Would you like to know what types of PCB directory are? Let’s explore FR4, Flexible, ceramic and metal core PCB directories through this blog together.
At Best Technology, we can provide you service:
- Competitive Price & Premium Quality– Maximize your budget with cost-effective PCBs that meet stringent quality standards.
- 24 Hours Rapid Prototyping– Accelerates product development cycles.
- Free âDFM (Design for Manufacturabilityâ) Support -Prevents manufacturing errors before production.
- Full Turnkey Solution-handle PCB fabrication to assembly, saving vendor coordination time cost and production cost.
Feel free to contact us if you have any inquiry for FR4 PCB, FPC PCB, ceramic PCB and MCPCB: sales@bestpcbs.com.
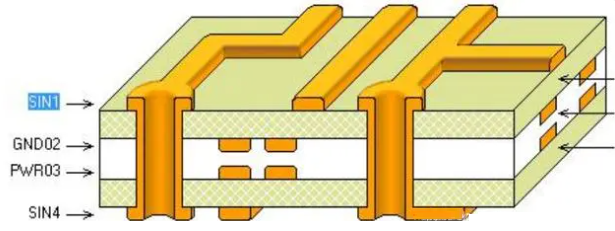
What Is PCB Directory?
PCB Directory is a professional online service platform dedicated to the global printed circuit board (PCB) industry. It aggregates resources from manufacturers, assembly providers, and design service firms, facilitating efficient supplier matching through parameter-based categorization (e.g., material type, layer count, thickness) and geographic filters. The platform supports specialized requirements such as flexible PCB and ceramic PCB, streamlining supply chain collaboration in electronics manufacturing and serving as a critical industry information hub.
What Are Types of PCB Directory?
Base Material Categories
1. FR4 PCB Directory
- Core Material: Fiberglass-reinforced epoxy composite.
- Parameters: Tg 130-180â, DK 4.2-4.8.
