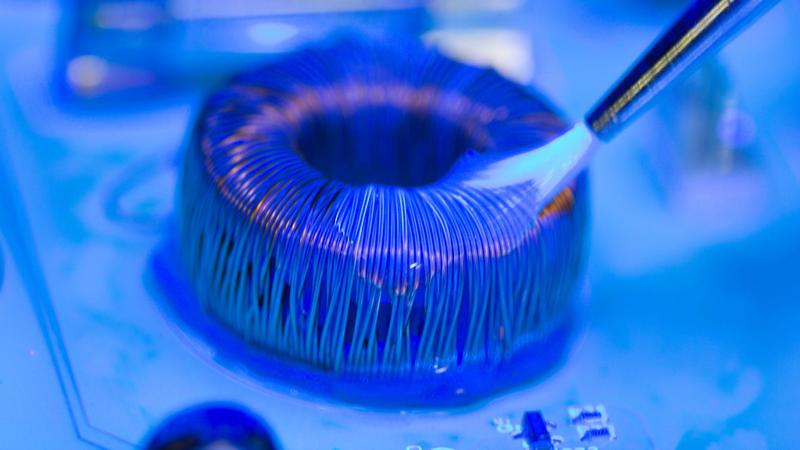
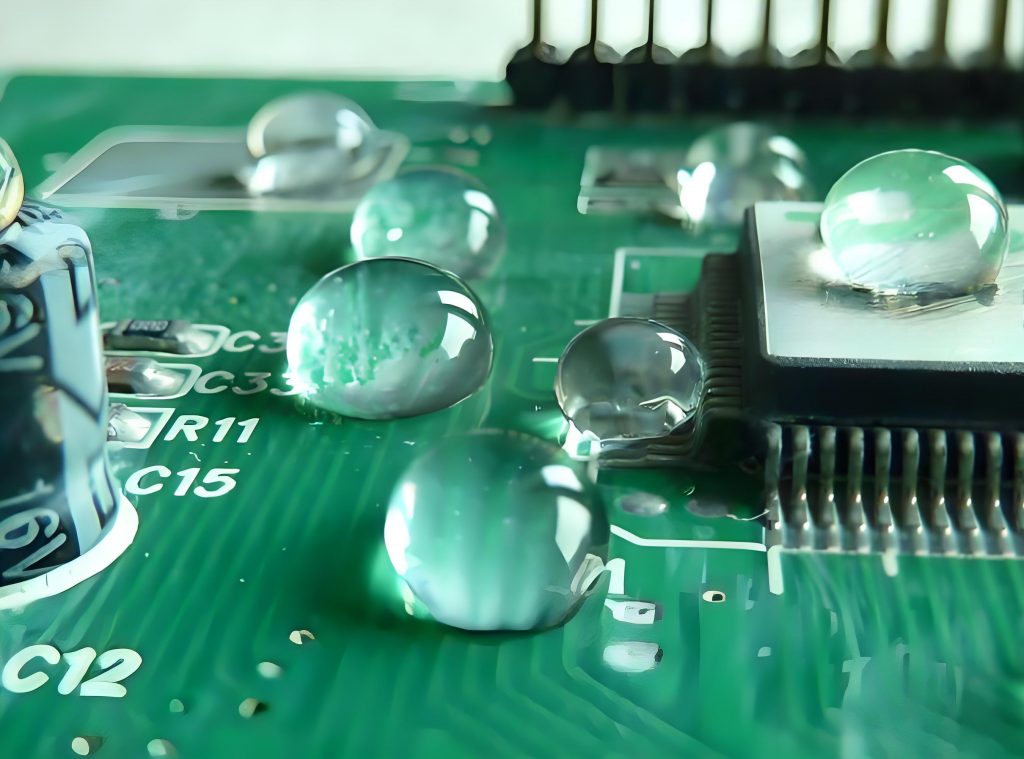
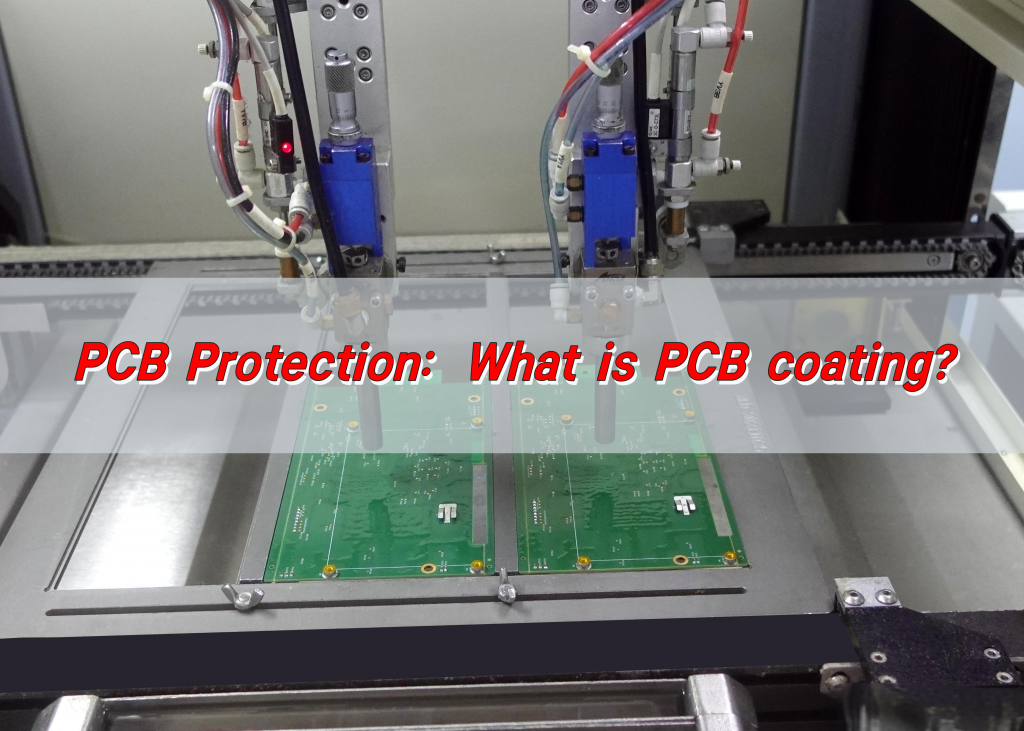
PCB conformal coating is a thin layer of polymer applied to the surface of a PCB to protect the circuits and board components from environmental stresses. The coating ensures that the PCB maintains high performance and reliability in the face of moisture, condensation, dust, dirt, chemicals, corrosion and other adverse environmental conditions.
What is Conformal Coating?
Conformal coating is a liquid polymer film applied to a printed circuit board (PCB) to protect it from environmental factors. It conforms to the board’s shape, covering components without affecting their function. This coating prevents damage from humidity, dust, salt spray, and chemical exposure, which can cause corrosion and electrical failures.
It is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, medical, and industrial electronics, where protection is crucial for long-term performance. The coating also helps prevent short circuits caused by contaminants and enhances the overall durability of the PCB.
What Are the 5 Types of Conformal Coating?
There are several types of conformal coatings, each offering unique benefits based on the application requirements. The five most commonly used coatings are:
- Acrylic acid (AR): After liquid coating, it is heated and cured at room temperature, providing cost-effective moisture protection, easy to apply and reworkable, suitable for conventional environments such as consumer electronics, but its high temperature resistance is limited.
- Silicone (SR): Ideal for extreme temperature environments, with excellent weather resistance and shock resistance, widely used in high reliability scenarios such as aerospace and automotive electronics.
