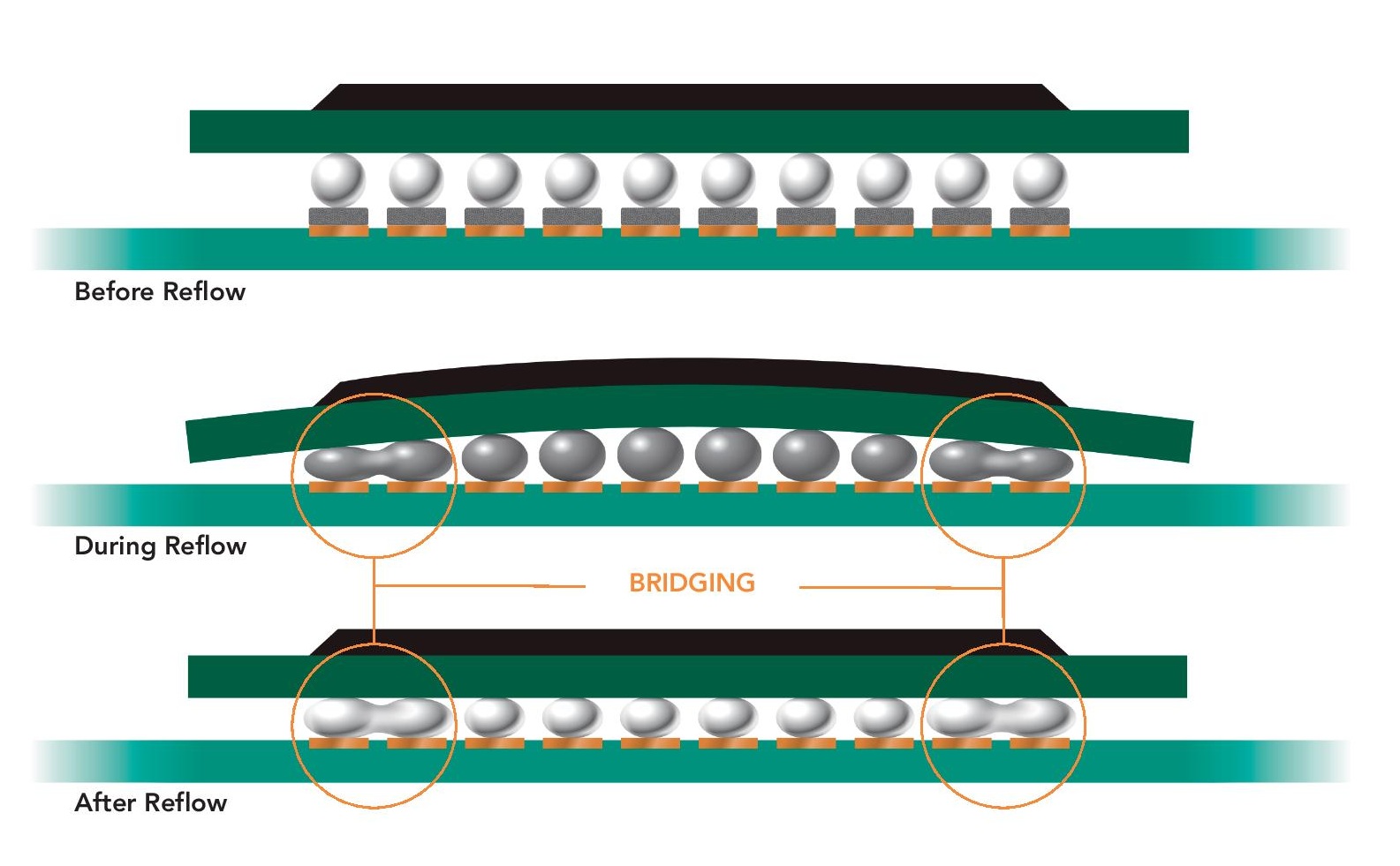
In the field of ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (UV LED), the integration of Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCB) plays a significant role in improving UV LED performance, thermal management, and overall reliability. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of MCPCB in UV LED applications, highlighting its advantages with concrete data to demonstrate its practicality.