- Applications: Consumer electronics mainboards, industrial control systems.
2. Flexible PCB (FPC) Directory
- Core Material: Polyimide (PI) or polyester film.
- Technical Features: Bend radius â¤1mm, >100,000 flex cycles.
- Applications: Foldable smartphones, medical endoscopy devices.
3. Ceramic PCB Directory
- Material Systems: AlâOâ (96%), AlN, BeO.
- Thermal Performance: AlN 170-230W/m·K > AlâOâ 24-28W/m·K.
- Applications: High-power LED modules, aerospace radar systems.
4. Metal Core PCB(MCPCB) Directory
- Structural Types: Aluminum-backed (MCPCB), Copper-backed (IMS).
- Thermal Management: Thermal resistance as low as 0.5â/W.
- Applications: Automotive headlamp drivers, photovoltaic inverters.
FR4 PCB Directory
- Single Layer PCB
- 2 Layers PCB
- Multi-Layer PCB
- Heavy Copper PCB
- Bus Bar PCB
- Extra Thin PCB
- High Tg PCB
- HDI PCB
- RF Board
Our FR4 PCB capabilities:
| Item | Capabilities |
| Layer Count | 1 – 32 Layers |
| Max Board Dimension | 2424″ (610610mm) |
| Min Board Thickness | 0.15mm |
| Max Board Thickness | 6.0mm – 8.0mm |
| Copper Thickness | Outer Layer: 1oz~30oz, Inner Layer: 0.5oz~30oz |
| Min Line Width/Line Space | Normal: 4/4mil (0.10mm); HDI: 3/3mil (0.076mm) |
| Min Hole Diameter | Normal: 8mil (0.20mm); HDI: 4mil (0.10mm) |
| Min Punch Hole Diameter | 0.1″ (2.5mm) |
| Min Hole Spacing | 12mil (0.3mm) |
| Min PAD Ring(Single) | 3mil (0.075mm) |
| PTH Wall Thickness | Normal: 0.59mil (15um); HDI: 0.48mil (12um) |
| Min Solder PAD Diameter | Normal: 14mil (0.35mm); HDI: 10mil (0.25mm) |