- Polyurethane (UR): It has strong chemical resistance and wear resistance, but it is difficult to remove after curing, suitable for industrial control panels that require long-term protection and low maintenance requirements.
- Epoxy resin (ER): Thermosetting materials require high temperature curing, provide a rigid protective layer, and are extremely resistant to solvents, moisture and mechanical stress, but the high hardness makes rework difficult, and is mostly used in military or harsh environment equipment.
- Parylene (XY): It is formed into a thin film through vacuum vapor deposition, has excellent moisture resistance and chemical resistance, and is suitable for precision scenarios such as medical implants and high-frequency circuits, but the process is complex and the cost is high.
Each type has its advantages depending on the operating environment, durability needs, and repairability of the PCB.
Do All PCBs Have Conformal Coating?
No, not all PCBs require conformal coating. It depends on the intended use of the board. Consumer electronics, such as smartphones and laptops, may not need it since they are protected within enclosures.
However, industrial, medical, and military PCBs often require this coating due to exposure to extreme conditions, moisture, or contaminants.
For products that must operate in outdoor, high-humidity, or chemical-rich environments, conformal coating is essential to maintain reliability.
What is the Point of Conformal Coating?
The primary purpose of conformal coating is to protect electronic circuits from environmental damage. It prevents issues like corrosion, oxidation, and short circuits caused by moisture or contaminants.
It also provides:
- Enhanced Reliability: Reduces the risk of failure in harsh conditions.
