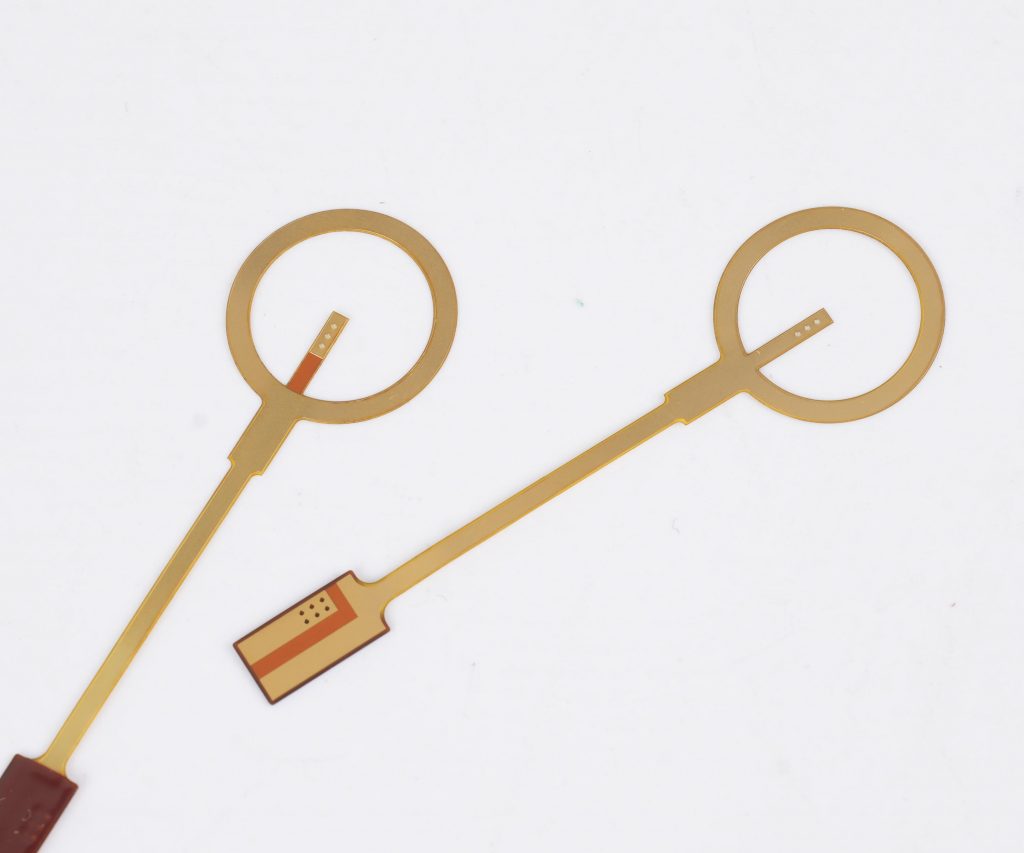
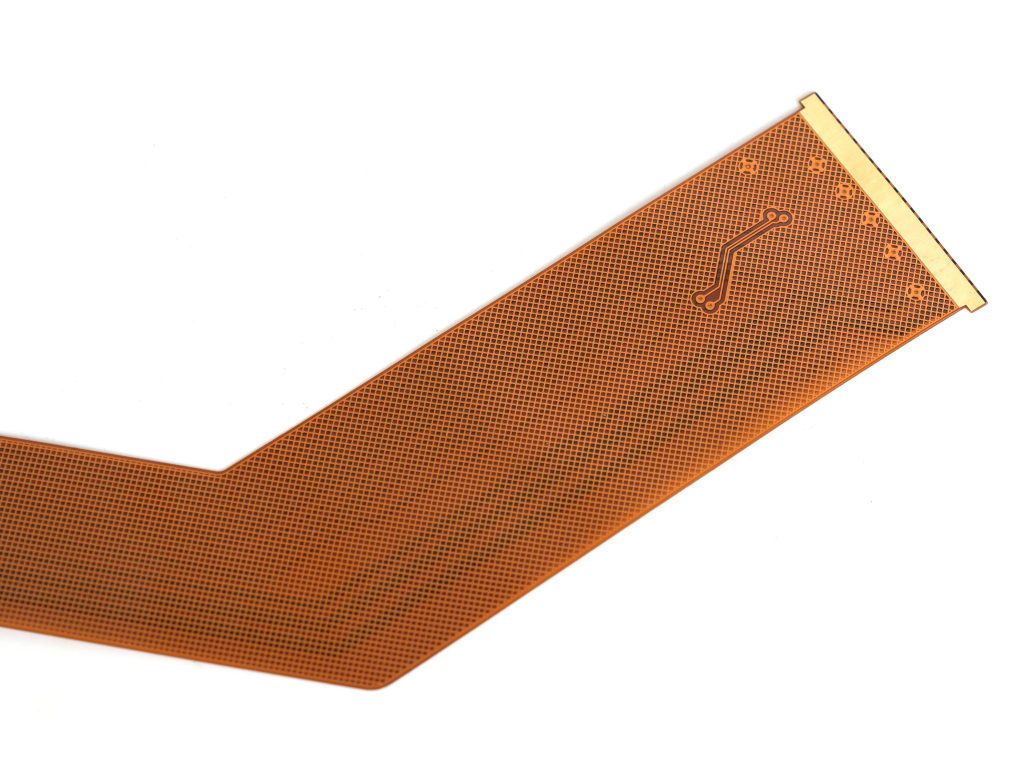
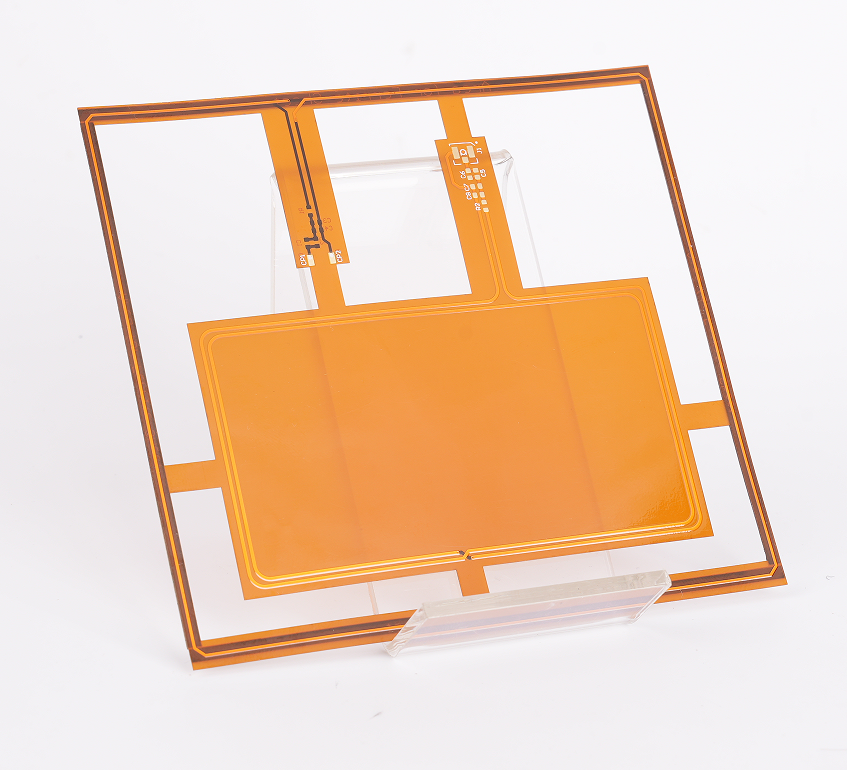
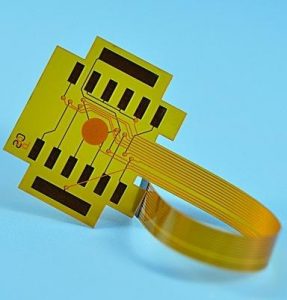
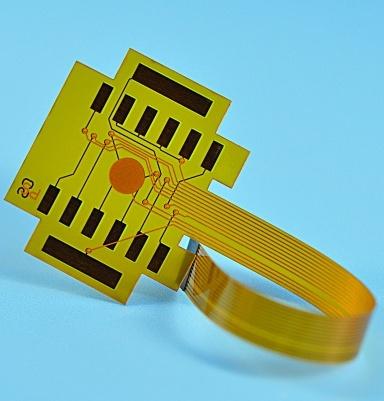
FFC cables refer to flexible flat cables, which are typically flat and can bend in multiple directions, making them ideal for compact, portable devices such as smartphones, laptops, and other electronics.
The unique design of FFC cables allows them to save space while ensuring a stable electrical signal transmission. These cables are often used when traditional, bulkier cables wouldn’t fit or could compromise the device’s design or functionality.
