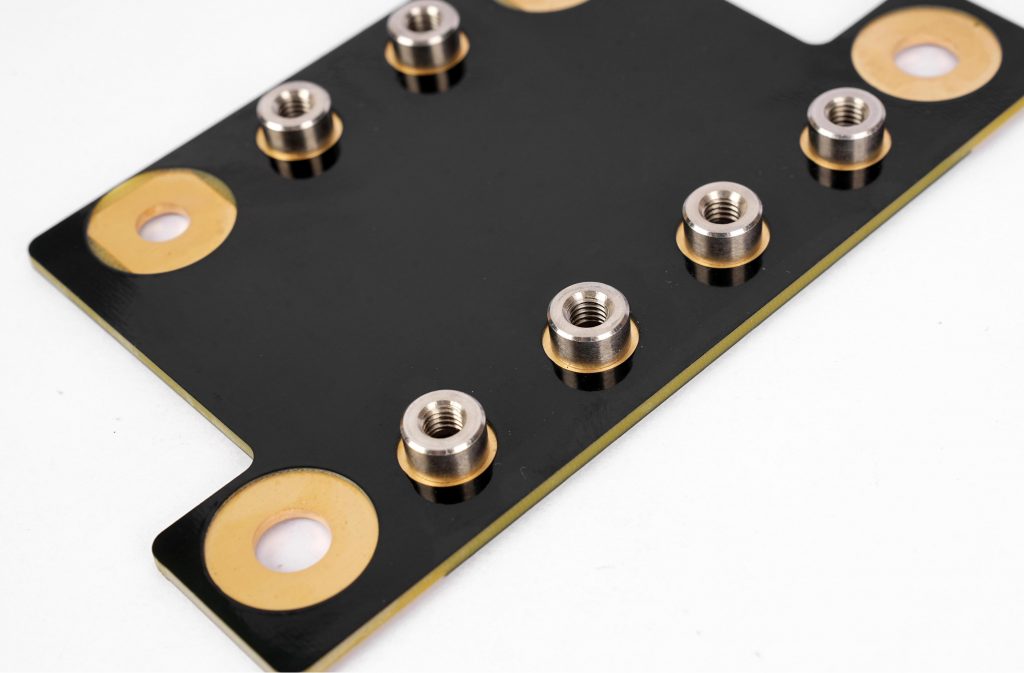
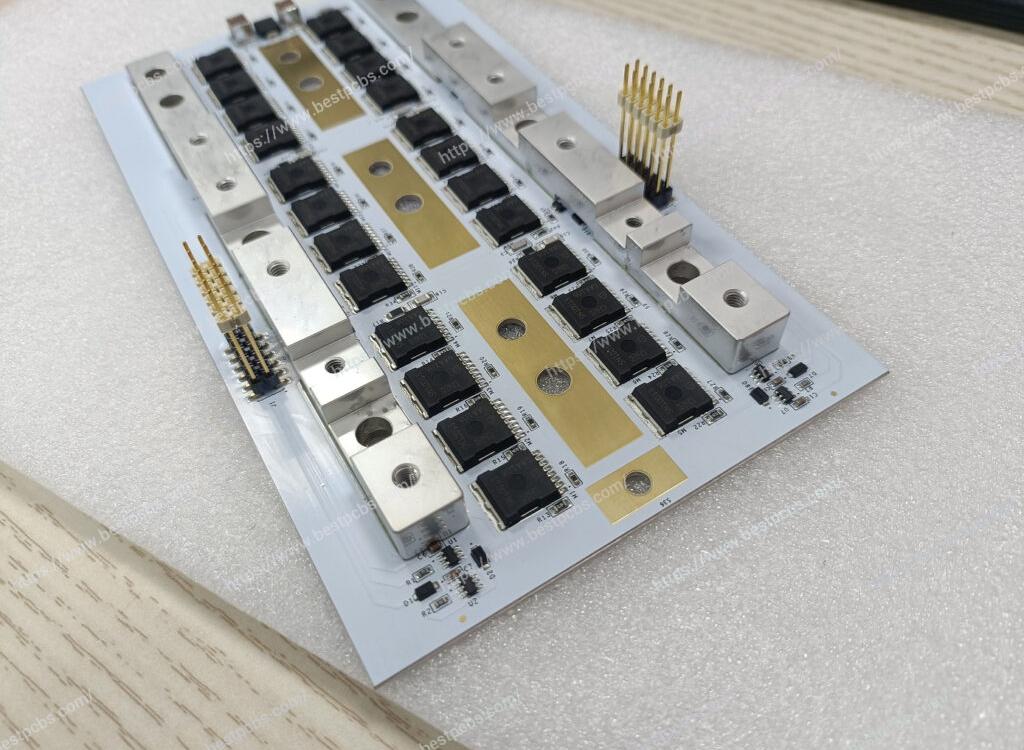
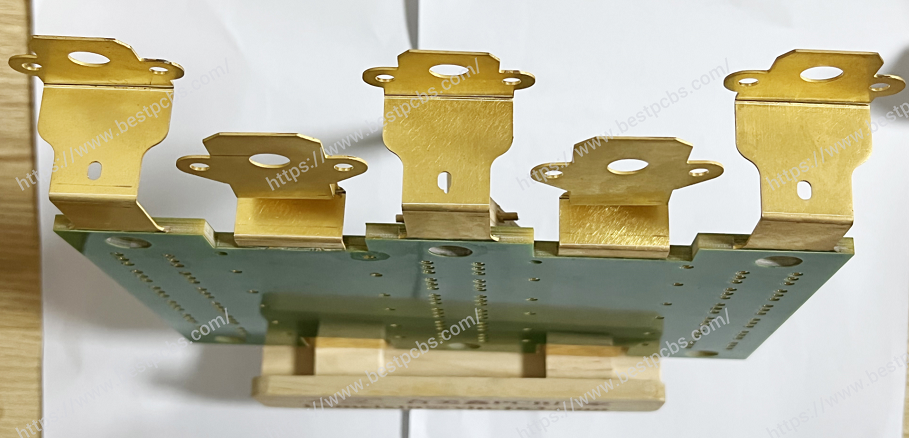
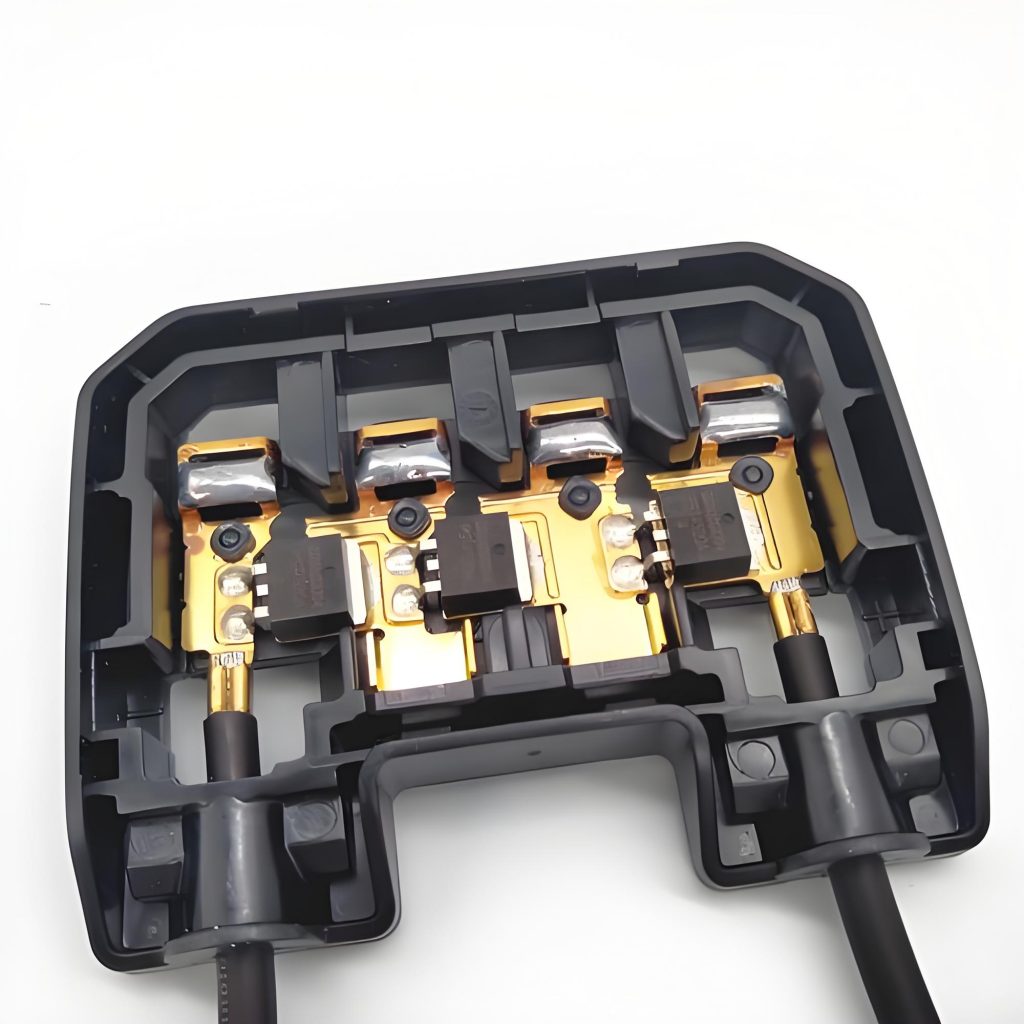
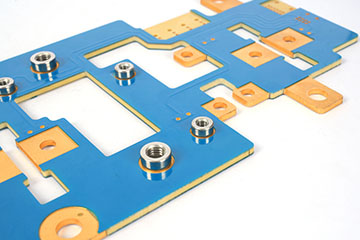
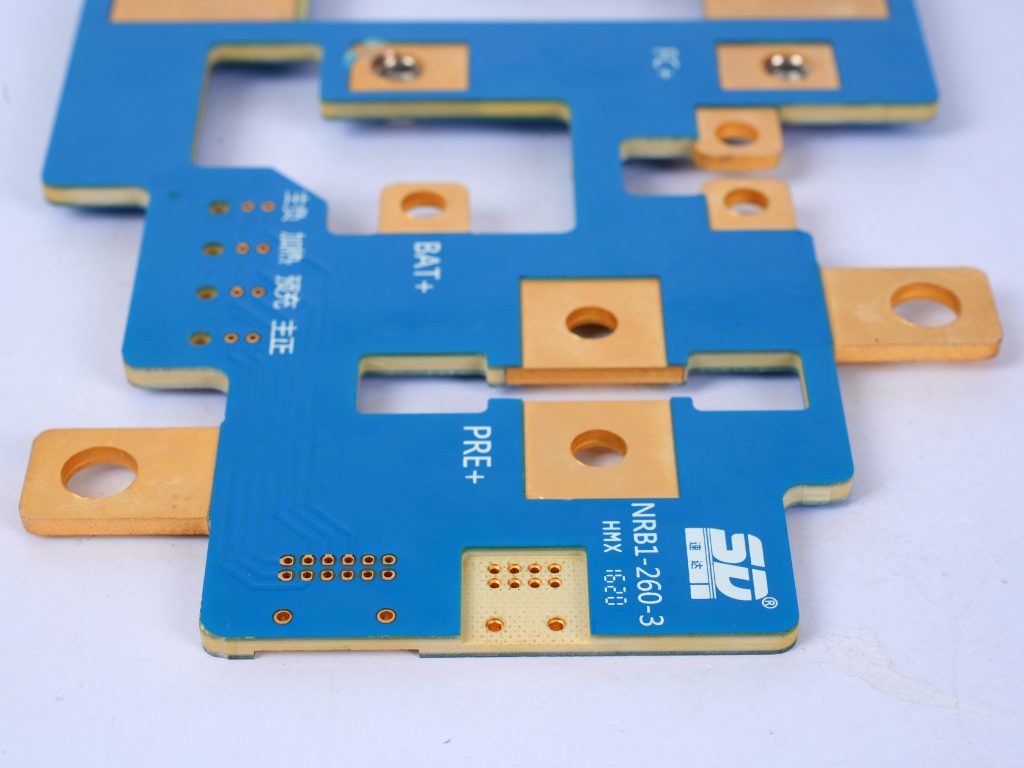
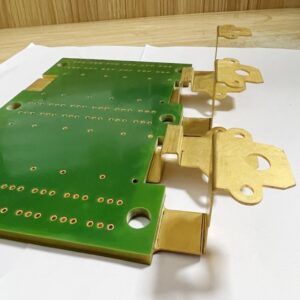
What are bus bar strips? A busbar is a conductive material used to transmit and distribute electrical energy in a power system. It is usually made of copper or aluminum and is long and used to connect multiple electrical devices or circuits to centrally supply power and distribute current.
What Are Bus Strips Used For?
Bus bar strips are used to distribute electrical power efficiently in complex systems. They consolidate multiple connections into a single point, reducing wiring complexity and improving organization. Common applications include:
- Power Distribution Panels: Used in industrial and residential setups to streamline power delivery.
- Automotive Systems: Found in vehicles to simplify wiring and enhance current flow.
- PCB Applications: Essential for compact and efficient circuit designs.