- Longer Lifespan: Protects components from physical and chemical wear.
- Improved Performance: Prevents signal interference from conductive debris.
- Cost Savings: Reduces maintenance and replacement costs over time.
With conformal coating, PCBs perform better, last longer, and withstand more challenging environments without degradation.
When to Apply Conformal Coating?
Conformal coating should be applied after the PCB assembly process but before final testing. This ensures that all components are correctly placed and functioning before adding the protective layer.
It is best applied when:
The PCB will be exposed to moisture, dust, or chemicals.
The circuit operates in high-temperature or high-humidity environments.
There is a risk of vibration or mechanical stress affecting performance.
Applying the coating at the right stage prevents contamination and defects while ensuring maximum protection.
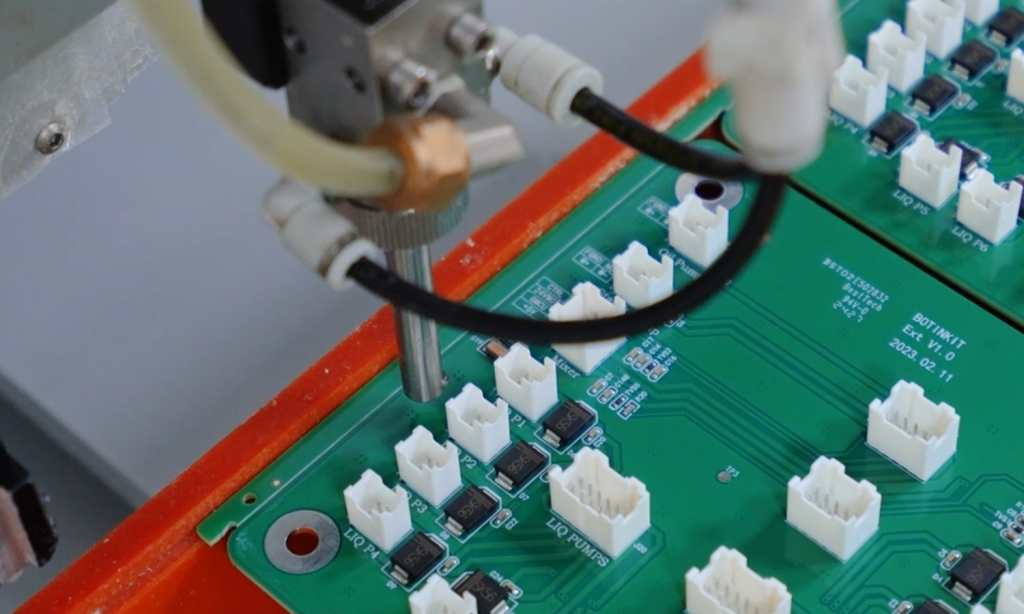
How to Apply Conformal Coating?
The application method depends on the type of coating, production volume, and precision requirements. The most common methods include:
- Brushing: Ideal for small-scale or repair applications. Simple and cost-effective but less precise.
- Spraying: Provides an even coating over large surfaces. Used for medium-scale production and manual application.
- Dipping: PCB is submerged in the coating liquid. Ensures full coverage but may lead to excess material buildup.
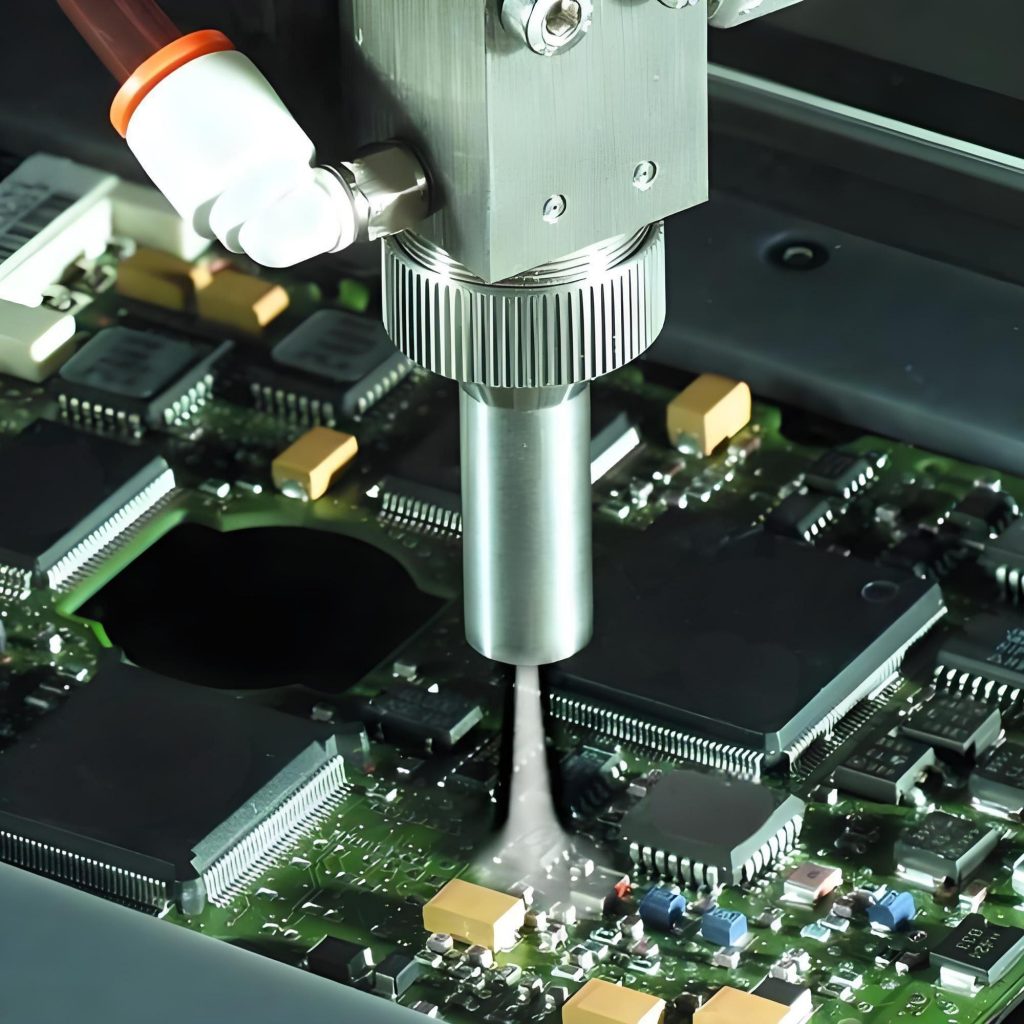
- Selective Coating Machines: Uses robotic arms to apply coating only where needed. Precise and efficient for high-volume production.
After application, the coating must cure using air drying, heat, or UV light, depending on the material used. Proper curing ensures maximum adhesion and durability.
How to Remove Conformal Coating?
Although conformal coatings are designed to be permanent, they can be removed when necessary, such as during repairs or modifications. The removal method depends on the type of coating:
- Solvent Removal: Works for acrylic and some urethane coatings. Chemical removers dissolve the coating without damaging the PCB.
- Thermal Removal: Applying heat softens some coatings, making them easier to scrape off.
- Mechanical Removal: Abrasive tools can scrape or sand away rigid coatings like epoxy.