| Min Solder mask Bridge | Normal: 8mil (0.2mm); HDI: 6mil (0.15mm) |
| Min BAG PAD Margin | 5mil (0.125mm) |
| PTH/NPTH Diameter Tolerance | PTH: ±3mil (0.075mm); NPTH: ±2mil (0.05mm) |
| Hole Position Deviation | ±2mil (0.05mm) |
| Outline Tolerance | CNC: ±6mil (0.15mm); Die Punch: ±4mil (0.1mm); Precision Die: ±2mil (0.05mm) |
| Impedance Controlled | Value>50ohm: ±10%; Valueâ¤50ohm: ±5ohm |
| Max Aspect Ratio | 0.334027778 |
| Surface Treatment | ENIG, Flash Gold, Hard Gold Finger, Gold Plating(50mil), Gold finger, Selected Gold plating, ENEPIG, ENIPIG; HAL, HASL(LF), OSP, Silver Immersion, Tin Immersion |
| Solder mask Color | Green/White/Black/Yellow/Blue/Red |
FPC PCB Directory
- Single Sided Flexible Circuits
- Double Sided Flexible Circuits
- Multilayer Flexible Circuits
- âFFC(Flat Flexible Cableâ)
- Dual Access Flexible Circuits
- Rigid-Flex Circuits
Our FPC PCB capabilities:
| Item | Capabilities |
| Layers Count | 1-10L |
| Max Board Dimension | 1L:500*2000mm; 2L:250*1380mm |
| Conductor Thickness | 1/3 OZ (12 um) – 4OZ (140um) |
| Min Line Width/Line Space | 2/2mil |
| Min Hole Spacing | NPTH:16mil; PTH:20mil |
| Hole Position Deviation | ±4mil (0.10mm) |
| Outline Tolerance | Laser: +0.15mm/-0.05mm; |
| Die Punch: +0.10/-0.20 mm | |
| Surface Treatment | ENIG(Au 4u”), Hard Gold Plating (Au 50u”), Immersion Silver, Immersion Tin, OSP, ENEPIG |
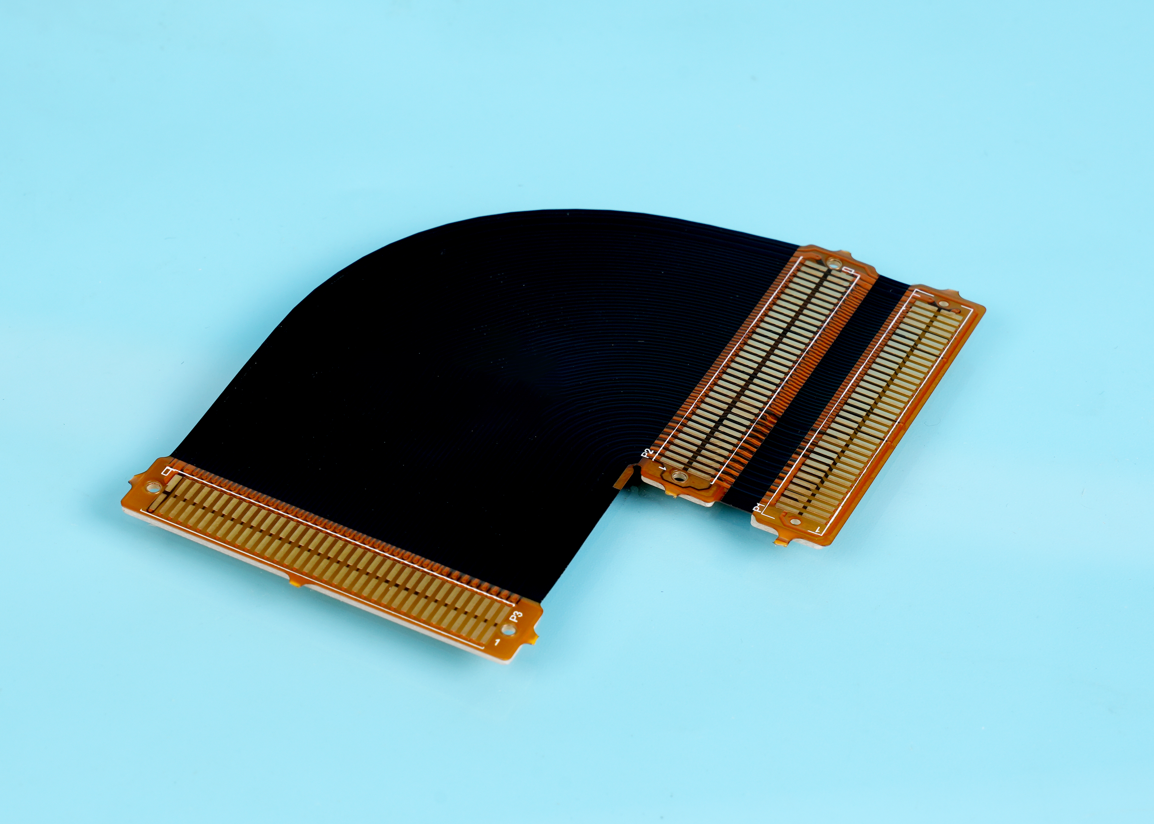
Our rigid-flex circuits capabilities:
| Item | Capabilities |
