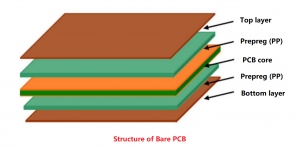
CEM1 PCB is a composite epoxy metal-based copper-clad laminate. It is made of flame-retardant epoxy resin impregnated paper or glass fiber cloth as the substrate, covered with copper foil on one side, and hot-pressed. CEM1 PCB has good mechanical strength, electrical properties and heat resistance, and is suitable for the manufacture of various electronic devices.
What is a CEM composite epoxy material?
CEM composite epoxy material is a material used for printed circuit boards (PCBs), mainly composed of epoxy resin, glass fiber cloth, wood pulp paper and copper foil. Its main features are excellent mechanical processing performance, lower cost than glass fiber cloth copper-clad laminate, and better performance than paper-based copper-clad laminate.
Types and applications of CEM composite epoxy materials:
CEM composite epoxy materials mainly include types such as CEM1 and CEM-3. CEM1 composite materials are made of glass fiber fabric surface and paper core combined with epoxy resin, and are mainly used in the printed circuit board industry.
CEM-3 is a composite copper-clad laminate that uses glass cloth and glass felt as a composite substrate. Unlike FR-4, its production process is similar to FR-4, but it uses a different substrate.
What type of PCB is FR4?
FR4 is a copper-clad laminate that is mainly used in printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing.
FR4, which stands for Flame-Retardant 4, is a composite material made of glass fiber and flame-retardant epoxy resin. It has excellent flame retardant properties and stable electrical properties, so it is widely used in the electronics industry.
FR4 board is mainly made of quadrifunctional epoxy resin plus filler and glass fiber cloth. Epoxy resin has good adhesion and electrical insulation, while glass fiber cloth provides mechanical strength and dimensional stability.
The specification standard of FR4 board is formulated by NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association), where FR represents the flame retardant grade.
FR4 copper clad laminate is divided into different grades according to performance and quality, mainly including:
- FR-4 A1 grade copper clad laminate: mainly used in high-end electronic products such as military industry, communications, computers, digital circuits, industrial instruments and meters, and automotive circuits.
- FR-4 A2 grade copper clad laminate: suitable for ordinary computers, instruments and meters, high-end home appliances and general electronic products, and its performance indicators meet the needs of general industrial electronic products.
- FR-4 A3 grade copper clad laminate: mainly used in the home appliance industry, computer peripheral products and general electronic products. On the premise that the performance meets the requirements, the price has a competitive advantage.
- FR-4 A4 grade copper clad laminate: It is a low-end material, but it can still meet the needs of ordinary home appliances, computers and general electronic products, and its price is the most competitive.
- FR-4 B grade copper clad laminate: The quality stability is poor, suitable for smaller circuit board products, and the price is the lowest.
In summary, FR4 is a high-performance copper clad laminate material, which is widely used in various electronic products and is favored for its excellent flame retardant properties and stable electrical properties.
What is the difference between CEM1 and FR4?
The main differences between CEM1 and FR4 are in terms of material composition, mechanical properties, electrical properties, heat resistance and cost.
Material composition and manufacturing process:
- FR4: It is composed of glass fiber and epoxy resin. Its manufacturing process is mature and the cost is relatively low, so it is widely used.
- CEM1: It is a composite epoxy resin material with wood pulp fiber paper or cotton pulp fiber paper as the core material, covered with glass fiber cloth on the surface, and impregnated with flame-retardant epoxy resin. Compared with FR4, CEM1 has slightly inferior mechanical properties and heat resistance, but lower cost.
Mechanical properties and heat resistance:
- FR4: It has high mechanical strength and rigidity, suitable for complex electronic equipment and structures. It has good heat resistance and can remain stable at higher temperatures.
- CEM1: It has slightly lower mechanical strength and is suitable for electronic products with low performance requirements. Its heat resistance is also relatively poor.
Electrical properties:
- FR4: has excellent electrical properties, including high insulation resistance and low dielectric constant, suitable for electronic devices with high frequency and high-speed transmission.
- CEM1: The electrical properties are slightly inferior to FR4, and it is not suitable for high-frequency applications.
In summary, FR4 performs better in mechanical properties, electrical properties and heat resistance, and is suitable for electronic devices with high performance requirements; while CEM1 has more advantages in cost and is suitable for electronic products with low performance requirements.
What are the advantages of CEM1 PCB?
The main advantages of CEM1 PCB include the following aspects:
- Excellent mechanical properties: CEM1 PCB has excellent mechanical properties, and its impact force can reach 0.093 inches. Compared with paper grades, CEM1 is easy to stamp and has higher bending strength.
- High cost-effectiveness: The cost of CEM1 PCB is lower than that of glass fiber cloth copper clad laminate, so it has significant advantages in cost control.
- Good electrical performance: The electrical performance of CEM1 PCB is also excellent, suitable for various electronic devices, especially in the LED lighting market, CEM1 is able to achieve the best balance between heat dissipation performance and PCB cost.
- Wide range of applications: CEM1 PCB is widely used in the printed circuit board industry, especially in some low-end and mid-range products.
