Aluminum Core PCB Material mainly consists of aluminum, copper foil, and an insulating layer. Aluminum PCB Stackup refers to the specific layer structure and arrangement of an aluminum-based printed circuit board (PCB).
The most distinguishing feature of an aluminum PCB is its metal core, which is typically made of aluminum. Above the aluminum core, there is an insulating layer made from a high-performance dielectric material. On top of the dielectric layer, there is a copper layer where the circuit traces are etched. In some cases, there is a final protective coating or layer, such as solder mask or a conformal coating, placed over the copper traces. Whether you’re designing a high-performance device or a simple circuit board, understanding the materials and structure behind aluminum PCBs can help you make the right choice.

What is the material of aluminum PCB?
Aluminum PCBs are made primarily from aluminum, a material known for its excellent thermal conductivity, light weight, and high durability. The core of these PCBs is made of a solid aluminum base, which helps in dissipating heat away from the components. This makes them ideal for applications that involve high power and heat generation, such as power supplies, LED lighting, and automotive electronics.
In addition to the aluminum base, the board also includes a layer of insulating material, usually made from epoxy resin or other high-performance substrates. The insulating layer is key to preventing electrical conductivity between the aluminum and the circuit traces.
What is the material of metal core PCB?
Metal core PCBs, often referred to as MCPCBs, are made from a variety of metal materials, with aluminum being the most common. Other metals, such as copper and iron, can also be used for the core. However, aluminum is favored due to its superior thermal conductivity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of fabrication.
The construction of metal core PCBs generally involves three main layers: the metal base, an insulating dielectric layer, and the copper circuitry. The insulating layer separates the metal core from the copper traces, ensuring that the circuit functions as intended while preventing short circuits.
What is PCB core made of?
The PCB core is typically made from a conductive metal base, which is then covered with a layer of insulating material. For aluminum core PCBs, the core is an aluminum sheet, which is highly effective at conducting heat away from the components mounted on the PCB. The aluminum is often coated with a thin layer of insulation, such as an epoxy resin, which helps protect the metal and ensures that electrical components do not come into direct contact with the aluminum.
In more traditional PCBs, the core is often made of materials like FR4 (a fiberglass-based material), which provides mechanical strength and electrical insulation. However, aluminum core PCBs are preferred in applications where heat management is crucial, as aluminum offers far superior heat dissipation properties.
What material is commonly used for PCBs?
The material commonly used for PCBs varies depending on the application and the specific needs of the circuit. Standard PCBs often use materials such as FR4, a composite material made of fiberglass and epoxy resin. This material is inexpensive and easy to work with, making it the most widely used in everyday electronic devices.
However, in high-performance applications, materials with better thermal conductivity, such as aluminum, are used. These are typically referred to as metal core PCBs or MCPCBs. Aluminum, in particular, is a popular choice because of its combination of excellent thermal management and cost-efficiency.
What is the structure of aluminum PCB?
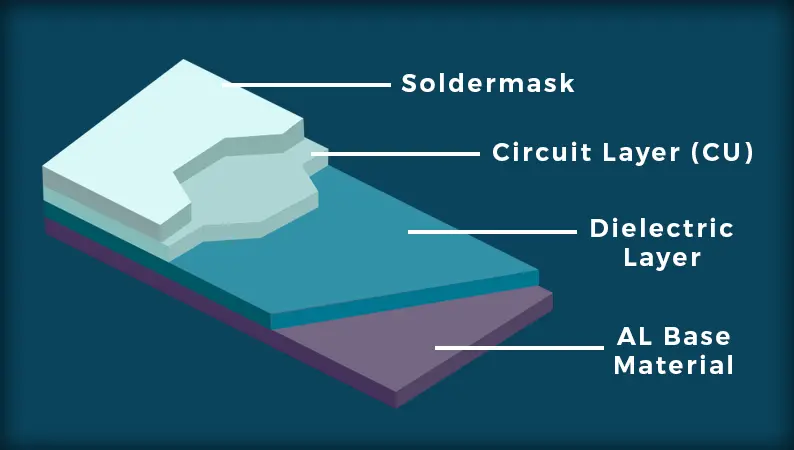
The structure of an aluminum PCB consists of several layers, each serving a specific purpose. The typical stackup includes:
Aluminum Core: The base layer made of aluminum, which provides heat dissipation.
Dielectric Insulating Layer: A layer of insulating material, typically made from epoxy or other high-performance resins, which electrically isolates the metal from the circuit traces.