| Layers Count | 2-50L |
| Max Board Dimension | 500 Ã 500mm |
| Conductor Thickness | 0.5oz (18μm) – 2oz (70μm) |
| Board Thickness | 0.3mm â 4.0mm |
| Min Line Width/Line Space | 4/4mil |
| Min Hole Spacing | NPTH: 16mil; PTH: 20mil |
| Min Solder Mask Bridge | 8mil |
| Impedance Controlled | ±10% (>50Ω); ±5Ω (â¤50Ω) |
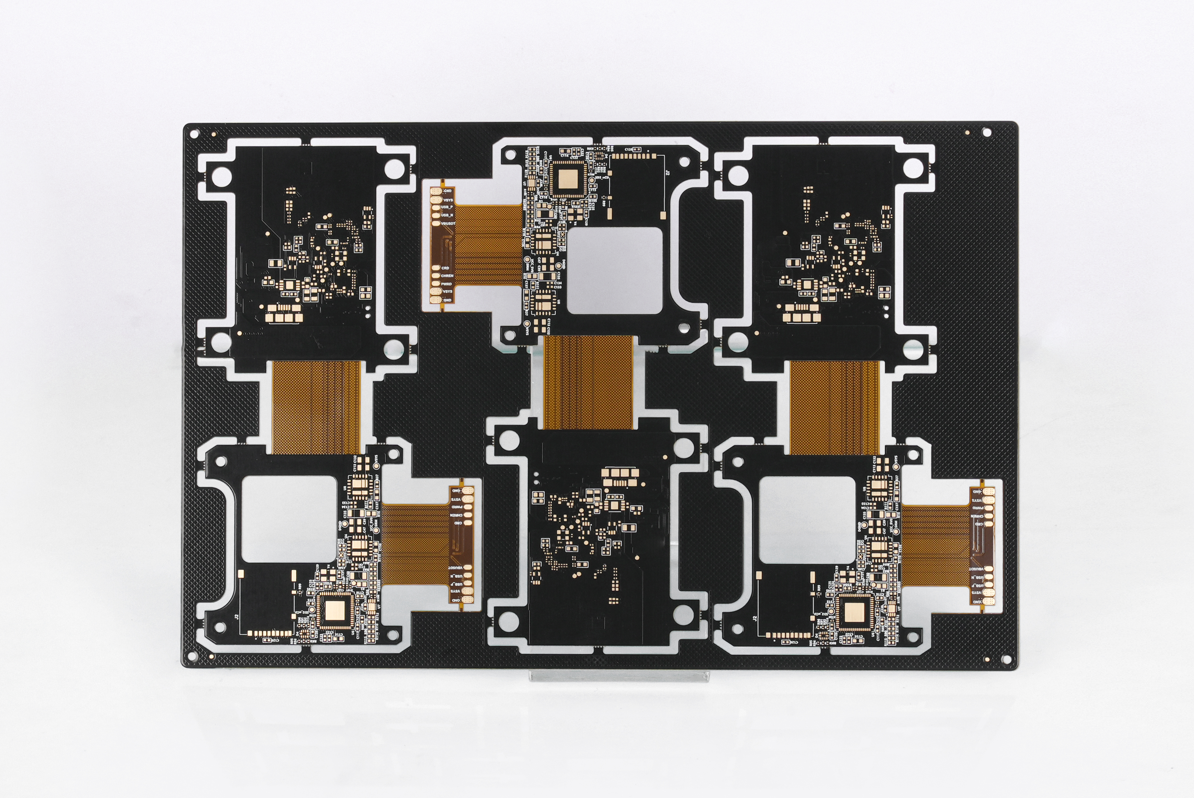
Ceramic PCB Directory
- Thick Film Ceramic PCB
- Thin Film Ceramic PCB
- DBC Ceramic PCB
- DPC Ceramic PCB
- AMB Ceramic PCB
- LTCC PCB
- HTCC PCB
Our ceramic PCB capabilities:
| Item | Capabilities |
| Layer Count | 1-6L (Thick Film) |
| 1-2L (DBC/DPC/AMB) | |
| 4-64L (LTCC/HTCC) | |
| Substrate Material | AlâOâ, AlN, BeO, ZrOâ, SiâNâ |
| Conductor Thickness | Copper: 0.035-0.30mm |
| AgPd: 10-20μm | |
| Au: 6-10μm | |
| Working Temperature | -50â to 800â |
| Bonded Resistors | ±0.5% Tolerance |
| PTH Diameter Tolerance | ±4mil (0.1mm) |
| NPTH Diameter Tolerance | ±2mil (0.05mm) |
| Outline Tolerance | Laser: +0.20/-0.05mm |
| Max Board Size | Thick Film: 200Ã200mm |
| DBC/DCB: 138Ã178mm | |
| DPC: 138Ã190mm AMB: 114Ã114mm | |
| Min Board Thickness | 0.25mm-0.40mm |
| Min Hole Spacing | NPTH: 16mil (0.30mm) |
| PTH: 20mil (0.5mm) | |
| Hole Vias Tolerance | ±4mil (0.1mm) |
| Cutting Tolerance | Laser: +0.2/-0.05mm |
| Mold | +0.25/-0.20mm |
| Line Width/Space Tolerance | ±5mil (0.125mm), ±1mil (0.025mm) |
| Surface Treatment | AgPd, AuPd, Mn/Ni (Thick Film), OSP, Nickel Plating, ENIG, ENEPIG |
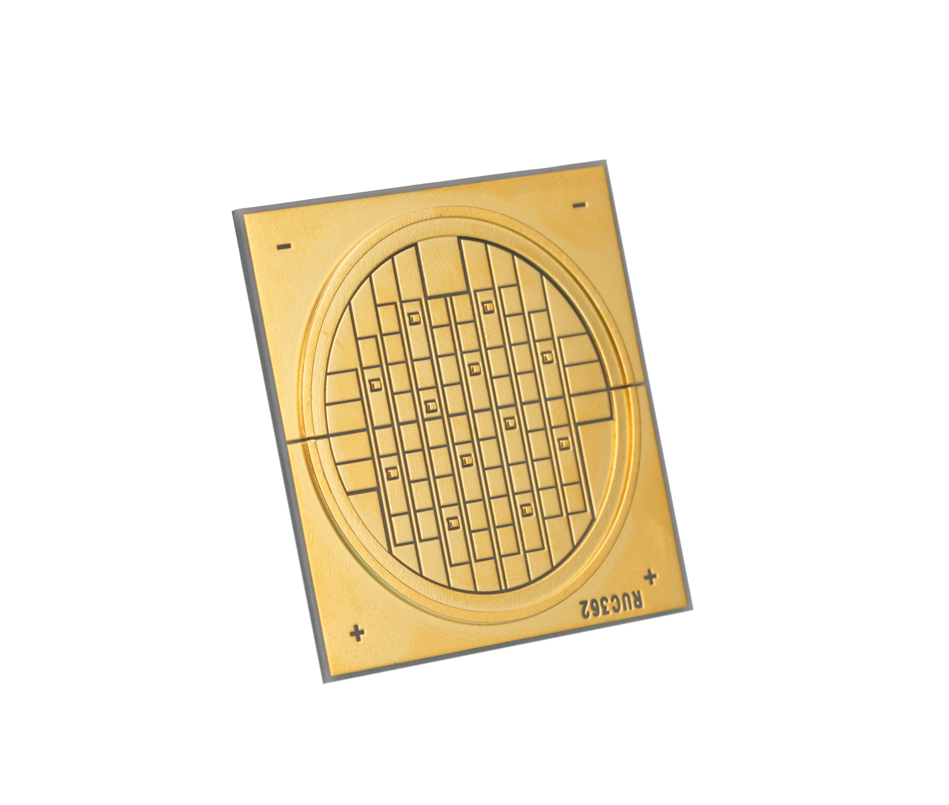
