Are you curious about aluminum LED PCB solutions? This guide explores their types, uses, cost-saving tips like âLED PCB separatorsââ, and how to select reliable manufacturersâ.
Best Technology specializes in âaluminum LED PCB with 48 hours rapid prototypingâ and âsmall volume orders at competitive pricingâ, leveraging advanced CNC routing and automated AOI systems for precision manufacturing. Our âISO 9001-certifiedâ facilities utilize ââ„2.5W/m·Kâ thermal-conductive substratesâ and âENIG-coated padsâ to ensure solder reliability, while âscalable production linesâ guarantee 20â30% cost savings for bulk projects. Trust us for âdurable, high-performance LED PCBsâ tailored to automotive, industrial, and consumer lighting needs. âRequest a quote todayâ: sales@bestpcbs.com
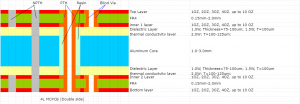
What Is Aluminum LED PCB?
An âaluminum LED PCB is a specialized circuit board designed to support high-performance LED systems by integrating an aluminum base layer. Unlike traditional boards, it leverages the metalâs âexceptional thermal conductivityâ to rapidly absorb and disperse heat generated by LEDs, preventing overheating and ensuring stable operation. This design prioritizes âefficient heat dissipationâ without relying on bulky cooling components, making it ideal for environments where space and reliability are critical. By maintaining lower operating temperatures, the Aluminum LED PCB directly enhances âLED brightness consistencyâ and extends the âlifespan of lighting systemsâ, offering a compact yet durable solution for modern LED technology.

What Are Types of Aluminum LED PCB?
Below are the types of aluminum LED PCB:
- Flexible Aluminum LED PCB –âBuilt with a bendable dielectric layer and thin aluminum core, this type supports curved or irregular designs while maintaining âheat dissipation efficiencyâ. Ideal for compact or dynamic lighting layouts, it avoids rigid structural limitationsâ.
- Hybrid Aluminum LED PCB -âCombines traditional FR-4 layers with an aluminum base layer, balancing cost and thermal management. The hybrid structure enhances rigidity and heat transfer compared to standard boards, offering a âcost-effective thermal solutionââ.
- Standard Single/Double Layer Aluminum LED PCB –âFeatures a single or dual conductive copper layer bonded to an aluminum substrate through an insulating dielectric layer. The single-layer variant is common for basic LED setups, while double-layer designs enable âcomplex circuitryâ for advanced lighting systemsâ.
- High Thermal Conductivity Aluminum LED PCB -âUses premium dielectric materials (e.g., ceramic-filled polymers) to achieve âthermal conductivity above 1.5W/m·Kâ, far exceeding standard boards. This type minimizes thermal resistance, ensuring rapid heat dispersion for high-power LEDsâ.

What Are Applications of Aluminum LED PCB Circuit Boards?
Here are application of aluminum LED PCB:
- Automotive Lighting Systemsâ-In âaluminum PCB LEDs for carsâ, these boards power headlights, taillights, and interior lighting. Their ârapid heat dissipationâ ensures stable performance in high-temperature environments, critical for safety and longevity in automotive designs.
- High-Intensity General Lightingâ-They are integral to LED streetlights, floodlights, and commercial fixtures, where âconsistent thermal controlâ prevents lumen degradation and extends operational life.
- Consumer Electronics–âCompact devices like LED displays, backlight units, and decorative lighting rely on aluminum PCBs to maintain âlow operating temperaturesâ in confined spaces.
- Industrial Equipment–âUsed in machinery lighting, UV curing systems, and medical devices, they withstand harsh conditions while ensuring âuninterrupted LED functionalityâ.
How to Test the Voltage Resistance of Aluminum LED PCB?â
Testing the âvoltage resistanceâ of aluminum LED PCBs ensures reliability in high-stress environments like automotive and industrial lighting. Below is a step-by-step guide to evaluate insulation integrity and withstand voltage performance:
1. Pre-Test Preparationâ
- Clean the PCB surfaceâ to remove dust, oxidation, or contaminants that could skew resultsâ.
Verify the âdielectric layer thicknessâ (â„75ÎŒm for automotive-grade PCBs) using calipers or microscopyâ.
2. Insulation Resistance Testingâ
- Use a âmegohmmeterâ (500â1,000V DC) to measure resistance between conductive traces and the aluminum base. Acceptable values exceed â10MΩâ at 25°Câ.
For humid environments, test at â85% relative humidityâ to simulate real-world degradation risksâ.
3. AC/DC Withstand Voltage Testingâ
- Apply â1,500V ACâ (or â2,120V DCâ) for 60 seconds between the circuit and aluminum substrateâ.
- Monitor for âleakage currentsâ (<10mA) and arcing. Failures indicate micro-cracks or dielectric flawsâ.
4. Dielectric Breakdown Voltage Testâ
Gradually increase voltage (500V/sec) until breakdown occurs. âTarget thresholdsâ:
- â„3kVâ for general LED stripsâ.
- â„5kVâ for automotive or aerospace applicationsâ.
- Conduct tests in âinsulated oil bathsâ to minimize external arcing risksâ.
5. Post-Test Validationâ
- Perform âmicroscopic inspectionâ to identify localized damage in dielectric layersâ.
- Use âthermal imagingâ to detect hotspots caused by residual leakage currentsâ.
- Safety Protocolsâ
- Ground the aluminum substrate to prevent electrostatic dischargeâ.
- Equip testers with âhigh-voltage glovesâ and isolation matsâ.

