Usually, direct current is mainly handled on PCB, but some people may ask: can alternating current be used in PCB? In the design and application of PCB, alternating current has specific usage. First of all, regarding the question of whether alternating current can be copper-plated, the answer is yes. Copper-plating can increase the grounding area, make the grounding firm, and make the signal return smooth.
What is Alternating Current?
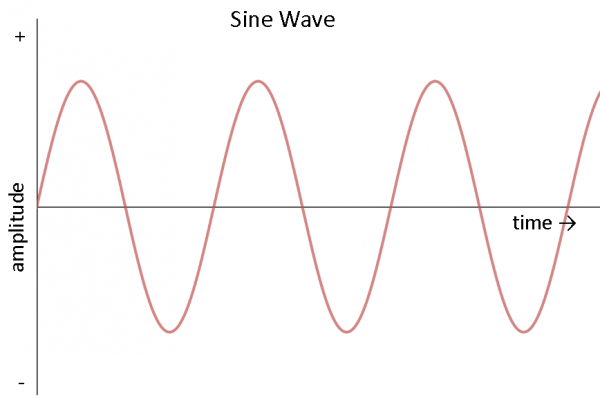
Alternating current (AC) refers to the current whose direction and magnitude change periodically over time. Unlike direct current (DC), the direction of direct current in the circuit remains unchanged, while alternating current will experience the process of flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode and then from the negative electrode back to the positive electrode during its cycle, forming a closed loop.
The main characteristics of alternating current include:
- ‚ÄĆPeriodic change‚ÄĆ: The current magnitude and direction of alternating current change periodically over time. The speed of this change is expressed by frequency, and the unit is Hertz (Hz). Common household AC frequencies are 50Hz or 60Hz, which means that the current changes direction 50 or 60 times per second.
- ‚ÄĆRMS‚ÄĆ: Since the current size and direction of AC are constantly changing, the Root Mean Square (RMS) is often used to describe its size.
- ‚ÄĆEasy to transmit and transform‚ÄĆ: AC can be easily increased or decreased in voltage through a transformer, which is of great significance for the long-distance transmission and distribution of electric energy.
- ‚ÄĆWidely used‚ÄĆ: Due to the above advantages, AC has been widely used in power systems, household appliances, industrial equipment and other fields.
In short, AC is a form of current whose direction and size change periodically over time, and it has the characteristics of convenient transmission and transformation and wide application.
Do PCBs use AC or DC?
PCBs mainly use direct current. ‚ÄĆ

In electronic circuits, direct current (DC) is a more common and used form of power supply. The purpose of power supply design is not only to convert AC to DC, but also to provide power to circuit components with the correct voltage and current.
Common voltage ranges include 1.8V to 12V, of which 1.2V, 1.8V, 3.3V, 5V, and 12V are the most commonly used voltages. Important parameters of the power supply include voltage, maximum current, voltage ripple, and heat loss at maximum current.
In PCB design, DC power is widely used to provide a stable power supply for the circuit, while AC power can be used for input, but before reaching the inside of the electronic device, it is usually converted into DC to meet the power needs of the electronic device.
In summary, PCB mainly uses DC because DC can provide stable and suitable power for electronic devices.
Can AC be used in PCB?
From an electrical principle, the conductive pattern on the PCB can transmit AC. As long as the design is reasonable and the parameters such as the width, thickness, and spacing of the conductive pattern can meet the transmission requirements of AC, AC can be used on the PCB.
In some electronic devices such as audio amplifiers and power adapters, AC is used on the PCB for signal transmission and power conversion.
What should be paid attention to when using AC in PCB?
1. Electromagnetic interference
- When AC is transmitted on PCB, electromagnetic radiation will be generated, which may interfere with surrounding electronic components and circuits.
- In order to reduce electromagnetic interference, reasonable layout, shielding measures, and filter capacitors can be adopted.
2. Insulation requirements
- The voltage of AC is usually higher than that of DC, and the insulation requirements are also higher. If the insulation is poor, it may cause safety problems such as leakage and short circuit.
- When designing PCB, it is necessary to select suitable insulating materials and ensure that there is sufficient insulation distance between the conductive line and the surrounding components and ground layer.
3. Heating problem
- AC generates heat due to the presence of resistance during transmission. If the heat cannot be dissipated in time, it may cause the PCB temperature to rise, affecting the performance and life of electronic components.
- The heating problem can be solved by optimizing the layout of PCB, adding heat sinks, and selecting low-resistance conductive materials.
What are the applications of using AC in PCB?
- Audio amplifier: Audio amplifiers usually need to process audio signals, which are essentially an AC. On the PCB of the audio amplifier, there will be special circuits for amplifying and processing audio signals, and these circuits will involve the transmission and processing of AC power.
- Power adapter: The power adapter usually needs to convert AC power to DC power to meet the power supply needs of electronic equipment. On the PCB of the power adapter, there will be components such as transformers and rectifier circuits to realize the conversion of AC power to DC power. These components will involve the transmission and processing of AC power.
- Communication circuit: In the field of communication, a modem is a device that converts digital signals into analog signals (modulation) for transmission on analog communication lines, and converts received analog signals into digital signals (demodulation). In the modulation process, AC signals are needed to carry digital information, and the circuits on the PCB are responsible for realizing the modulation and demodulation functions of these signals.
- Lighting circuit: Although LEDs are driven by DC power, in some large lighting systems, in order to facilitate power access and management, AC power is first converted to DC power and then drives the LED. In this process, the circuit on the PCB plays the role of power conversion and control, ensuring the stability and reliability of LED lighting.
What happens if you connect DC to AC?
Connecting DC to AC in a PCB can cause the device to not work properly or even be damaged. ‚ÄĆ
DC power and AC power are handled differently in circuits. DC power provides a constant current direction, while AC power provides a current direction that changes periodically.
In PCB design, it is critical to connect the power supply correctly, as incorrect connections can cause device failure or damage.
- ‚ÄĆDevice damage‚ÄĆ: If a DC device is designed to work only with DC power, connecting it to AC power may cause the electronic components inside the device to overheat, burn out, or otherwise be damaged.
- ‚ÄĆFunctional abnormality‚ÄĆ: Even if the device is able to operate briefly, the performance of the device will be affected due to the mismatch in design and may not achieve the expected working state.
- ‚ÄĆSafety issues‚ÄĆ: Improper power connection may also cause safety risks such as fire or electric shock, as the voltage and current changes of the AC power supply may cause circuit overload or power supply damage.
AC can be used safely and effectively in PCBs by properly designing circuits, taking effective electromagnetic shielding measures, ensuring good insulation performance, and solving heating problems. In practical applications, it is necessary to comprehensively consider various factors and select a suitable solution to realize the transmission and processing of AC on PCB according to the specific requirements of electronic equipment and working environment.