- LED Lighting Systems: Help in connecting multiple strips or components seamlessly.
By using bus bar strips, engineers and electricians can save space, improve system reliability, and enhance overall performance.
What Is the Purpose of a Busbar?
The primary purpose of a busbar is to act as a centralized conductor for distributing electrical power. It minimizes energy loss and provides:
- Efficient Current Distribution: Ensures a stable flow of electricity across multiple connections.
- Simplified Wiring: Reduces the need for individual connections, making systems more organized.
- Improved Safety: Lowers the risk of loose connections and overheating.
In essence, busbars enhance the efficiency and reliability of electrical systems, making them indispensable in both small-scale and large-scale applications.
Why Is a Bus Bar So Called?
The term “bus bar” originates from the Latin word “buss,” meaning a large container or a vessel. In electrical systems, a busbar “contains” and distributes electrical power. The term also draws from the concept of a “bus” as a shared pathway, emphasizing its role as a common connection point for multiple circuits.
What Are the Advantages of a Busbar?
Busbars offer numerous benefits that make them a preferred choice in modern electrical systems:
- Compact Design: Reduces the need for bulky wiring and creates a cleaner layout.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Minimizes resistance, reducing energy loss.
- High Current Capacity: Capable of handling large currents without overheating.
- Scalability: Easily adaptable for expanding systems.
- Durability: Often made from robust materials like copper or aluminum, ensuring long-term reliability.
These advantages make busbars ideal for use in industries where efficiency and reliability are critical.
What Is the Best Material for a Busbar?
The best material selection for busbars requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, including conductivity, mechanical properties, cost, and application scenarios.
Copper busbars are the preferred material for many demanding occasions due to their excellent conductivity, high mechanical strength, and good chemical stability. They can effectively reduce power loss and have excellent heat dissipation performance, making them very suitable for scenarios with extremely high reliability requirements, such as industrial power distribution systems.
However, copper has a high density, heavy weight, and high cost, which may become a limiting factor in some applications that are sensitive to weight and cost.
In contrast, aluminum busbars have significant advantages in weight and cost. The density of aluminum is only about one-third of that of copper, which makes aluminum busbars perform well in situations where equipment weight needs to be reduced (such as electric vehicles, new energy equipment, etc.).
In addition, aluminum has good corrosion resistance, and its anti-oxidation ability can be further improved through surface treatment.
However, aluminum is not as conductive as copper. Under the same cross-sectional area, the current carrying capacity of aluminum busbars is usually 35% to 40% lower than that of copper busbars, and its mechanical strength is also low, which is easy to deform.
How Do I Choose a Busbar Size?
Selecting the right busbar size is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. Key considerations include:
- Current Carrying Capacity: Determine the maximum current the busbar will handle.
- Material: Copper handles higher currents in smaller sizes compared to aluminum.
- Dimensions: Consider the width, thickness, and length based on the application.
- Temperature Rise: Ensure the busbar can operate without excessive heat generation.
Consulting industry standards or an experienced manufacturer can help you choose the ideal size for your needs.
What Is the Difference Between a Terminal Strip and a Bus Bar?
While both terminal strips and bus bars facilitate connections, their functions differ:
- Terminal Strip: Used for connecting and organizing wires. Each wire connects to an individual terminal.
- Bus Bar: Distributes electrical power among multiple circuits from a common point.
Terminal strips are ideal for low-power, detailed connections, whereas bus bars excel in high-power, streamlined applications.
Why Choose Best Technology for PCB Bus Bar Strips?
At Best Technology, we specialize in providing premium PCB bus bar strips tailored to your specific needs. Our products are designed for optimal performance and reliability, making them suitable for various industries. With over 18 years of experience, we offer:
- Custom Solutions: Tailored designs to meet unique requirements.
- High-Quality Materials: Ensuring durability and efficiency.
- Advanced Manufacturing: Equipped with state-of-the-art facilities in China and Vietnam.
- Global Support: Seamless delivery and dedicated customer service worldwide.
Whether you need copper bus bar strips for high-performance applications or lightweight aluminum options, we have the expertise to deliver excellence.
Conclusion:
Bus bar strips play a pivotal role in modern electrical systems, ensuring efficient power distribution and simplified wiring. Their versatility and reliability make them a valuable component in various applications. By choosing the right material, size, and design, you can enhance the performance of your systems.
For top-quality PCB bus bar strips and expert guidance, contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com. Let Best Technology be your trusted partner in achieving superior electrical solutions.