- Efficient Heat Dissipation:
MCPCBs excel in efficient heat dissipation, ensuring optimal UV LED performance and longevity. With a metal core typically made of aluminum or copper, MCPCBs possess high thermal conductivity. For instance, MCPCBs have a thermal conductivity coefficient of normally 1.0-3.0 W/mK, it needs to be customized if the thermal conductivity exceeds 3.0W/mk. this exceptional thermal conductivity allows for rapid dissipation of generated heat, preventing heat accumulation and ensuring UV LEDs operate within their optimal temperature range.
2. Enhanced Thermal Conductivity:
MCPCBs contribute to effective heat dissipation through improved thermal conductivity. Studies indicate that MCPCBs can enhance thermal conductivity up to ten times higher than standard FR4 PCBs. Because the stack up of MCPCB is different with PCB, please see below stack up. This enhanced thermal conductivity aids in achieving a uniform temperature distribution across the entire MCPCB, reducing the risks of hotspots and thermal stress on UV LEDs. Consequently, UV LEDs can maintain their performance and reliability even during extended operation.
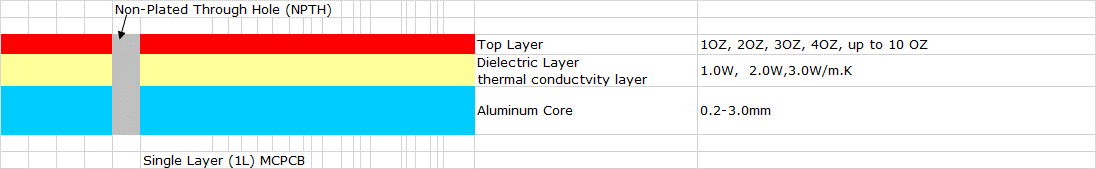
| 1oz | Copper layer |
| 1.5mm without copper | Core base |
3. Reliability in Harsh Environments:
MCPCBs are designed to withstand harsh environments, ensuring reliability in UV LED applications. The metal core of MCPCBs provides higher mechanical strength and resistance to thermal stress. For example, the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of an MCPCB can be matched with UV LEDs, minimizing the risk of mechanical failures caused by thermal mismatch. These features enable MCPCBs to operate reliably even in high-temperature environments or under exposure to ultraviolet radiation, thereby extending the lifespan of UV LED devices.

4. Electrical Isolation:
MCPCBs offer electrical isolation between the metal core and circuit layers, ensuring safe and reliable operation of UV LEDs. The dielectric layer, typically made of materials such as epoxy resin or thermally conductive dielectric (TCF), exhibits high breakdown voltage and insulation resistance. This electrical isolation minimizes the risk of short circuits or electrical interference, protecting UV LEDs and the entire system from potential damage.
5. Performance Optimization:
By incorporating MCPCBs into UV LED technology, manufacturers can optimize the performance of their UV LED devices. The improved heat dissipation and thermal conductivity of MCPCBs enable UV LEDs to operate at maximum efficiency. Research shows that using MCPCBs can reduce LED junction temperatures by up to 20-30┬░C, improving light output and enhancing overall performance. This optimal performance ensures consistent UV light generation, making MCPCBs an ideal choice for various UV LED applications, including curing, sterilization, and phototherapy.
Conclusion:
The use of MCPCBs in UV LED technology offers practical benefits in heat dissipation, thermal conductivity, reliability, and electrical isolation. Concrete data and research support the effectiveness of MCPCBs in efficient heat management, even in harsh environments, enabling reliable operation of UV LEDs. With enhanced performance provided by MCPCBs, UV LED systems can deliver consistent, efficient, and durable UV light output, expanding the possibilities of UV applications in various industries. The utilization of MCPCBs further solidifies their critical role as a key supporting technology in the UV LED field.
If you are designing a metal core PCB and seeking for a reliable manufacturer, welcome to leave you message or contact us directly.