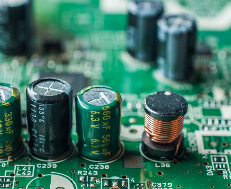
Capacitors are very common electronic components used in a wide range of applications, from simple circuits to complex devices. They store and release energy, regulate voltage, and filter signals. A crucial concept when working with capacitors is polarity—the orientation of the capacitor in the circuit. Some capacitors are sensitive to polarity and must be installed correctly to function as intended. Today, Best Team will take you know what is the capacitor polarity, and how to distinguish it correctly. Just keep reading!
What Is Capacitor Polarity?
First of all, let’s know what is polarity of capacitor. Capacitor polarity refers to the orientation of a capacitor’s terminals within an electronic circuit. Capacitors can be broadly categorized into two types: polarized and non-polarized. Polarized capacitors have a specific positive and negative terminal and must be installed accordingly. Non-polarized capacitors, on the other hand, can be placed in any orientation.

Polarity is really crucial in DC circuits, where current flows in one direction. For polarized capacitors, incorrect orientation can cause performance issues, damage to the component, or even safety risks. Recognizing and respecting polarity markings is a fundamental skill for anyone working with electronic circuits, like PCB assembly operators.
Types of Capacitors
Capacitors are categorized based on their structure, material, and usage. Each type has distinct properties for specific applications. Today, let’s introduce from non-polarized capacitor and polarized capacitor.
- Non-Polarized Capacitors
Non-polarized capacitors can be installed in either orientation, as they do not have designated positive and negative terminals. They are commonly used in applications involving alternating current (AC) or signals that change direction, such as in coupling, decoupling, and filtering circuits. Here we listing some common non-polarized capacitors used in the PCB manufacturing.
1. Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors are among the most widely used capacitors due to their small size, and reliability. They are constructed using ceramic material as the dielectric. Ceramic capacitors have high stability and can operate at high frequencies. They exhibit low loss, so they perform well in RF circuits like decoupling applications, timing circuits, and power supply bypassing.
2. Film Capacitors
Film capacitors use a thin plastic film as the dielectric. They have excellent stability, precision, and long lifespan. Film capacitors have low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and low distortion, that’s why they are popular in motor run circuits, high-power applications, and audio systems where sound clarity is critical.
3. Mica Capacitors
Mica capacitors use natural mica as the dielectric. These capacitors exhibit extremely low capacitance variation and high voltage handling. Therefore, they are primarily used in RF transmitters, resonant circuits, and precision filtering systems.
4. Polymer Capacitors
Polymer capacitors are a subtype of film capacitors that use conductive polymers as the dielectric. They offer a longer lifespan and higher reliability compared to traditional electrolytic capacitors. Commonly found in high-frequency and high-temperature environments, such as in automotive and industrial circuits.
- Polarized Capacitors
Polarized capacitors have designated positive and negative terminals and must be oriented correctly in a circuit. These capacitors are typically used in direct current (DC) circuits where high capacitance is required.
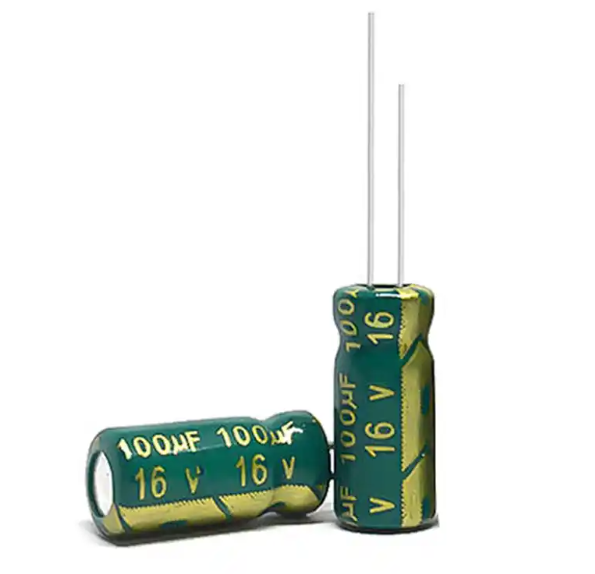
1. Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are the most common type of polarized capacitors. They use an electrolyte as the dielectric, allows a higher capacitance in a smaller size. These capacitors are capable of storing large amounts of energy and are relatively inexpensive.
2. Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors are smaller and more stable than electrolytic capacitors. They use tantalum metal as the dielectric. These capacitors are often used in space-constrained applications such as smartphones, laptops, and medical devices.
3. Supercapacitors
Supercapacitors, also known as ultracapacitors, are designed for extremely high capacitance values. They can store and release energy very quickly, widely used in backup power systems, regenerative braking in electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage.
Importance of Capacitor Polarity in PCB Design
The importance of capacitor polarity in PCB design is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Make sure the normal work
The correct capacitor polarity connection is to ensure the normal work of the circuit premise. If the polarity of the capacitor is reversed, the circuit will not work normally, and even damage the circuit board and components.
