ICT Test Full Form
The full form of ICT is In-Circuit Testing. It is a method that always used to test assembled circuit board during manufacturing.
What is ICT in PCB?
In-circuit testing (ICT) is a method used to test assembled circuit boards during production. It ensures that every component on the PCB functions as expected. By applying electrical signals to the board, it checks for faults like open circuits, shorts, and wrong component values.
In PCB assembly, ICT is used for final testing after surface-mount components and through-hole components have been soldered onto the board. This test is highly effective in identifying assembly defects that might compromise the functionality of the final product.
ICT vs. FCT
Although ICT and FCT look similar, their purposes and focus are different.
In-Circuit Testing (ICT) is like a thorough quality check for individual components. It tests each resistor, capacitor, inductor, and IC on the board to make sure they’re installed and working as expected. ICT does this without focusing on the PCB’s complete function as a whole; instead, it looks for manufacturing faults or placement errors on each part of the circuit. This is perfect for catching problems before the PCB reaches final assembly.
Functional Circuit Testing (FCT), on the other hand, looks at the bigger picture. FCT checks if the assembled board works as intended in a simulated working environment. It mimics the real-world conditions the PCB will face once in use, testing the board as a whole rather than individual components. FCT aims to ensure that all parts are correctly interacting and that the board behaves as it should under operating conditions.

Together, ICT and FCT form a powerful duo: ICT focuses on each component’s accuracy, while FCT ensures that all the elements work smoothly as a cohesive unit. Using both tests provides a comprehensive check, enhancing the PCB’s overall quality and reliability before it reaches the end-user.
What Items Does ICT Test for on a PCBA?
When ICT tests a PCBA, it’s really looking for any faults or failures in the components and connections that could cause problems later on. Here’s what ICT commonly checks:
- Resistors – It verifies that each resistor has the right resistance value and is correctly placed. If a resistor value is wrong, it can disrupt the whole circuit.
- Capacitors – ICT checks capacitance levels and polarity (in specific cases) to make sure each capacitor is installed properly. Incorrect capacitors can lead to unstable performance.
- Inductors – The test examines if inductors have the correct inductance values. Faulty inductors can cause power issues or signal problems.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs) – ICT verifies that ICs are in the right orientation and connected properly to avoid shorts or opens, both of which can make the board malfunction.
- Transistors – By checking transistor functionality, ICT ensures they won’t cause signal or power issues within the PCB.
- Diodes – ICT makes sure diodes have correct polarity and work properly. Misplaced or faulty diodes can impact the flow of current, leading to circuit failure.
- Solder Joints – ICT evaluates each solder joint, checking for breaks or poor connections. Bad solder joints lead to unstable electrical contact, which could cause intermittent issues or complete failure.
What is an ICT Machine?
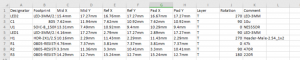
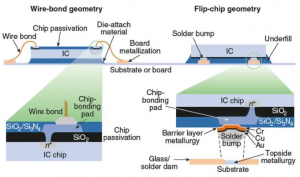
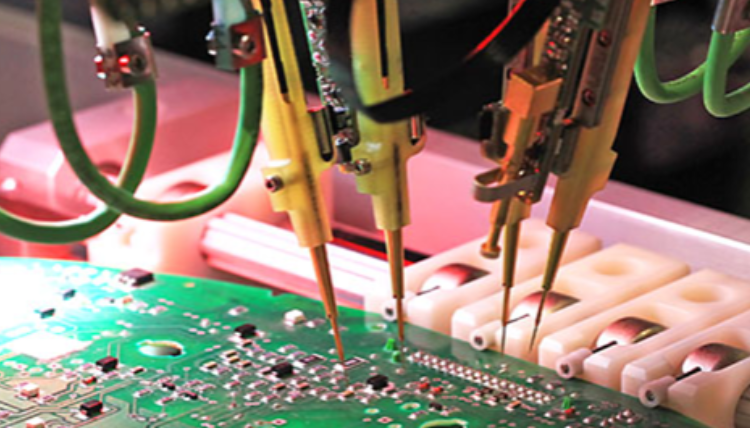
An ICT machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed to perform in-circuit tests on PCBs. You can see it from below picture. The ICT machine uses a test fixture, also called a “bed of nails,” containing numerous tiny probes or pins. Each probe aligns with a specific point on the PCB, making contact with various circuit points to evaluate the electrical connections.