Proper removal ensures that the PCB remains intact while allowing for necessary repairs or modifications.
What Are the Disadvantages of Conformal Coating?
Although conformal coating provides excellent protection, it has some limitations:
- Difficult Repairs: Once coated, components can be harder to access for modifications.
- Extended Drying Time: Some coatings take longer to cure, delaying production.
- Application Complexity: Requires specialized equipment for precision coating.
- Removal Challenges: Hard coatings like epoxy are difficult to remove without damaging the PCB.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of conformal coating far outweigh the drawbacks, making it a valuable solution for electronic protection.
Is Solder Mask the Same as Conformal Coating?
No, solder mask and conformal coating serve different purposes.
- Solder Mask: A permanent protective layer applied during PCB manufacturing. It prevents solder bridges and protects copper traces from oxidation.
- Conformal Coating: Applied after assembly to protect against moisture, dust, and chemicals. It is a transparent layer that shields the entire circuit.
While both offer protection, solder mask is built into the PCB, while conformal coating is an additional layer for enhanced durability.
Can We Apply Conformal Coating?
Yes, BEST Technology provides professional conformal coating services backed by 18+ years of PCB manufacturing expertise.
With advanced conformal coating equipment and a team of skilled professionals, BEST Technology ensures precise application, superior protection, and long-lasting performance for circuit boards. Whether you need acrylic, silicone, urethane, epoxy, or parylene coatings, BEST Technology can meet specific requirements with high-quality, industry-standard solutions.
Conclusionļ¼
Conformal coating is an essential protective solution for PCBs operating in challenging environments. It ensures long-term reliability, prevents corrosion, and enhances performance in critical applications.
Though it adds complexity to the production process, the benefits of conformal coating far outweigh the disadvantages. It extends the lifespan of electronic devices. For professional PCB solutions, contact sales@bestpcbs.com