What Are FFC Cables?
FFC cables, or Flexible Flat Cables, are a type of electrical cable designed to transmit power and signals in a compact and flexible manner. These cables are made up of flat, thin conductors that are arranged in a specific pattern. What makes them stand out is their flexibility, allowing them to be bent, twisted, and routed through tight spaces without compromising their functionality. FFC cables are typically used in applications where space is limited but high performance is essential.
Their compact size and flexibility make FFC cables ideal for devices like mobile phones, laptops, cameras, and printers, where flexibility and space optimization are key. The design of FFC cables ensures they can be easily routed around corners or into confined spaces, making them invaluable in modern electronics.
What Are the Different Types of Flat Flex Cables?
Flat Flex Cables (FFC) are generally classified into two main types based on the alignment of their conductive contact points:
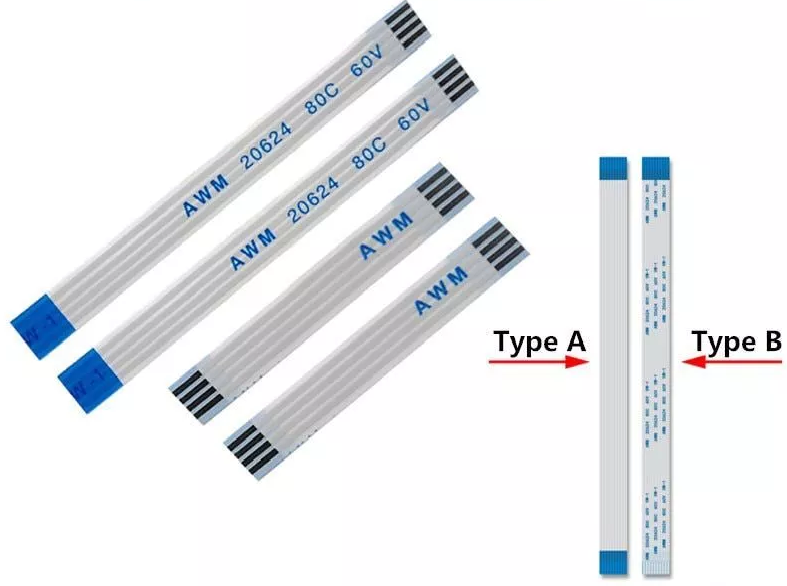
1. Type A (Same-Side Contact): The conductive contacts on both ends of the cable are on the same side. Commonly used when the connectors or devices at both ends have contacts facing the same direction. Ideal for straightforward and simple wiring setups.
2. Type B (Reverse-Side Contact): The conductive contacts on the two ends of the cable are on opposite sides. Typically used when connectors or devices at both ends require contacts on opposing sides.
What Does the Pitch of FFC Cables Refer to?
The pitch of FFC cables refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent conductive strips (or contacts) on the cable. It is measured in millimeters (mm) and is a critical specification for ensuring compatibility with connectors or devices.
The pitch indicates how closely the conductive strips are spaced. Common pitch sizes for FFC cables include 0.5mm, 1.0mm, 1.25mm, and 2.54mm, among others.
The pitch must match the spacing of the pins in the connector. Mismatched pitches can lead to poor connections or damage to the cable or device.
Smaller pitches (e.g., 0.5mm) are often used in compact electronic devices like smartphones and laptops. Larger pitches (e.g., 2.54mm) are preferred for applications requiring higher current or mechanical durability.
What Is the Size of Flexible Flat Cable?
The size of a flexible flat cable (FFC) can vary widely, depending on its application and design. In terms of width, FFC cables are typically available in sizes ranging from 1.0 mm to 1.5 mm. However, the size can be customized to meet the specific requirements of the application. The thickness of these cables is usually quite thin, with typical FFC cables measuring only a few millimeters thick. This compact size allows them to fit into tight spaces and be routed easily in small devices.
As for the number of conductors, FFC cables can come with anywhere from a few to several dozen conductors, depending on the complexity of the signal or power they need to carry. This makes them highly adaptable to a wide variety of uses, from simple connections to complex multi-wire systems.
What Is the Maximum Length of FFC Cables?
The maximum length of FFC cables depends on several factors, including the type of cable and the power or signal it carries. Generally, FFC cables are available in lengths ranging from a few millimeters up to several meters. However, the longer the cable, the more important it becomes to consider factors like signal integrity, resistance, and the quality of the materials used.
