Why Battery Corrosion Occurs?
Battery corrosion happens mostly with alkaline batteries. These batteries can leak potassium hydroxide. This chemical reacts with air, forming a white or bluish crust. That crust is the corrosion you see.
There are a few reasons why this happens. Old batteries left inside devices too long can leak. Extreme heat or cold can also make them expand and crack. Sometimes, poor-quality batteries just break down faster. Corrosion doesn’t mean the battery was faulty. But it does show that the battery has aged or faced rough conditions.
Some other causes include:
- Overcharging or overheating: In devices that try to draw too much power, batteries can heat up and burst.
- Poor storage conditions: Dampness or extreme cold can stress the battery casing.
- Mixing old and new batteries: This creates uneven discharge, often stressing the older cell until it leaks.

Is Battery Corrosion Dangerous?
Yes, but only if you’re careless. Battery corrosion is not highly dangerous, but it can still be irritating if it gets on your skin or in your eyes. Potassium hydroxide is a skin irritant. It may cause mild burns, itching, or redness if touched directly. If accidentally ingested or inhaled, it can be more harmful—but that’s rare and usually avoidable.
In terms of your electronics, corrosion is more dangerous. The leaked compound can damage the metal connectors inside your device. If left untreated, it might eat away the contacts, cause shorts, or completely block the flow of power. That means your device might stop working even after the batteries are replaced.
However, with quick action, most devices can be restored to working condition. As long as you catch the corrosion early and clean it properly, there’s a good chance your device will recover fully.
How to Identify Corrosion on Batteries?
Battery corrosion usually appears as white, gray, or blue powder by visual. You’ll see it around the battery terminals or on the spring contacts. Sometimes, the battery might look bloated or cracked. But sometimes, we can’t identify whether it is corrosion from appearance, so how to identify it? Here we listing some other methods to recognize the battery corrosion:
1. Electrochemical test: By measuring the electrochemical parameters inside the battery, such as voltage, current and internal resistance, the degree of corrosion inside the battery can be indirectly inferred.
2. X-ray or CT scan: This is a non-destructive detection method that can perform a full-scale scan and imaging of the inside of the battery without disassembling the battery, and can clearly see the corrosion inside the battery, including the location, degree and type of corrosion.
3. Check the polarity of the battery: Observe whether the positive and negative poles of the battery are clearly visible and whether there are signs of corrosion or damage. If the positive and negative poles are corroded or damaged, the battery may be unusable.
4. Measure voltage: Use a voltmeter to measure the battery voltage. Under normal circumstances, the voltage should be within a certain range (such as around 12V). If the voltage is lower than the normal value, it means that the battery is damaged.
5. Measure specific gravity: Determine the battery health by measuring the specific gravity of the battery electrolyte. The normal specific gravity is about 1.25-1.28g/cm³. If the specific gravity is lower than 1.2g/cm³, it means that the battery is damaged.
6. Discharge test: Evaluate the actual capacity of the battery through the discharge test. Discharge the battery to the specified termination voltage, and then calculate the actual capacity of the battery based on the discharge time and capacity.
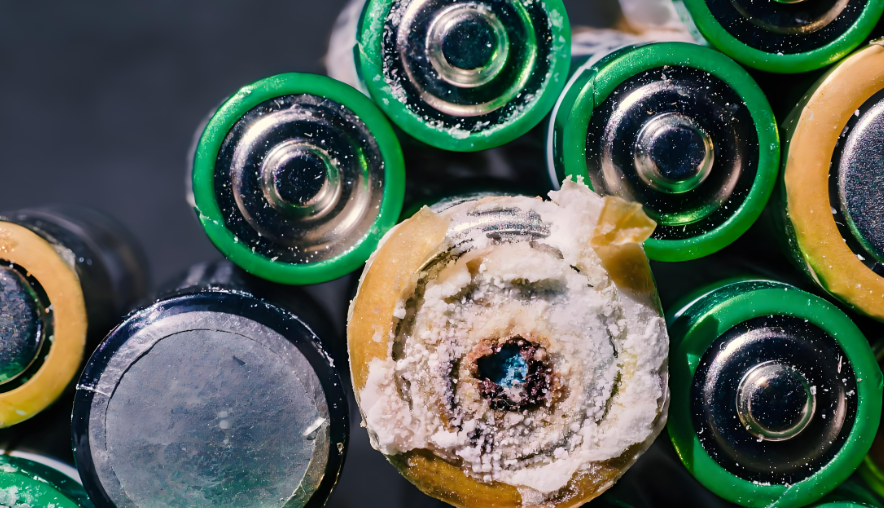

What is the Best Solvent to Clean Battery Corrosion?