Metal Core PCB Directory
- Aluminum Base PCB
- Copper Base PCB
- COB PCB
- SinkPAD PCB
Our MCPCB capabilities:
| Item | Capabilities |
| Layer Count | 1-10L |
| Max Board Dimension | 610Ã1625mm |
| Conductor Thickness | 0.5oz – 10oz |
| Min Line Width/Line Space | 4/4mil |
| Wall Copper Thickness | Normal: 0.59mil; HDI: 0.48mil |
| Special Hole Types | Counterbore hole, Countersunk hole, Blind, Buried, Vias |
| Max Aspect Ratio | 10:1 |
| Min Board Thickness | 0.8mm |
| Max Board Thickness | 5.0mm |
| Min Hole Diameter | 0.8mm |
| Min Hole Spacing | 1mm |
| Min Solder mask Bridge | 0.15mm |
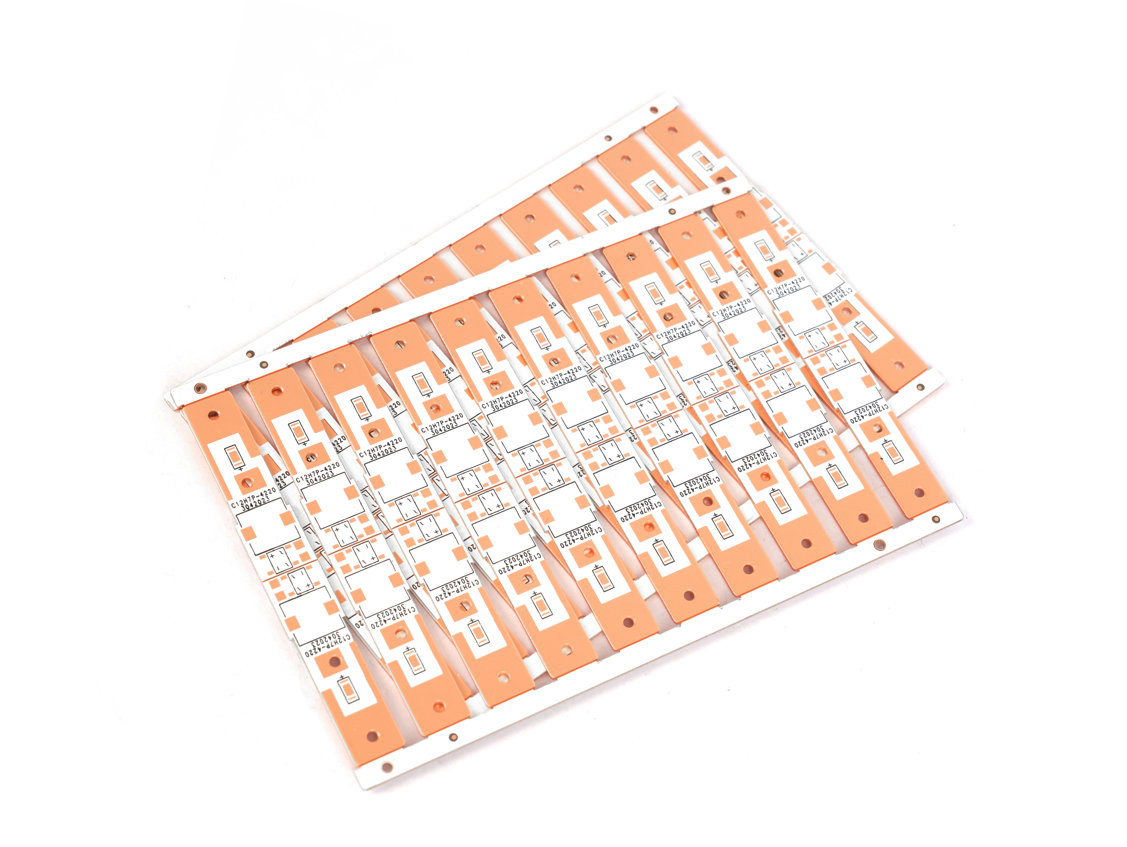
Our Prototyping Lead Time
Lead time for FR4 PCB prototyping
| Layers | Normal Service | Fastest Service |
| 1 | 7 Days | 24 H |
| 2 | 8 Days | 24 H |
| 4 | 10 Days | 48 H |
| 6 | 10 Days | 72 H |
| 8 | 12 Days | 72 H |
| â¥10 | TBD | TBD |
Lead time for MCPCB prototyping
| Layers | Normal Service | Fastest Service |
| 1 | 4 Days | 24 H |
| 2 | 14 Days | 168 H |
| 4 | 21 Days | TBD |
Lead time for FPC, Rigid- Flex & Ceramic PCB Prototyping
| Items | Normal Service | Fastest Service |
| FPC | 48-72 H | 24 H |
| Rigid- Flex | 2 Weeks for 4L | 1.5 Weeks for 4L |
| >4L: TBD | >4L: TBD | |
| Ceramic | 3 Weeks | 2 Weeks |
Our Quality Certifications
- ISO9001:2015
- ISO13485:2016
- REACH
- RoHS
- IATF16949
Attaches is our FR4 PCB prototype video for your reference:
Welcome to contact us if you need any help for FR4 PCB, FPC PCB, ceramic PCB and MCPCB : sales@bestpcbs.com.