2. Affects the circuit performance
The polarity of the capacitor will cause the capacitor cannot play its due role. For example, if the electrolytic capacitor is reversed, the capacitor cannot be charged and discharged normally, which affects its filtering and energy storage functions .
3. Avoiding circuit failure
In PCB design, correctly marking and identifying the polarity of the capacitor can avoid circuit failure and ensure the stability and reliability of the circuit. Wrong polarity connections can cause short circuits, open circuits, or other electrical problems .
The specific application and mark method of capacitor polarity in PCB design:
- Tantalum capacitors and aluminum capacitors: These two types of capacitors are polar, usually by a ribbon, “+”, or beveled to indicate the positive terminal.
- Diode: Diode has unidirectional conductivity, and the negative electrode is identified by screen printing or pin length.
- Inductors: Multi-pin inductors have polarity, usually marked by a round dot or “*”.
How Do You Determine the Polarity of a Capacitor?
Determining the polarity of a capacitor is a straightforward process, thanks to the visible markings and conventions used by manufacturers. Here are some practical tips for identifying capacitor polarity:
Visible Markings
- Electrolytic Capacitors: These capacitors often have a stripe on the negative side, accompanied by a minus (-) sign.
- Lead Length: For through-hole capacitors, the longer lead typically indicates the positive terminal.
- Surface-Mounted Capacitors: Polarity is often marked on the component body or the PCB itself.
Datasheets and Manuals
If markings are unclear, consult the capacitor’s datasheet or the device’s manual. These documents provide detailed information about the component, including polarity.
What Happens if You Put a Capacitor in Backwards?
The consequences of installing a polarized capacitor backwards depend on the type of capacitor and the circuit’s conditions.
Performance Issues
A reversed capacitor may not function correctly. For instance, it may fail to store or release energy as required, leading to instability in the circuit.
Component Damage
Reverse polarity can cause internal damage to the capacitor. Electrolytic capacitors, in particular, are sensitive to incorrect orientation. Over time, the dielectric layer inside the capacitor may break down, resulting in leakage or failure.
Safety Risks
In extreme cases, a capacitor installed backwards may overheat or explode. This occurs when the internal pressure builds up due to chemical reactions. Such incidents can damage nearby components and pose safety risks.
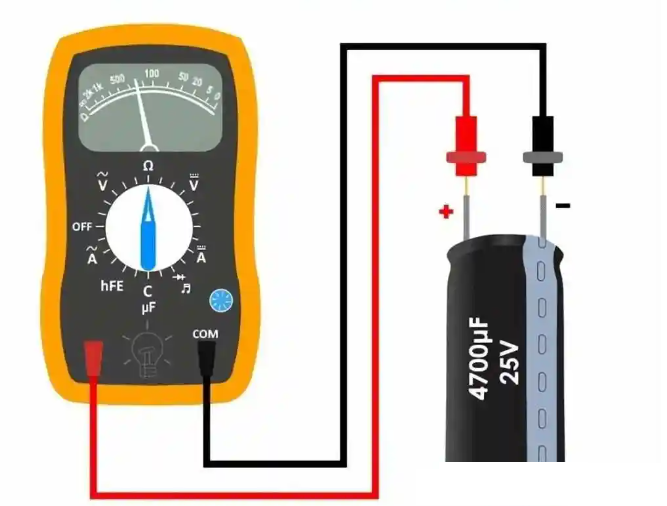
Can You Test the Polarity of a Capacitor with a Multimeter?
A multimeter is a valuable tool for testing the polarity of a capacitor. While multimeters are commonly used for measuring resistance, voltage, and continuity, they can also confirm the polarity of polarized capacitors. You can follow below steps to test it:
1. Set the Multimeter: Switch the multimeter to continuity or diode test mode.
2. Connect the Probes: Attach the probes to the capacitor leads.
3. Observe the Reading: A brief low reading indicates the positive probe is on the positive terminal. Switch the probes if no reading appears.
Applications of Capacitors
- Power Supplies
In power supply circuits, capacitors stabilize voltage and filter noise. Polarized capacitors are commonly used here due to their high capacitance values.
- Audio Systems
Capacitors improve sound quality by filtering signals and maintaining consistent performance. Non-polarized capacitors are often chosen for their ability to handle AC signals.
- Communication Devices
Capacitors play a crucial role in signal processing, ensuring accurate data transmission in communication systems. Both polarized and non-polarized capacitors are used depending on the application.
Tips for Ensuring Proper Capacitor Polarity
- Double-Check Markings: Always verify polarity markings on the capacitor and PCB before installation.
- Use Automated Tools: In production environments, automated testing equipment can confirm correct polarity placement.
- Consult Documentation: Datasheets and circuit diagrams provide essential information about capacitor orientation.
If you have any questions about capacitor, welcome to contact us.