The most trusted solvents are white vinegar and lemon juice. They’re safe, gentle, and effective. These mild acids react with the potassium hydroxide and break it down. You don’t need harsh chemicals or expensive products.
Some people also use baking soda and water for acidic battery leaks, like those from lithium or rechargeable cells. But for most alkaline batteries, vinegar works better.
Avoid using alcohol or bleach. These don’t neutralize the leak and might damage plastics. Always test the solvent on a small area first.
How to Remove Battery Corrosion from PCBs?
Removing battery corrosion from PCBs takes a bit more care than cleaning corrosion from regular battery compartments, mainly because PCBs are more sensitive and often house fine components. Here’s a simple, professional, and safe way to clean corrosion from a PCB:
1. Power Down and Disconnect
First, completely power off the device. Disconnect all power sources, including batteries, power cords, and any external peripherals.
2. Wear Gloves and Safety Gear
Battery corrosion contains potassium hydroxide (alkaline batteries) or other chemical residues that can irritate skin or eyes. Use gloves, goggles, and work in a well-ventilated area.
3. Inspect the Corrosion Area
Look closely at the board under good lighting or even a magnifier. Corrosion usually appears as white or greenish deposits on the metal traces or battery terminals.
4. Neutralize the Corrosion
- Use white vinegar or lemon juice to neutralize alkaline corrosion.
- Apply it carefully with a cotton swab or soft brush directly on the affected area.
- Let it sit for 3–5 minutes to break down the residue.
5. Scrub Gently
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush or anti-static brush to scrub the area. Be gentle—too much pressure can lift pads or traces from the PCB.
6. Rinse with Isopropyl Alcohol
After cleaning, rinse the area with 99% isopropyl alcohol to remove moisture and leftover acid. This step helps clean off the vinegar/lemon juice and dries quickly.
7. Dry Thoroughly
Pat the board dry with a lint-free cloth or allow it to air-dry. Use compressed air to blow out moisture under chips or between components.
8. Check for Damage
Look for broken traces, lifted pads, or corrosion under components. If corrosion went deep, you might need professional rework or replacement parts.
9. Reassemble and Test
Once you’re sure everything’s dry and clean, reassemble the board, add a fresh battery (if applicable), and power it up. In many cases, your board will work just fine again.
Can I Still Use Something If a Battery Corroded in It?
Often, yes. If the corrosion hasn’t spread too far, you can save the device. Most electronics are still fine once cleaned properly. The key is to act fast. The longer corrosion sits, the more damage it causes.
If contacts are lightly corroded, cleaning will fix it. But if they’re broken or rusted through, repair might be needed. Sometimes, replacing a contact spring is all it takes.
Check for signs of deeper damage like melted parts or burnt smell. If it looks too far gone, it may be time for a replacement. But don’t give up too quickly. Many items bounce back with just a simple cleanup.
How to Prevent Battery from Corrosion?
Good habits make all the difference. Here are a few tips to keep your devices corrosion-free:
- Remove batteries when not in use. If you’re storing something for months, take them out.
- Store devices in a cool, dry place. Avoid hot cars or damp basements.
- Use high-quality batteries. Cheap ones often leak sooner.
- Check expiration dates. Old batteries are more likely to corrode.
- Inspect devices regularly. A quick glance now can save repairs later.
- Avoid mixing old and new batteries. This creates imbalance and increases leakage risk.
- You can also use a small dab of dielectric grease on contacts. This helps prevent moisture from reaching the metal.
Battery corrosion is a common issue, but it’s not the end of your device. With the right handling and preventive measures, you can extend the life of your electronics and avoid long-term damage. At Best Technology, we take battery care and component storage seriously. All components are stored at controlled temperatures to reduce chemical reactions that lead to corrosion.
To add another layer of protection, we pack our products using ESD bags, which not only prevent electrostatic discharge but also act as a barrier against moisture and airborne contaminants—two major triggers of battery and PCB corrosion.
We understand how important reliability is in electronics manufacturing. That’s why our quality control process includes moisture-sensitive labeling (MSL), humidity indicator cards, and dry-pack sealing for sensitive parts. If you’re looking for a PCB & PCBA supplier that takes every detail seriously, from component protection to customer satisfaction, Best Technology is here to support your goals with the expertise and care your products deserve.