What is a CCA Circuit Card Assembly?
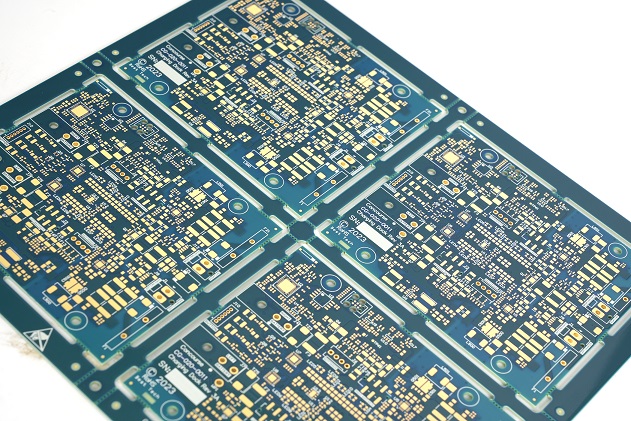
A circuit card assembly, often abbreviated as CCA, is a fundamental component in modern electronic devices. It is essentially a populated printed circuit board (PCB). A PCB is a flat board made of insulating material with conductive pathways etched or printed on it. The CCA takes this a step further by having electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and connectors mounted and soldered onto the PCB. These components are carefully placed and connected according to a specific circuit design, which enables the board to perform a particular function or set of functions within an electronic system. For example, in a smartphone, the CCA might be responsible for handling the communication functions, power management, or display control.
CCAs are essential in transforming electronic designs into physical devices. Without them, modern technology would lack the precision and functionality we rely on daily. They are not standalone products but rather building blocks for larger systems. Whether in smartphones, automotive controls, or industrial machinery, CCAs ensure devices operate as intended.
Circuit Card Assembly vs. PCB
When comparing a CCA to a PCB, there are several key distinctions. A PCB is the basic platform, typically a flat panel made of non-conductive material like fiberglass epoxy laminate, onto which conductive paths or traces are etched or printed. It serves as the foundation, providing the physical and electrical interconnectivity layout.
On the other hand, a CCA is a more complete and functional entity. It is a PCB that has been populated with various electronic components. These components, such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and connectors, are carefully mounted and soldered onto the PCB in accordance with a specific circuit design. For example, a PCB for a simple amplifier circuit might just have the etched traces for the signal path, but the CCA would have the actual transistors, resistors, and capacitors attached to perform the amplification function.
In terms of manufacturing, the PCB manufacturing process focuses on creating the board itself. This involves steps like preparing the substrate, imaging the circuit layout, etching the traces, and drilling holes for component mounting. The CCA manufacturing process builds upon this. It requires additional steps such as component sourcing, accurate component placement using pick-and-place machines, and soldering the components to the PCB. The quality of the PCB is vital for the success of the CCA. If the PCB has flaws in its traces, such as breaks or shorts, it can lead to malfunctioning CCAs.
Circuit Card Assembly Diagram
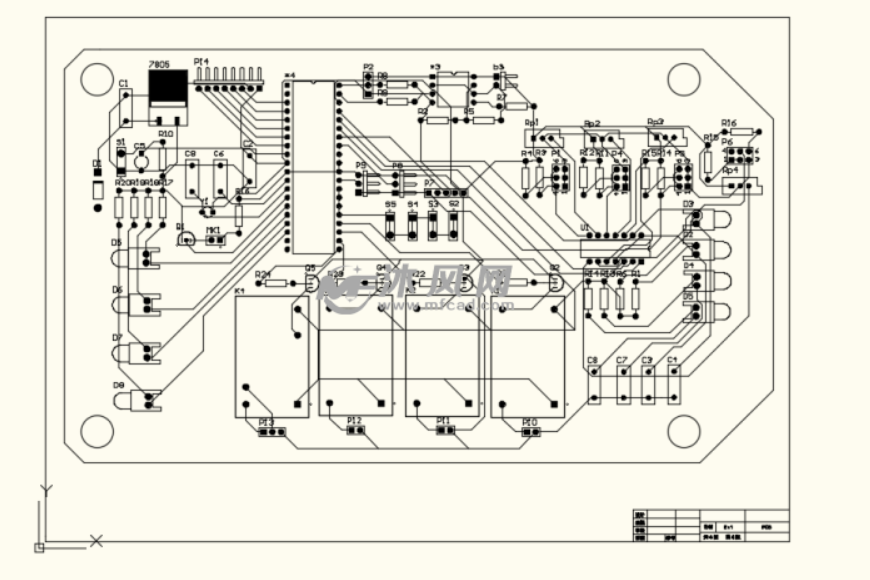
Circuit Card Assembly Design
Designing a circuit card assembly is a meticulous process. It begins with a clear understanding of the product’s purpose and functionality. Engineers follow these steps:
1. Schematic Creation:
The schematic acts as a blueprint, detailing the electrical connections between components. It defines how the circuit should operate.
2. PCB Layout Design:
The layout focuses on arranging components efficiently while ensuring signal integrity. Tools like CAD software help optimize space and performance.
3. Simulation and Testing:
Before physical production, simulations verify that the design meets all specifications. This minimizes errors in the final product.
4. Bill of Materials (BOM):
A BOM lists every component, including specifications and quantities. It ensures all necessary parts are available for assembly.
5. Prototyping:
A prototype is built to test the design under real-world conditions. Any issues are addressed before mass production.
If the prototype are verified, then you can go to next step – PCB mass production.
What is a Circuit Card Assembly Used For?
Circuit card assemblies are used in virtually every electronic application. Below are some examples of their widespread utility:
- Consumer Electronics
- Medical Equipment
- Aerospace and Defense
- Automotive Systems
- Industrial Automation
- Communication Devices
- Health-care
Circuit Card Assembly HS Code
What is Circuit Card Assembly HS Code? The Harmonized System (HS) Code for circuit card assemblies is 8538.90, which covers parts suitable for use solely or principally with the apparatus of heading 8537. This classification includes CCAs as essential components in various electronic systems. Correctly identifying HS codes ensures compliance with international trade regulations. Here are some commonly used HS codes in the electronics and circuit board industry:
- 8534.00: Printed circuits (excluding assembly). This code applies to bare PCBs, which have copper tracks and pads but no mounted components.
- 8537.10: Boards, panels, and consoles with electronic components for controlling electrical circuits.
- 8542.39: Electronic integrated circuits, including microprocessors and memory chips, which are often used in CCAs.
- 8473.30: Parts and accessories for computers, which may include PCBs and CCAs.
- 9030.90: Parts for measuring or testing instruments, often used for CCA inspection during manufacturing.
Circuit Card Assembly Manufacturers
If you are looking for a relibale circuit card assembly manufacturer, then Best Technology is your best-choice. Best Technology located in Shenzhen and Vietnam, it is a professional PCB and PCBA manufacturer. Our complete CCA manufacturing services are tailored to our customersâ needs in assemblies. We mainly focus on saving our clients time and money by delivering the highest quality box build assembly solutions:
- Complete Testing and Burn-In
- Pin Through-hole Assembly
- Selective Wave Soldering
- Conformal Coating
- Software Loading
- Complete box build for a variety of applications