Copper Layer: The top layer where the circuit traces are etched. This layer is where the components are mounted, and electrical connections are made.
The aluminum core helps dissipate the heat generated by the components, ensuring that the PCB can handle high-power applications without overheating. The insulating layer prevents short circuits by isolating the copper traces from the aluminum base.
Why use aluminum PCB?
Aluminum PCBs are used primarily for their ability to manage heat effectively. In applications where excessive heat is generated, such as in LED lighting systems or power electronics, aluminum PCBs are essential. The aluminum core helps in quickly transferring heat away from sensitive components, preventing damage and ensuring the device operates efficiently for longer periods.
Another benefit of aluminum PCBs is their lightweight nature, which makes them ideal for applications where weight is a consideration. The low cost of aluminum, compared to other materials like copper, also makes aluminum PCBs a more budget-friendly option without compromising on performance.
Furthermore, aluminum PCBs are extremely durable, offering high resistance to physical wear and corrosion. This makes them a good choice for outdoor or harsh environment applications, such as automotive or industrial equipment.
How do you make Aluminum PCB?
Manufacturing an aluminum PCB involves several steps. Below is a simplified process:
Designing the PCB: The first step is designing the PCB using CAD software. This includes specifying the copper traces, component placement, and thermal management requirements.
Creating the Aluminum Base: The aluminum base is cut and shaped to the required size. It is then coated with a thin layer of insulating material to electrically isolate the aluminum from the circuit traces.
Etching the Copper Layer: The copper layer is then applied to the insulating layer, and the circuit traces are etched into the copper using a photolithography process. This step defines the electrical pathways.
Drilling and Component Mounting: Holes are drilled into the PCB to allow for component placement, and the components are then soldered onto the board.
Testing and Inspection: Once assembled, the PCB undergoes thorough testing to ensure it meets quality standards and functions as intended. This includes thermal testing to check the heat dissipation capabilities of the aluminum core.
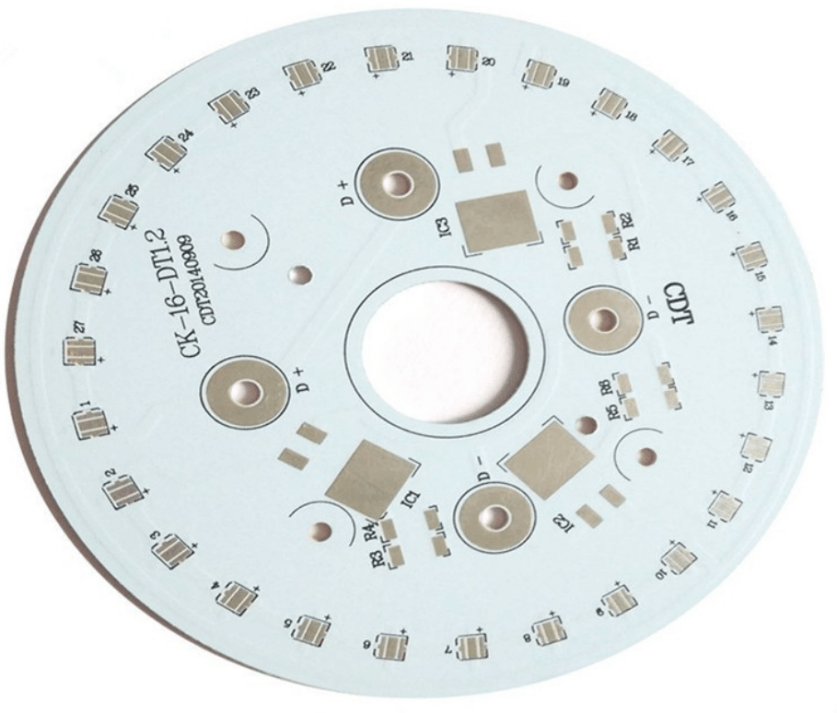
Aluminum core PCBs are an excellent choice for applications that require efficient heat dissipation and durability. Their unique structure, consisting of an aluminum base, insulating layer, and copper circuitry, makes them ideal for power-hungry devices like LEDs, power supplies, and automotive electronics. Understanding the materials used in aluminum PCBs and the stackup structure can help you make informed decisions when designing your own boards. When it comes to sourcing aluminum PCBs, choosing the right supplier is critical. Best Technology provides high-quality aluminum core PCBs that meet stringent performance standards and are customizable for your specific needs. Reach out to us at sales@bestpcbs.com for more details.