What is the Thermal Conductivity Coefficient?
The thermal conductivity coefficient is a measure of how well a material conducts heat. Itâs represented by the symbol k or λ, and it is measured in units of watts per meter-kelvin (W/m·K). Itâs defined as the amount of heat that passes through a material 1 meter thick, with a temperature difference of 1 degree (K or °C) between its two sides, in one second, over an area of 1 square meter.
In general, the higher the thermal conductivity coefficient, the better the material is at transferring heat, so in some high power or power supply electronics, thermal conductivity value is important to transfer heat out. Materials with a high k value, like metals such as copper, allow heat to flow through them easily, which is why they are used in applications that require efficient heat dissipation. In contrast, materials with low thermal conductivity coefficients, such as insulators, are used to minimize heat transfer and preserve energy.
The thermal conductivity is only for the heat transfer form with thermal conductivity. When there are other forms of heat transfer, such as radiation, convection, mass transfer and other forms of heat transfer, the composite heat transfer relationship. The composite heat transfer relationship is often referred to as the apparent thermal conductivity, the dominant thermal conductivity, or the effective thermal transmissivity of material. In addition, the thermal conductivity is for homogeneous materials, in the actual situation, there are also porous, multi-layer, multi-structure, anisotropic materials, the thermal conductivity obtained by this material is actually a comprehensive thermal conductivity performance, also known as the average thermal conductivity.
According to Fourier’s law, the thermal conductivity is defined as
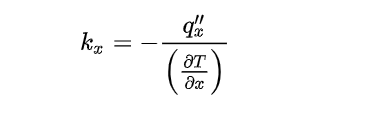
Where x is the direction of heat flow.
qxââ is the heat flux in this direction in W/m2, and another is the temperature gradient in this direction, expressed in K/m.
For an isotropic material, the thermal conductivity is the same in all directions.
What Is the k Value of Copper?
The thermal conductivity of copper is about 401W/m.K. Copper is a transition element, pure copper is a soft metal, when it is cut on the surface, it is red-orange, and its ductility is good, thermal conductivity is relatively high, so it is a more commonly used material in cables and electronic components, can be used as building materials, and it is composed of many kinds of alloys.

Copper’s high k value meaning it can quickly absorb and distribute heat. That is why copper is used extensively in heat sinks, electrical wiring, and cooling systems. Because of this, it’s highly valued in industries that rely on rapid heat dissipation. Whether in electronics or heavy machinery, the high thermal conductivity of copper ensures that heat does not build up, preventing overheating.
Thermal Conductivity of Common Solid Materials
Here are the thermal conductivity values of some common materials:
- Aluminum: 237 W/m·K at 300°C
- Copper: 401 W/m·K at 100°C
- Iron: 61 W/m·K at 18°C
- Steel: 45 W/m·K at 18°C (for carbon steel with 1% carbon)
- Silver: 412 W/m·K at 100°C
- Graphite: 151 W/m·K at 0°C
These values highlight the differences in heat conduction across materials, with metals like copper and silver being among the most efficient conductors of heat, while materials like steel and graphite have comparatively lower conductivity.
Is Copper a Good Conductor of Heat?
Yes, copper is an exceptionally good conductor of heat. For example, in electronics, copper is often used to cool down processors by transferring heat away quickly, thus ensuring systems run smoothly without overheating. In plumbing, copper pipes help distribute hot water faster, enhancing energy efficiency. From cookware to cooling systems, copper’s outstanding ability to conduct heat makes it indispensable across many fields.
Copper vs. Aluminum PCB: Which is Better?
Both copper and aluminum are excellent conductors of heat in circuit boards manufacturing, but how do they compare? Letâs discuss them from below aspects:
1. Thermal conductivity
First, let’s take a look at the thermal conductivity of aluminum and copper, which is a key indicator of the material’s heat dissipation performance. The higher the thermal conductivity, the better the material’s ability to transfer heat.
- Copper: 401W/m.k
- Aluminum: 237W/m.k
It can be seen from the data that the thermal conductivity of copper is almost twice that of aluminum, which means that under the same conditions, copper can transfer heat more efficiently. For this reason, copper is often the material of choice in applications that require extremely high thermal performance.
2. Density
- Aluminum: Density of about 2.7 g/cm³.
- Copper: Density of about 8.96 g/cm³.
Copper is nearly three times as dense as aluminum, which makes copper much heavier than aluminum. In some weight-sensitive applications, such as portable electronic devices, heavy cooling components may affect the portability and user experience of the product. Therefore, in these scenarios, although aluminum is not as conductive as copper, it is still a very popular choice due to its lower weight.
3. Cost
The prices of aluminum materials are low, and processing costs are relatively low. At the same time, aluminum is easy to process into a variety of shapes, which makes aluminum very cost-effective in the manufacturing process. However, the cost of copper is much higher and the manufacturing process is more complex, so the overall cost is much higher than aluminum.
4. Corrosion resistance
Aluminum and copper also have significant differences in corrosion resistance. Aluminum has good oxidation resistance, and the aluminum oxide layer formed on the surface can effectively protect the internal material from further corrosion. However, the corrosion resistance of copper is relatively poor, and it is easy to generate patina (carbonate of copper) in humid environments, which not only affects the appearance but also reduces the heat dissipation performance.
Why Does Copper Have the Highest Thermal and Electrical Conductivity?
Copper has very good conductivity because it has a large number of freely moving electrons in its interior. When a voltage is added to both ends of a metal, the positive electrode piles up positive charges, and the negative electrode piles up negative charges, because the same charges attract each other and the dissimilar charges repel each other, forcing the electrons to move in a directional way, thus forming a current. In addition, copper has a very low resistivity of only 1.68Ã10^-8Ω·m, second only to silver, and is the second most widely used conductive material.
Copper’s good thermal conductivity is also related to its internal free electrons. Metal nuclei have a weak ability to bind electrons, allowing free electrons to move freely within the metal and transfer heat rapidly. When one end of a metal is heated, the electrons of atoms or molecules at that end absorb energy and begin to vibrate. These vibrations are passed on to the electrons of neighboring atoms or molecules, forming a heat flow â4. Copper is metal-bonded in a way that makes it easier for its electrons to transfer energy inside the metal, and thus heat faster.
Here is the end of this blog sharing, if you have other questions about copper material, welcome to e-mail us: sales@bestpcbs.com.