In most cases, FFC cables are designed for short to medium distances, typically within the range of 50 cm to 2 meters. However, for specialized applications, custom lengths can be manufactured. It’s important to note that longer cables may require additional shielding or signal conditioning to maintain signal quality over the distance.
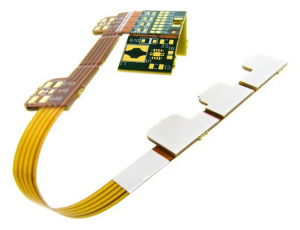
What Is the Difference Between FFC and FPC Cables?
While both FFC and FPC cables share similar characteristics, there are key differences that set them apart:

Design: FFC cables are made up of flat conductors that are spaced apart, whereas FPC cables have conductors printed directly onto a flexible substrate. This means that FPC cables can offer more complex circuit designs.
Application: FFC cables are generally used for more straightforward applications that require flexibility and simplicity, such as in consumer electronics. On the other hand, FPC cables are often used in highly specialized applications, including medical devices and aerospace, due to their ability to support more complex layouts.
Flexibility: While both types are flexible, FPC cables are often more flexible than FFC cables due to their thinner and more precise construction. This gives FPC Cables an advantage in applications that require frequent bending or folding. Best Technology offers a wide range of FPC products with high quality, tailored to meet the specific needs of each customer. Reach out to us at sales@bestfpc.com for more details.
Cost: FFC cables are usually less expensive to produce, while FPC cables, with their intricate designs and specialized applications, can be costlier.
Choosing between FFC and FPC cables depends largely on the complexity and requirements of the application. Both offer distinct advantages depending on your needs.
How to Choose FFC Cables?
Choosing the right FFC cables requires understanding the specific needs of your project. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting FFC cables:
Width and Pitch: Determine the width and pitch of the cable to ensure it fits in the space and connectors you are working with. Common pitch sizes are 0.5 mm, 1.0 mm, and 1.25 mm.
Conductor Count: Consider how many conductors you need for your application. More conductors are necessary for complex circuits or multiple connections.
Shielding: If your application is sensitive to electromagnetic interference (EMI), choose a shielded FFC cable to protect your signal integrity.
Length: Consider how far the signal needs to travel. Shorter cables are usually more efficient, but longer cables can be customized as needed.
Environment: If the cable will be exposed to extreme temperatures or harsh conditions, make sure to select a cable with the appropriate protective coatings or materials.
By evaluating these factors, you can ensure you choose the right FFC cables for your application.
What Are FFC Cables Used For?
FFC cables are used in a wide variety of applications where space is limited and flexibility is required. Some of the most common uses include:

Consumer Electronics: In devices like smartphones, laptops, tablets, and cameras, FFC cables connect internal components while maintaining a small profile.
Automotive Applications: FFC cables are used to connect sensors, controls, and displays in vehicles, providing both flexibility and reliability.
Medical Devices: These cables are often used in diagnostic equipment, portable devices, and other medical technologies where compact and flexible wiring is essential.
Industrial Equipment: FFC cables play a key role in controlling robotics, automation, and other industrial equipment that requires flexible connections.
Consumer Appliances: They are also used in household appliances like printers, washing machines, and microwaves for internal wiring connections.
The versatility of FFC cables makes them an ideal solution for numerous industries that require reliable, flexible, and space-saving connectivity.
What Are the Benefits of Flexible Flat Cable?
Flexible flat cables provide a number of key advantages that make them ideal for modern applications:
Space Efficiency: Due to their flat and thin design, FFC cables are perfect for applications where space is limited. They can be routed through tight spaces, making them ideal for compact devices.
Flexibility: These cables can be bent and twisted, allowing them to be routed around corners or other obstacles without damaging the conductors. This flexibility is particularly useful in dynamic environments where cables need to move.
Ease of Use: FFC cables are easy to install and require minimal space for connections. Their flat design allows for quick connections in a variety of environments.
Signal Integrity: Shielded FFC cables can provide excellent protection against electromagnetic interference, ensuring that your signals remain clear and strong.
Customization: FFC cables can be tailored to meet the specific needs of your application, with various pitches, lengths, and conductor counts available.
Overall, the benefits of flexible flat cables make them an excellent choice for many modern electronic and industrial applications, offering a balance of performance, flexibility, and compact design.
By focusing on the advantages and versatility of FFC cables, this blog provides readers with a comprehensive understanding of their types, uses, and benefits while maintaining a clear, approachable, and professional tone.