What are the disadvantages of CEM1 PCB?
- Mechanical durability: CEM1 printed circuit board lacks good mechanical durability.
- Production applicable type: CEM1 can be used to produce single-sided PCBs because its laminate is not compatible with through-holes.
- Fragility: PCBs produced by CEM1 are very fragile and can easily break if not handled properly.
- Substitutability and limitations: FR-4 can be used to replace CEM1. But in case FR-4 needs to be replaced, CEM1 can only replace single-layer FR-4 PCBs with limited functions.
Why is CEM1 PCB single-layer?
The main reason why CEM1 PCB is single-layer is due to its material properties and cost-effectiveness.
CEM1 PCB is a single-layer printed circuit board. Its material properties determine that it can only be made into a single-layer structure. CEM1 material is mainly composed of glass cloth and epoxy resin. This material structure makes the PCB board have only one conductive layer.
Although technological advances have made multi-layer PCBs possible, PCBs made of CEM1 materials still maintain a single-layer structure, mainly because of its cost-effectiveness and design complexity.
The design and manufacturing of single-sided PCBs are relatively simple and low-cost, suitable for low-density design requirements. Since there is only one conductive layer, more winding is required during wiring design, but this is acceptable in low-density designs.
In addition, the manufacturing process of single-sided PCBs is relatively fast and low-cost, which is one of the reasons why it is widely used.
What are the applications of CEM1 PCB?
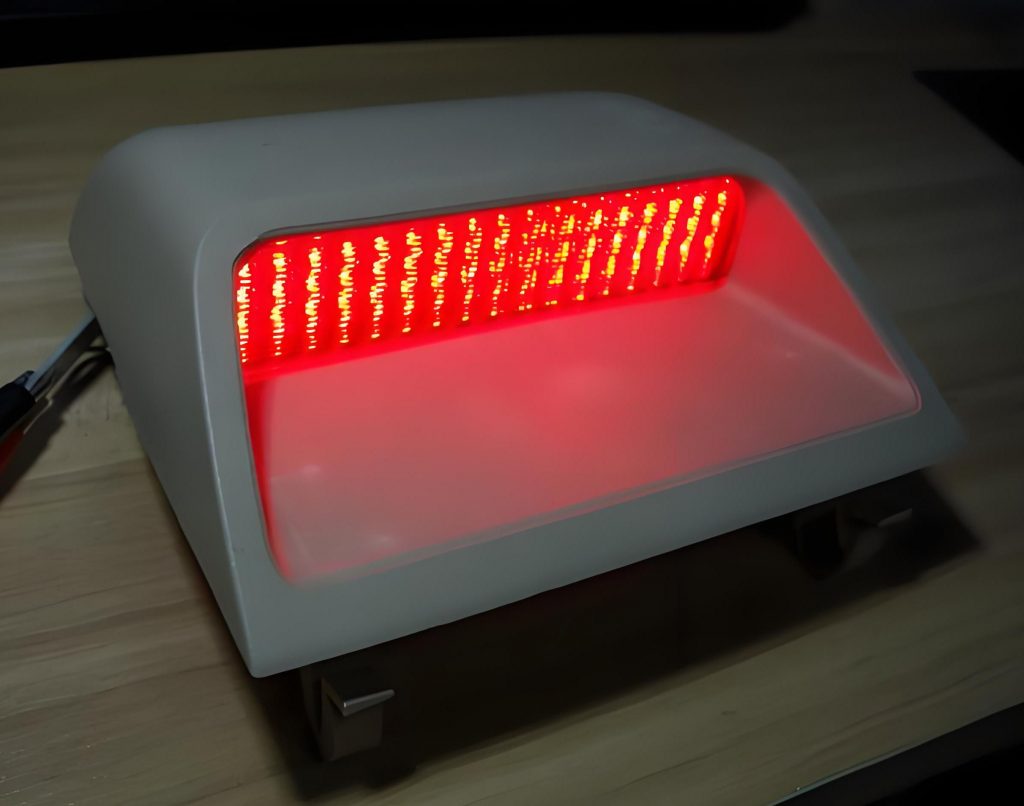
Simple applications and LED lighting: It can be used to make simple applications such as toys, remote controls, calculators, and home appliances. At the same time, headlights, indicator lights, and brake lights in LED lighting can also be made of CEM1 PCBs.
Computer Components: Computers are sensitive to heat, and LED CEM1 PCBs can conduct heat effectively, so computer components such as CPUs, floppy disk drives, and power supply units are made of them.
Industrial and Electronic Equipment: Used in the production of industrial controls, converters, instrumentation, UPS systems, hard disks, and telephone systems.
Medical Field: Tools used to perform surgeries are made of CEM1 LED PCBs, and even medical scanning technology uses such PCBs to manufacture scanning equipment.
As a special type of PCB, CEM1 PCB is widely used in the electronics industry for its good mechanical strength, electrical properties, heat resistance, and low cost. As electronic equipment continues to develop, CEM1 PCBs will also continue to innovate and develop to meet the needs of electronic equipment.