How to Solder LED Lamp Beads on Aluminum PCB?
Here is how to solder LED Lamp Beads on aluminum PCBs:
1. Workspace Preparation
Essential Tools:
- Hot air rework station (ensures even heat distribution).
- Lead-free solder paste (Sn96.5Ag3.0Cu0.5 recommended).
- Precision stencil (matches LED pad layout).
- ESD-safe equipment (prevents electrostatic damage).
2. Surface Cleaning
- Why It Matters: Aluminum alloy porous surface traps contaminants.
- Action: Wipe the PCB with isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and lint-free cloth. Avoid bare-hand contact post-cleaning.
3. Solder Paste Application
Technique:
- Secure the PCB on a flat surface.
- Align the stencil over LED pads.
- Spread paste evenly using a squeegee (45° angle, single pass).
- Tip: For dense LED arrays, use Type 4 solder paste to avoid slumping.
4. LED Placement
Precision Matters:
- Use a vacuum pick-and-place tool for accurate component alignment.
- Verify LED polarity matches PCB markings.
- Gently press LEDs into paste to ensure adhesion.
5. Reflow Soldering
Optimized Profile:
- Preheat: 120â150°C (ramp rate: 1â2°C/sec).
- Soak: 150â180°C (hold 60â90 sec).
- Peak: 217â227°C (hold 20â40 sec).
- Cooling: Gradual cooldown to avoid thermal shock.
- Critical Adjustment: Reduce peak temperature by 10â15°C compared to FR-4 PCBs due to the conductivity of aluminum alloy.
6. Final Inspection
Quality Checks:
- Visual: Uniform, conical fillets with no cold joints.
- Advanced: Use X-ray inspection to confirm void-free joints (<30% voids acceptable).
How to Choose a Reliable Aluminum LED PCB Manufacturer?
Hereâs how to identify a trusted aluminum LED PCB manufacturer:
1. Verify Material Expertise
- Black-Anodized Aluminum : Confirms compatibility with high-power LEDs.
- Thermal Conductivity Testing: Ask for reports proving â„2.0 W/m·K performance.
2. Assess Production Capabilities
- In-House Fabrication: Prioritize manufacturers with CNC machining and laser cutting facilities for tight tolerances.
- Surface Finish Options: Ensure they offer smooth matte finishes to enhance solder adhesion.
3. Quality Certifications
- Mandatory Standards: Look for ISO 9001, UL, and RoHS compliance.
- Advanced Testing: Request details on thermal cycling and vibration testing protocols.
4. Customization Flexibility
- Design Support: Choose partners offering DFM (Design for Manufacturing) reviews.
- Prototype Turnaround: Aim for â€5 days for sample delivery.
5. Client References
- Case Studies: Seek projects matching your application (e.g., automotive lighting, industrial panels).
- Review Feedback: Check third-party platforms for unbiased testimonials.
How to Reduce Production Cost of LED Aluminum PCB?
Here are practical strategies to reduce cost of LED aluminum PCB board:
- Optimize Material Selectionâ: Choose cost-effective aluminum substrates like 5052 or 6061 alloys, which balance thermal conductivity and affordability. Pair these with thin, high-performance dielectric layers to reduce material waste.
- Integrate LED PCB Separator Technology: Automated LED PCB separators, such as precision CNC routers, minimize material loss during panelization. This ensures maximum board yield and reduces scrap rates by 15-20%.
- Simplify Design Complexityâ: Avoid over-engineering by limiting layers and using standardized trace widths. Fewer laser-drilled vias and simplified layouts lower machining time and material consumption.
- Streamline Production Workflowsâ: Adopt automated processes like AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) to catch defects early, reducing rework costs. Bulk purchasing of raw materials (e.g., copper foil) also cuts expenses.
- Recycle Aluminum Wasteâ: Reuse scrap aluminum from separator processes for non-critical components. Recycling programs can offset up to 10-15% of raw material expenses.
FAQs of Aluminum PCB LED Strip Production
Q1: Why do my LED strips overheat?
A1: Overheating often stems from poor thermal design. Use aluminum PCBs with â„2.0 W/m·K thermal conductivity and add thermal vias to improve heat dissipation. Ensure airflow around the strips isnât obstructed.
Q2: How can I prevent delamination?
A2: Delamination occurs due to low-quality adhesives or improper curing. Choose high-temperature epoxy resins and follow curing guidelines strictly. Avoid exposing strips to excessive humidity during bonding.
Q3: What causes LED color inconsistency?
A3: Inconsistent binning of LEDs or voltage drops across the strip often cause color variation. Use LEDs from the same bin and implement current-limiting resistors to stabilize voltage.
Q4: Can I solder directly onto aluminum PCBs?
A4: Yes, but use low-temperature solder (â€220°C) to avoid damaging the aluminum oxide layer. Apply flux evenly to ensure proper adhesion.
Q5: How do I clean aluminum PCBs without damage?
A5: Use isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and a soft brush to remove debris. Avoid abrasive cleaners or ultrasonic cleaners, as they may erode the PCB surface.