Once a PCB is placed in the test fixture, the machine applies signals through the probes to test individual components. It checks electrical properties such as resistance, capacitance, and voltage at each node. If a component is misplaced, missing, or faulty, the machine flags it immediately.

With its speed and precision, an ICT machine is an invaluable tool in high-volume production lines. While setting up an ICT machine requires creating a test fixture for each PCB, they save much time and human during the manufacturing process, make sure a fast delivery.
What Are the 7 Types of PCB Testing Methods?
In addition to ICT testing, there are other 6 types of PCB testing methods that widely used. Let’s talk about them one by one.
1. Flying Probe Testing
A testing method mainly used for prototypes or small/low volume orders. In Flying Probe Testing, multiple movable probes make contact with test points on the board. Unlike ICT, it doesn’t require a fixture, making it highly flexible and cost-effective for small production runs. However, compared with ICT testing, it’s relatively slower than ICT because it tests points sequentially.
2. Functional Circuit Testing (FCT)
FCT is a method that check whether PCBA works correctly. It is typically come after ICT, and in almost factory, it is the last process to confirm that every component works together correctly.
3. Burn-In Testing
Burn-in Testing (also called aging test) pushes the board to its limits by applying high temperatures, loads, or voltages for extended periods. It can spot failures in components that might not withstand the stress of real-world conditions. Burn-in testing is often used for products that need high reliability, such as aerospace and medical devices.
4. X-Ray Inspection
For multilayer or densely packed PCBs, X-ray inspection is must to do. It helps visualize hidden solder joints and component placements that inspectors can’t found by naked eyes. X-ray inspection is invaluable for boards with fine-pitch components such as BGAs, QFNs, or those where hidden joints can’t be inspected visually.
5. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI uses cameras to visually inspect the board for common issues like misalignment, missing components, or faulty solder joints. This is a quick and effective way to catch visible defects. AOI is widely used in automated production lines, as it quickly flags any boards that require closer examination. To get highest quality and no-defect products, Best Technology equipped with online dual track AOI to inspect PCBA.
6. Boundary Scan Testing
Boundary Scan Testing is particularly useful for complex boards where physical probing is challenging. It involves using ICs that support scan testing, so that engineers to check connectivity between ICs and other critical points. Boundary scan is common in high-density boards like those found in telecommunications.
Each method brings a unique advantage to PCB testing. In-Circuit Testing (ICT) is highly effective for large-scale quality control, while Flying Probe Testing is better suited for prototypes and smaller batches. Together, these tests form a complete strategy for delivering reliable, high-quality PCBs across various production needs.
How does ICT Testing?
ICT works by using a bed-of-nails (BON) tester or test probes to connect to specific test points on a PCB. Electrical signals are then sent through the board, and the responses are analyzed. Here’s how it works in simple steps:
- Connection: The PCB is placed on the ICT machine, where test pins contact the board at designated points.
- Signal Application: The ICT machine applies electrical signals to test the components individually or in groups.
- Data Collection: The responses from each component are recorded to determine if it matches the expected output.
- Fault Identification: Any deviations from expected responses are flagged, identifying potential defects like soldering errors, component failures, or incorrect placements.
FAQs about ICT
Q: What is ICT?
A: ICT (In-Circuit Test System), commonly known as online tester In Chinese, is mainly used for the test of assembled Circuit boards (PCBA).
Q: Which components can ICT basic functions measure?
A: On, short circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, diode, IC protection diode test, etc.
Q: Why use ICT?
A: According to the statistical data of the circuit board assembly industry, assembly defects are mainly reflected in the welding open circuit, short circuit, offset, missing parts and other aspects, accounting for more than 90%, so the principle of online testing technology application is to quickly detect faulty components or assembly defects, and can accurately locate defects and defect classification.
Q: Can ICT be regarded as a universal meter?
A: ICT can be regarded as an automated high-level multipurpose meter, and because it has the function of circuit isolation, it can accurately measure the actual value of each component in the circuit.
Q: What is the relationship between ICT and AOI?
A: ICT is mainly carried out by electrical measurement methods, while AOI is carried out by optical image processing technology. Both have their own strengths and complement each other. In the process arrangement, AOI is generally the first, then ICT.